These organs are called organs of speech. The organs involved in the production of speech can be divided into three groups: 1. The respiratory system- lungs, muscles, trachea. 2.The phonetary system- larynx, vocal cords. 3. The articulatory system- nose, mouth, tongue, teeth, lips. Lungs: It is a bladder-like structure which is made up of alveolic. Three more parts of the speech mechanism and organs of speech are the larynx, epiglottis and vocal folds. The larynx is covered by a flap of skin called the epiglottis. The epiglottis blocks the trachea to keep food from going into your lungs when you swallow. Across the larynx are two thin bands of tissue called the vocal folds or vocal cords.

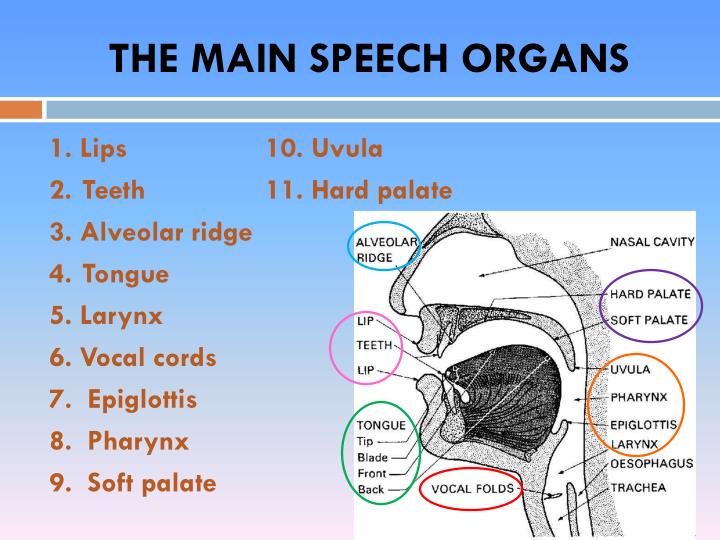
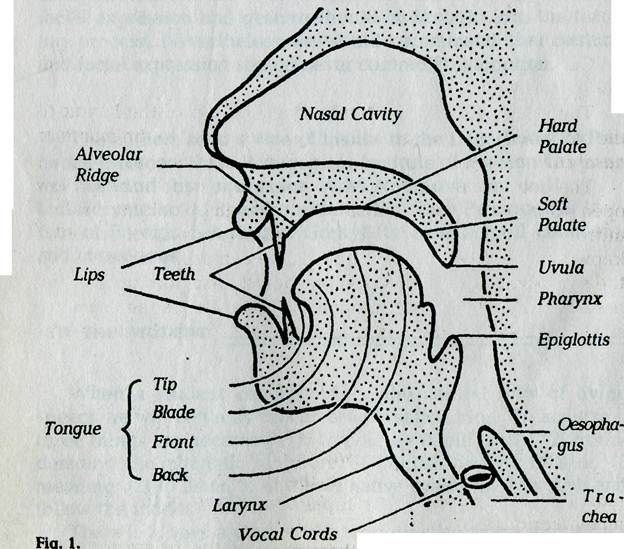
The sounds of English THE ORGANS OF SPEECH
Otto Jespersen phonetics, the study of speech sounds and their physiological production and acoustic qualities. Lips The two lips are flexible organs of speech. They can combine with each other to produce certain sounds, e.g. /p, b/. sometimes the lower lip can combine with upper front teeth to produce certain sounds, e.g. /f, v/ The Roof of the Mouth It consists of the upper front teeth, alveolar ridge, palate or hard palate and soft palate Teeth Conventionally, these are called the organs of speech, and the use in several languages of the same word for the tongue as a part of the body and for language shows the awareness people have of the role played by this part of the mouth in speaking. But few if any of the major organs of speech are exclusively or even mainly concerned with speaking. speech disorder oratory utterance articulation voice See all related content → speech, human communication through spoken language. Although many animals possess voices of various types and inflectional capabilities, humans have learned to modulate their voices by articulating the laryngeal tones into audible oral speech. The regulators
PPT SPEECH ORGANS & ARTICULATION PowerPoint Presentation ID3028381
The vocal cords are two thin membranes that stretch across the larynx. They open when we breath, but they vibrate against each other when we make certain sounds (called "voiced" sounds), as you can see in the following videos: Video Stroboscopy of Vocal Cords Share Watch on The scientific study of the way speech sounds are produced by our vocal organs, the way they are perceived by the listeners and the way different sounds are combined into syllables, words and sentences is known as phonetics. Type Chapter Information Introduction to English Phonetics and Phonology , pp. 1 - 10 articulation, in phonetics, a configuration of the vocal tract (the larynx and the pharyngeal, oral, and nasal cavities) resulting from the positioning of the mobile organs of the vocal tract ( e.g., tongue) relative to other parts of the vocal tract that may be rigid ( e.g., hard palate). The organs of speech are shown on the diagram below. Learn their names and locations, and be prepared to write the names into a blank diagram.

Speech organs YouTube
Direct damage to the speech organs can result in a condition called peripheral dysarthria. Typical symptoms of dysarthria include speech that is too fast or slow, slurred, or mumbled. People with dysarthria may also have trouble moving their jaw, tongue, or lips. Another condition affecting speech articulation is a developmental disorder. The Larynx This organ of speech contains the vocal cord. Yule (2002) calls it the "voice box" which can act as "a resonator for any sound produced". Yule, however, laments that this organ of speech has the possibility for the human to choke on pieces of food thereby distorting the smooth production of sounds. Manette and Madrid (2015) state that:
i k e 46K views 3 years ago HSA English - Easy Learning A SIMPLE INTRODUCTION to the organs of speech. Organs of Speech and Speech Mechanism are two important sections in the study of. The organs of speech 1. Cricoid 2. Thyroid 3. Pyramidal Cartilages 4. Vocal Chords 5. Tip of the Tongue 6. Blade of the Tongue 7. Front of the Tongue 8. Back of the Tongue 9. Root of the Tongue 10, 11. Teeth 12. Alveoli 13. Hard Palate 14. Soft Palate 15. Uvula
Chapter 1. THE ORGANS OF SPEECH AND THEIR WORK
> The Organs of Speech; A Handbook of Phonetics. Including a Popular Exposition of the Principles of Spelling Reform. Buy print or eBook [Opens in a new window] Book contents. Frontmatter. Preface. List of Symbols. Contents. PART I. The Organs of Speech. PART II. Analysis. PART III. Synthesis. PART IV. Organs of Speech. There are approximately 100 muscles in the human body, and most work closely together in a coordinated manner in order to produce speech. These muscles are part of several organ.




