© Draco2008 Turingery and Delilah In July 1942, Turing developed a complex code-breaking technique he named 'Turingery'. This method fed into work by others at Bletchley in understanding the 'Lorenz' cipher machine. In 1939, with the growing likelihood of a German invasion, the Poles turned their information over to the British, who set up a secret code-breaking group known as Ultra, under mathematician Alan M. Turing. Because the Germans shared their encryption device with the Japanese, Ultra also contributed to Allied victories in the Pacific.

100 Years Alan Turing the Enigma machine HITS gGmbH
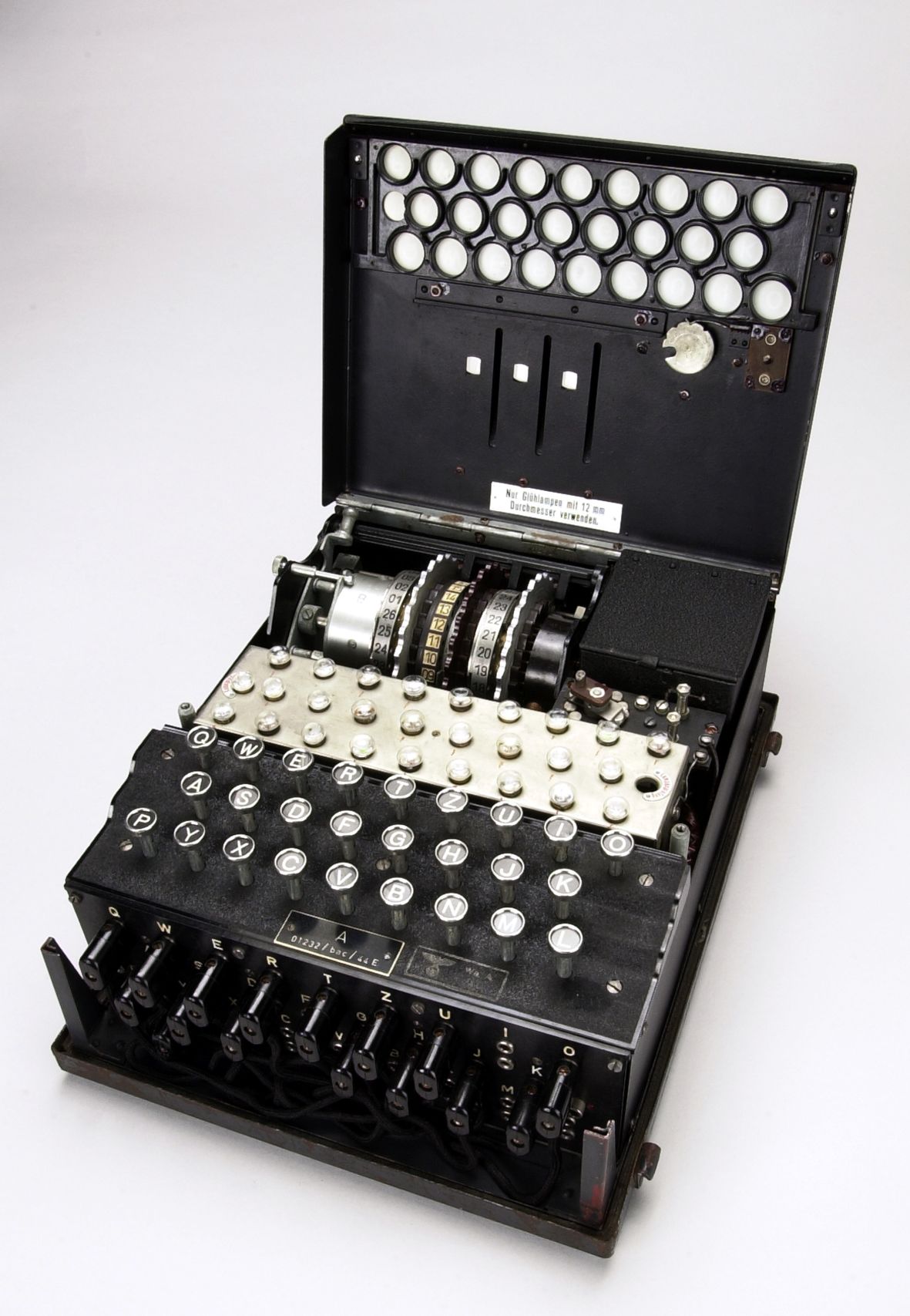
Alan Mathison Turing OBE FRS ( / ˈtjʊərɪŋ /; 23 June 1912 - 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. [5] It is a process of testing a machine's ability to "think." The basic premise of the Turing Test is that a human judge would be placed in isolation and have two conversations — one with a computer and one with another person — except the judge wouldn't be told which was which. The Enigma machines were a family of portable cipher machines with rotor scramblers. [1] Good operating procedures, properly enforced, would have made the plugboard Enigma machine unbreakable. [2] [3] [4] The German plugboard-equipped Enigma became the principal crypto-system of the German Reich and later of other Axis powers. Alan Turing - the Bletchley Park codebreaker - would have been 100 years old on 23 June had he lived to the present day. To mark the occasion the BBC commissioned a week-long series of articles.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/1062357/vs04-16_18-00-16x640.jpg)
The Enigma machine, on the centenary of the man who brought it down
Alan Turing (born June 23, 1912, London, England—died June 7, 1954, Wilmslow, Cheshire) British mathematician and logician who made major contributions to mathematics, cryptanalysis, logic, philosophy, and mathematical biology and also to the new areas later named computer science, cognitive science, artificial intelligence, and artificial life. More than 70 years after the Enigma was cracked by Alan Turing and his colleagues at Bletchley Park, innovative technology housed at The University of Manchester has provided a detailed peek beneath the bonnet of the German wartime cipher machine. A deadly weapon PG-13 1h 54m IMDb RATING 8.0 /10 814K YOUR RATING Rate POPULARITY 829 49 Play trailer 2:26 21 Videos 99+ Photos Biography Drama Thriller During World War II, the English mathematical genius Alan Turing tries to crack the German Enigma code with help from fellow mathematicians while attempting to come to terms with his troubled private life. Alan Turing and other researchers exploited a few weaknesses in the implementation of the Enigma code and gained access to German codebooks, and this allowed them to design a machine called a Bombe machine, which helped to crack the most challenging versions of Enigma.
Alan Turing Enigma Machine Museum / German Divers Hand Over Enigma
Alan Turing was a British scientist and a pioneer in computer science. During World War II, he developed a machine that helped break the German Enigma code. He also laid the groundwork for modern. The author focuses on the mathematics underpinning the story of the Enigma Machine, setting out the process both of the code's creation and of its decryption. Following the story of Alan Turing, a mathematician and one of the code breakers at Bletchley Park, the chapter emphasises both the necessity of collaborative labours to solve.
Alan Turing. A team of scientists, mathematicians and cryptographers are credited with cracking the Enigma code. Alan Turing was the head of this historic team. He, along with his colleague Gordon Welchman, made his own version of the Bombe Machine (the Bombe Machine was originally invented by the Poles, but it was unable to effectively. Turing, played by Benedict Cumberbatch in the film, is credited as the father of computer science. He cracked codes produced by the German military's seemingly unbreakable Enigma machine.

Nazicode breaker Alan Turing's notebook fetches over 1 million CTV News
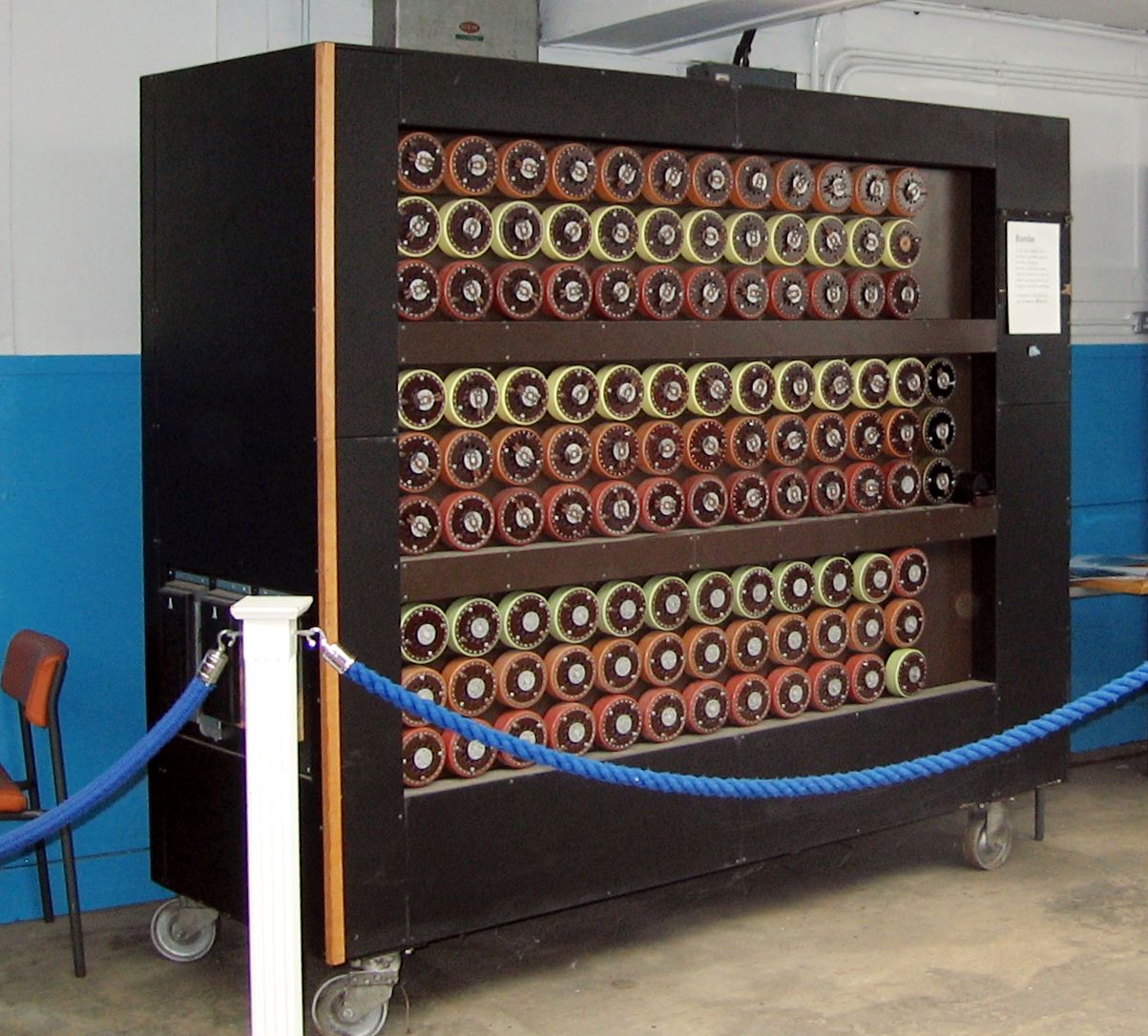
Turing was responsible for another major development in breaking Enigma.In March 1940, Turing's first Bombe, a code-breaking machine, was installed at Bletchley Park; improvements suggested by British mathematician Gordon Welchman were incorporated by August.This complex machine consisted of approximately 100 rotating drums, 10 miles of wire, and about 1 million soldered connections. Alan Turing, whose reputation as a central figure in computer science and artificial intelligence has only grown since his untimely death in 1954, applied his genius to problems such as this one in an age before computers as we know them existed.

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/1062357/vs04-16_18-00-16x640.jpg)


