2. No. It's called UTF-8 because the code unit is 8 bits. Each code unit provides some of the bits needed for the 21-bit Unicode codepoint. A codepoint requires 1 to 4 UTF-8 code units. Similarly for UTF-16 and UTF-32. However, by design, a codepoint would never need more than one UTF-32 code unit. - Tom Blodget. The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits.Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures.To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as the.
Bits y Bytes Platzi
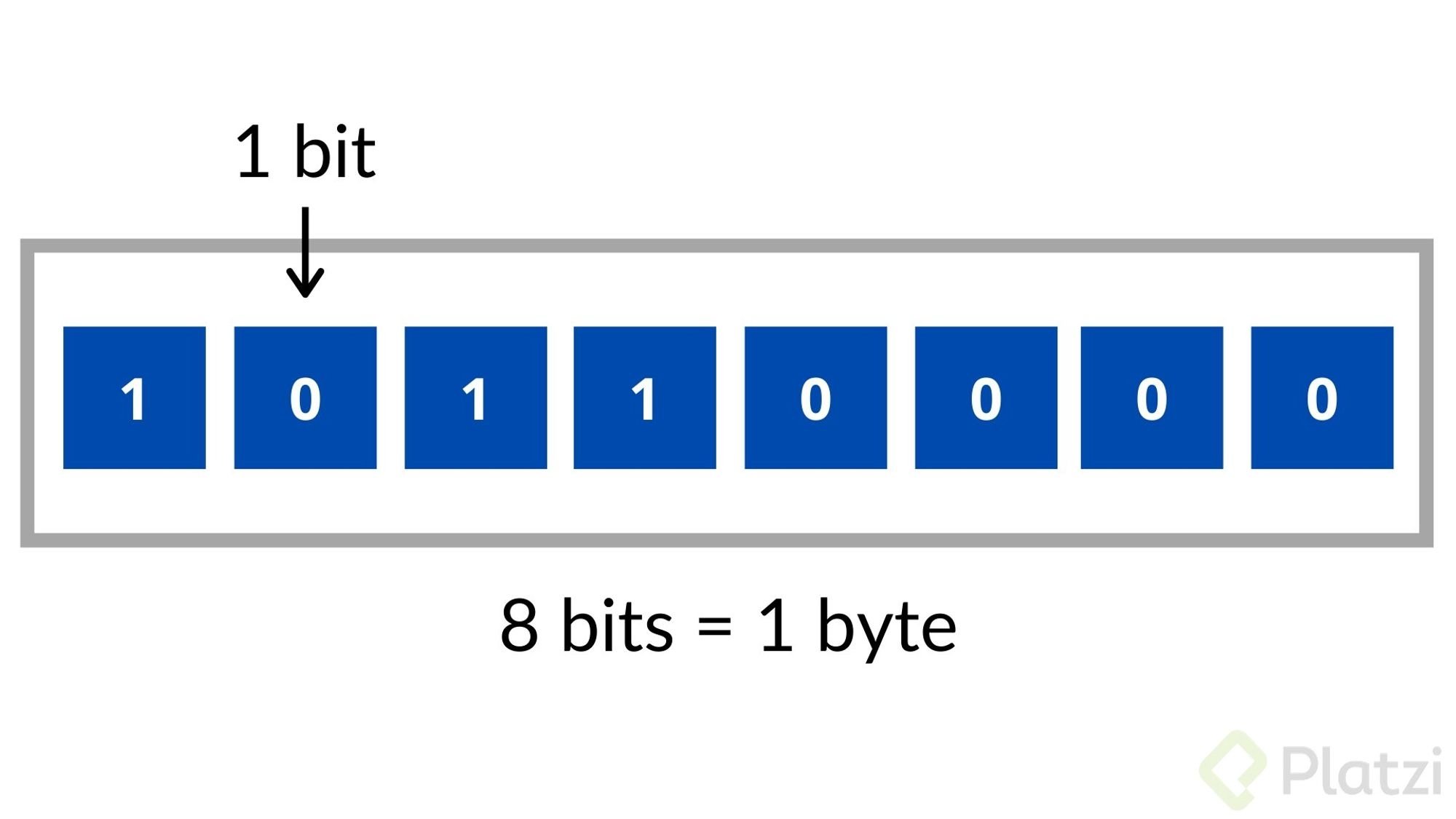
For older architectures, "byte" indicated the size of the data bus, and as the original question states, a lot of different bus sizes existed (4, 5, 6, 8, 12 etc.). But since 1993 a byte has been defined as 8 bits, in order to have a standardized SI unit for data sizes. These two states in terms of memory are represented by a 0 or 1. To count higher than 1, such bits (Binary Digits) are suspended together. A group of eight bits is known as a Byte. 1 Byte can represent numbers between zero (00000000) and 255 (11111111), or 2 8 = 256 distinct positions. Of course, these bytes may also be combined to represent. Everything in a computer is 0's and 1's. The stores just a 0 or 1: it's the smallest building block of storage. One byte = collection of 8 bits. One byte can store one character, e.g. 'A' or 'x' or '$'. Consider just the leftmost bit. It can only be 0 or 1. Leftmost bit is 0, then append 2-bit patterns. Leftmost bit is 1, then append 2-bit. Byte and Bytes! When we combine eight bits together, we form a byte. A byte is a human concept, not one which a computer can understand at it cores. Very early computer developers decided to create bytes out of 8 bits. Let's see how many combinations we can create using eight bits, set to a state of 0 or 1: 0000 0000 = 0. 0000 0001 = 1.

Gazdasági Deform munka 8 bit 256 Pénelopé A nyomtatvány több mint
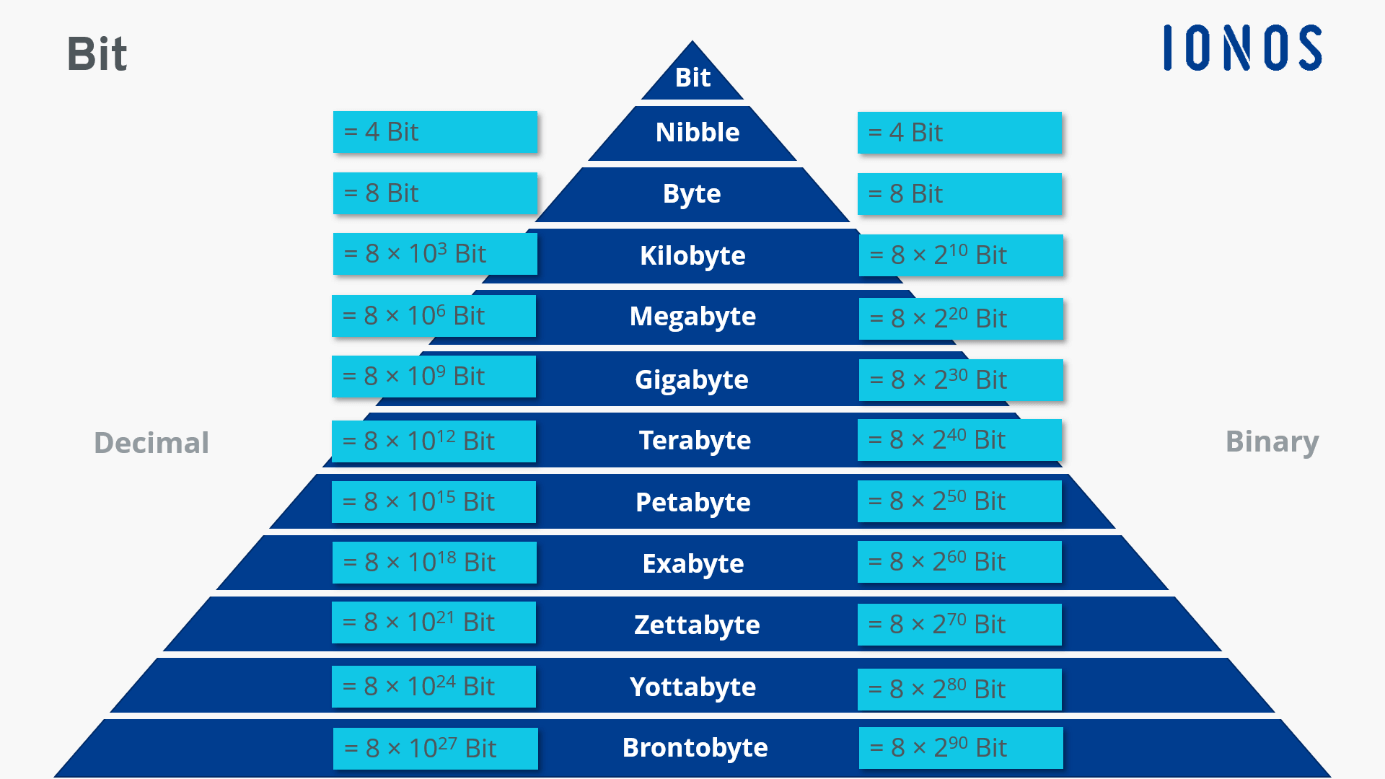
Bytes. Google Classroom. A bit is the smallest piece of information in a computer, a single value storing either 0 or 1 . A byte is a unit of digital information that consists of 8 of those bits. Here's a single byte of information: 11110110. Here are three more bytes of information: 0 0 0 0 1010 0 101010 0 11011011. With 8 bits in a byte, you can represent 256 values ranging from 0 to 255, as shown here: 0 = 00000000 1 = 00000001 2 = 00000010. 254 = 11111110 255 = 11111111. In the article How CDs Work, you learn that a CD uses 2 bytes, or 16 bits, per sample. That gives each sample a range from 0 to 65,535, like this: 1 byte is equal to exactly 8 bits. In Scientific Notation. 1 byte = 1 x 10 0 bytes = 8 x 10 0 bits. Bytes. A byte is 8 bits. It can store up to 2 8 (256) different values, or one character of ASCII text. Bits. A bit is the basic unit of information. It can only have two possible values: 0 or 1. The Fujitsu FACOM 128, one is still operational, uses 5 bits as a byte to represent one decimal digit. The Digital Equipment Corp. PDP8 has a 12 bit word and does not use 8-bit bytes at all. 8-bits per byte became a de-facto standard with the IBM System 360.
What is a bit? Bits and bytes explained IONOS
A 1-bit image is monochrome; an 8-bit image supports 256 colors or grayscales; and a 24- or 32-bit graphic supports true color. nibble: Half a byte - four bits. Nibbles are important in hexadecimal and BCD representations. The term is sometimes spelled nybble. byte: Abbreviation for binary term, a unit of storage capable of holding a single. While in general 8-bit CPUs have 16-bit addressing, in some architectures you have both, such as in the MOS Technology 6502 CPU, where the zero page is used extensively, saving one byte in the instructions accessing that page, and also having 16-bit addressing instructions that take 2 bytes for the address plus 1 for the opcode. Commonly index registers are 8-bit (while other "8-bit" CPUs.
Bits. Bit (b) is a measurement unit used in binary system to store or transmit data, like internet connection speed or the quality scale of an audio or a video recording. A bit is usually represented with a 0 or a 1. 8 bits make 1 byte. A bit can also be represented by other values like yes/no, true/false, plus/minus, and so on. The bit rate refers to how many bits are transmitted per second. Bytes, on the other hand, are used to express storage sizes. 1 byte is equal to 8 bits. This means that one byte can represent 256 (2 8) different states. A byte is usually the smallest unit that can represent a letter of the alphabet, for example. The kilobyte is the next largest.

Bits and bytes stock illustration. Illustration of cyberspace 6931475
1 Bytes to Bits (1 Byte to bit) Convert 1 Bytes to Bits (Byte to bit) with our conversion calculator and conversion tables. To convert 1 Byte to bit use direct conversion formula below. 1 Byte = 8 bit. You also can convert 1 Bytes to other Storage (popular) units. The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications.The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values.These values are most commonly represented as either " 1" or "0 ", but other representations such as true/false, yes/no, on/off, or +/− are also widely used.. The relation between these values and.




