In signal processing, a band-stop filter or band-rejection filter is a filter that passes most frequencies unaltered, but attenuates those in a specific range to very low levels. [1] It is the opposite of a band-pass filter. A notch filter is a band-stop filter with a narrow stopband (high Q factor ). The band stop filter, also known as a band reject filter, passes all frequencies with the exception of those within a specified stop band which are greatly attenuated.
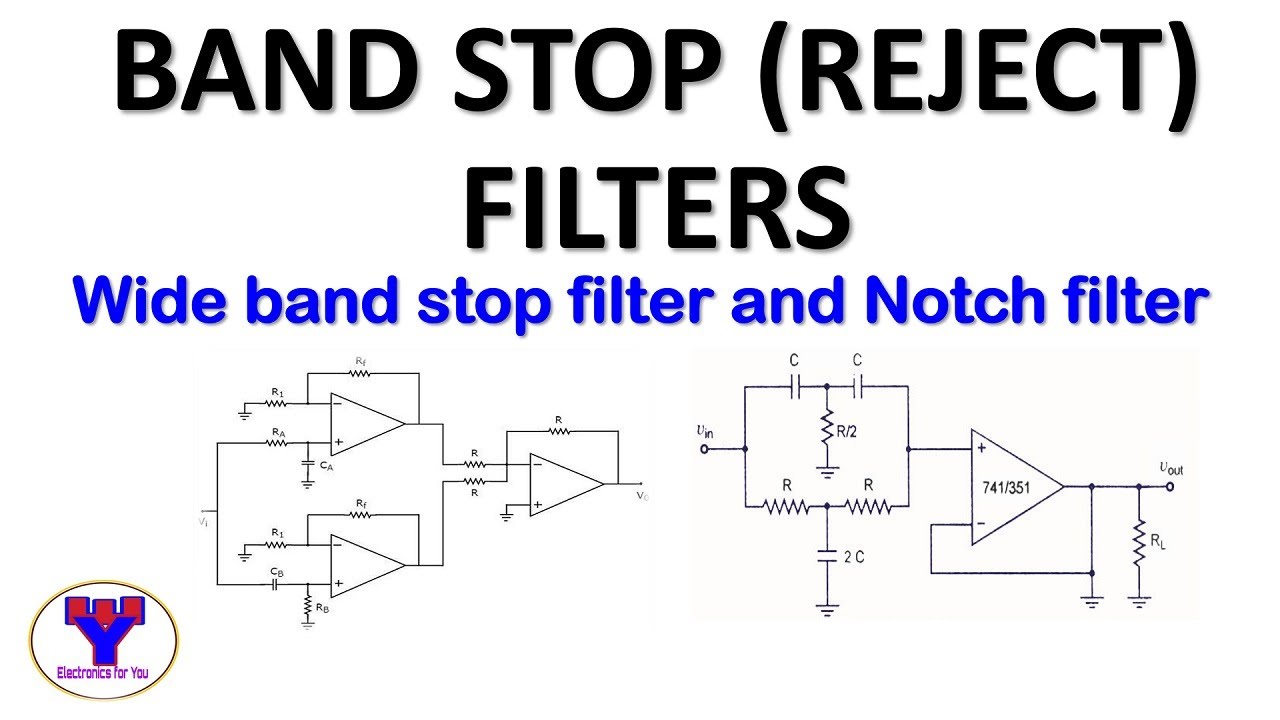
Active band stop filters using opamp Band reject filter YouTube
A Band Pass or Band Reject Filter stops or attenuates a band of frequencies while the frequencies outside this range are passed. The attenuated frequencies range is known as Stop Band. The band reject filter is also called a band stop or band elimination filter because it eliminates a certain band of frequencies. Wide Band Reject Filter: Figure 15.20 (a) shows wide band reject filter circuit using a low pass filter, a high pass filter and a summing amplifier. A band-stop filter works to screen out frequencies that are within a certain range, giving easy passage only to frequencies outside of that range. Also known as band-elimination, band-reject, or notch filters. Band-stop filters can be made by placing a low-pass filter in parallel with a high-pass filter. Band-reject filters are the inverse of a bandpass filter: they filter out unwanted power within a specific frequency range. The transfer function of a band-reject filter can be calculated by hand or using a SPICE simulator. Anyone who has played an analog synthesizer probably understands filters

Band Reject Filter OR Band Elimination Filter Electrical Revolution
A band-reject filter rejects frequencies between the lower limit fL f L and the higher limit fH f H, and passes other frequencies. As for the band-pass filter, you can get this result in two steps. In the first step, you apply a low-pass filter with cutoff frequency fL f L, xlpf,L[n] = x[n] ∗hlpf,L[n], x l p f, L [ n] = x [ n] ∗ h l p f, L [ n], If the filter is wideband, it is referred to as a band-reject filter and if the filter is narrow-band, it is referred to as a notch filter. The characteristics of a band-stop filter are exactly the reverse of the bandpass filter. Hence, the notch filter is a complement of the bandpass filter. Filters are networks that process signals in a frequency-dependent manner. The basic concept of a filter can be explained by examining the frequency dependent nature of the impedance of capacitors and inductors. Consider a voltage divider where the shunt leg is a reactive impedance. By summing the high-pass and low-pass outputs of the state-variable filter, a notch, or band-reject, filter may be formed. Filters of this type are commonly used to remove interference signals. The summation is easily performed with a simple parallel-parallel summing amplifier, as shown in Figure 11.8.1. Figure 11.8.1: Notch filter.

Band reject filter Configurations & Applications Ranatec
When a band-pass response is needed, you can use a high-pass filter followed by a low-pass filter. When a band-reject response is needed, you can use a summation stage to add a low-pass-filtered signal to a high-pass-filtered signal. The cutoff frequencies of the two filters are adjusted such that the frequency responses overlap in a way that. The filter that allows above and below the particular range of frequencies and rejects all other frequencies of a given input signal, is known as band stop filter. It is also known as a band-reject filter or band elimination filter or notch filter. It allows all the frequencies below and above the cut-off frequency of low pass and high pass.
Full line of customizable Band Reject Filters of varying frequencies, bandwidths and Q requirements. Available in various topologies - MPG Formula to calculate the band stop filter. In the simple RC band stop, the resistors and capacitors are usually the same size. The band stop filter transfer function is based on the following formula in this case: A = 1 - ( ω R C) 2 1 + 4 ω R C - ( ω R C) 2. R is the ohmic resistance and C is the capacitance of the capacitors.

CBand Bandstop Filter Cavity filter for Radar and
Nevertheless, the block diagram and the response of our idealised band-reject filter are shown in Figures 9 and 10, below. Step 3: Sweeping The Filter. Figure 9: [top] An idealised band-reject filter. Figure 10: [middle] The response of our ideal band-reject filter. Figure 11: [bottom] Controlling a filter by applying an external voltage to a. Band stop filters are generally classified as: Wide band stop filter; Narrow band stop filters; The narrow band-reject filters are sometimes referred to as notch filters due to the fact that these possess high-value quality factor i.e., Q more than 10 where the bandwidth is very small in comparison to wide band reject filters.




