Sulfur at the Solfatara crater 1911 map of the area Topographic relief map. The Phlegraean Fields (Italian: Campi Flegrei [ˈkampi fleˈɡrɛi]; Neapolitan: Campe Flegree) is a large volcanic caldera situated to the west of Naples, Italy. It is part of the Campanian volcanic arc, which includes Mount Vesuvius on the east side of Naples. The Phlegraean Fields is monitored by the Vesuvius. The Campi Flegrei ("burning fields") or Phlegrean Fields is a large, 13-km-wide nested caldera located under the western outskirts of the citiy of Naples and under the Gulf of Pozzuoli.. Location map of the Phlegrean Fields. Latest news. Tue, 17 Oct 2023, 04:47.

Map of the Campi Flegrei caldera (NaplesItaly). The map, modified
A Huge Italian Volcano Could Be Ready to Erupt. Italy's Campi Flegrei volcano has caused thousands of recent earthquakes and pushed up the ground, worrying 1.3 million residents. View of the. Campi Flegrei, which means "burning fields" or "fiery fields," is a sprawling, mostly-hidden network of 24 craters and edifices that stretches from its vast caldera opposite Vesuvius at the. Campi Flegrei is a 13-km-wide caldera that encompasses part of Naples and extends to the south beneath the Gulf of Pozzuoli. Episodes of significant uplift and subsidence within the dominantly trachytic caldera have occurred since Roman times. The earliest known eruptive products are dated 47,000 years BP. The caldera formed following two large explosive eruptions, the massive Campanian. The Campi Flegrei, or "Fiery Fields," is built from a series of overlapping volcanic features—calderas, domes, and cinder cones—that are historically active. The Campi Flegrei calderas have produced two of the largest eruptions Europe has seen in the past 40,000 years. The Neopolitan Yellow Tuff (rock composed of fragments of material.

Structural map of Campi Flegrei caldera, redrawn from Vilardo et al
The Italian name Campi Flegrei can be translated as "The Fiery Fields", and it is a fitting moniker for this stretch of coastline west of Naples that lies above the the largest volcanic area in Europe. This fascinating area is home to a number of important archaeological sites, coastal lakes, beaches, thermal springs, and nature reserves and is worth a day trip from the bustling capital city. Campi Flegrei (CF) is an active and densely populated caldera in Southern Italy, which has manifested signs of significant unrest in the last 50 years.. Campi Flegrei caldera map (UTM) showing. The retrieved ground velocity maps and displacement time series offer an overview on the temporal behaviour of Campi Flegrei ground displacement along an unprecedented time window of about 30 years. Slide A: Plot of the Campi Flegrei map with the indication of faults (blue lines) that overlap with the relocated swarms. The faults are taken by Vilardo et al. 29. The swarms are: 2000-yellow.

Pyroclastic currents hazard map of the Campi Flegrei caldera Download
The resulting impact maps provide useful insight into the effects future unrest could have on businesses, buildings and livelihoods within Campi Flegrei. The impact maps show that, depending on the location of unrest, evacuations associated with future unrest may involve displacement of large numbers of residents, and significant damage to. Both Campi Flegrei and the Long Valley Caldera are known as supervolcanoes, a term used to describe a volcano that at one time has erupted more than 240 cubic miles of material. Michael Poland, a.
The active Campi Flegrei caldera in southern Italy has a remarkably long history of coexistence between volcanism and human settlements, and it is famous for its peculiar slow ground movement. The ground around Italy's awakening supervolcano rose by up to 66 feet (20 meters) before its previous eruption, a new study has revealed. In 1538, the ground below Campi Flegrei, near Naples.
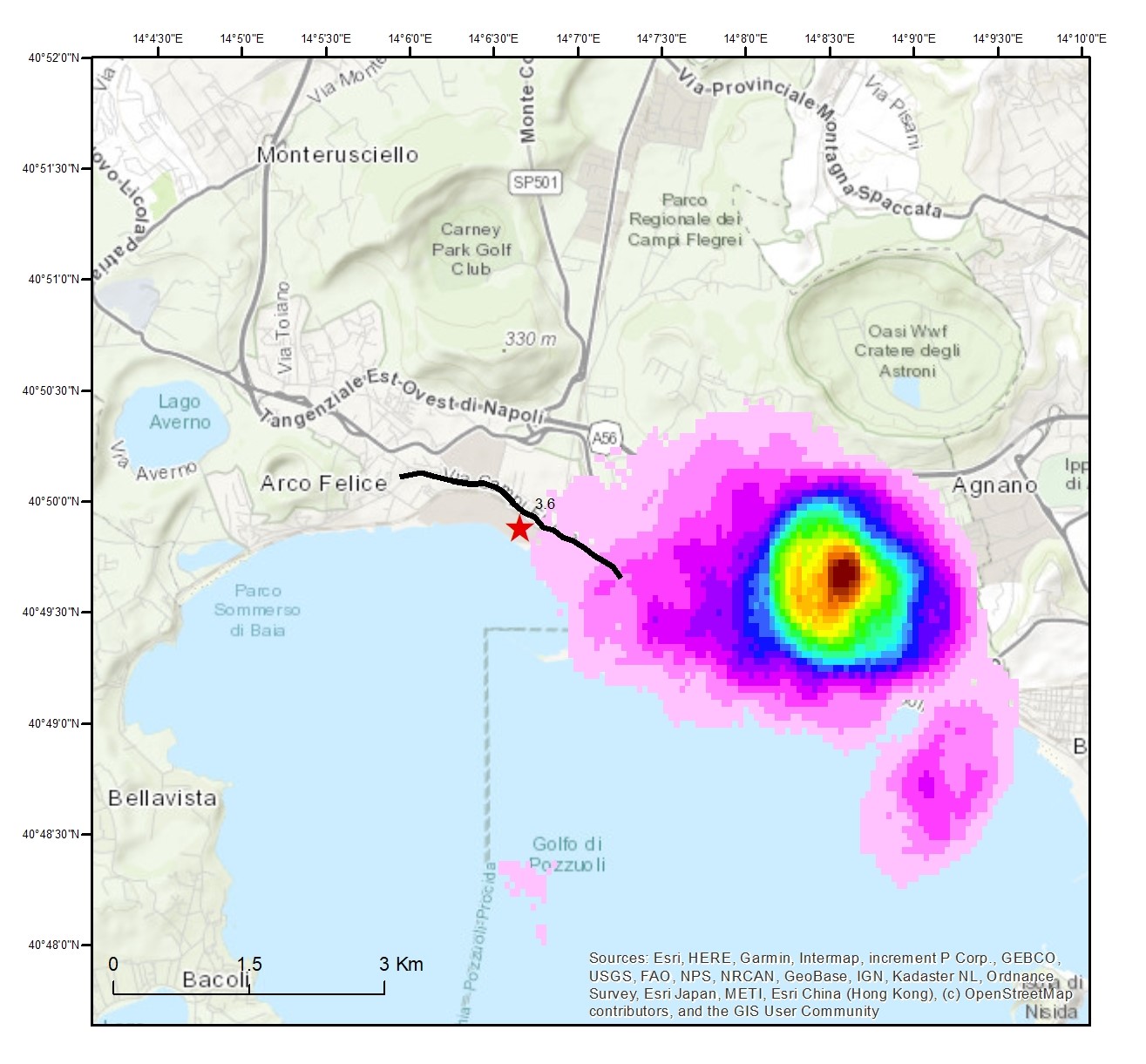
Campi Flegrei Is a volcanic eruption more likely? Erdbebennews
Campi Flegrei caldera, Campania, Italy. volcano number: 0101-01= summit elevation: 458 m. location: 40.827 N, 14.139 E . Introduction: Geological sketch map of the Campi Flegrei caldera, kindly supplied by Roberto Scandone of Roma, Terza Università. Vesuvius wiped Pompeii off the map almost two millennia ago, while the vast volcanic Campi Flegrei area near Naples last spewed lava, ashes and rocks in 1538.




