A relative clause is a clause that usually modifies a noun or noun phrase and is introduced by a relative pronoun ( which, that, who, whom, whose ), a relative adverb ( where, when, why ), or a zero relative. Also known as an adjective clause, an adjectival clause, and a relative construction . What is a Relative Clause? A relative clause is a type that modifies a word, phrase, or idea in the sentence. These clauses are usually introduced by a relative pronoun, such as which, who, whom, whose, and that. Some examples of clauses of this type include which I got, whose book she lost, and that Rosie gave.
Relative Clauses 928 plays Quizizz
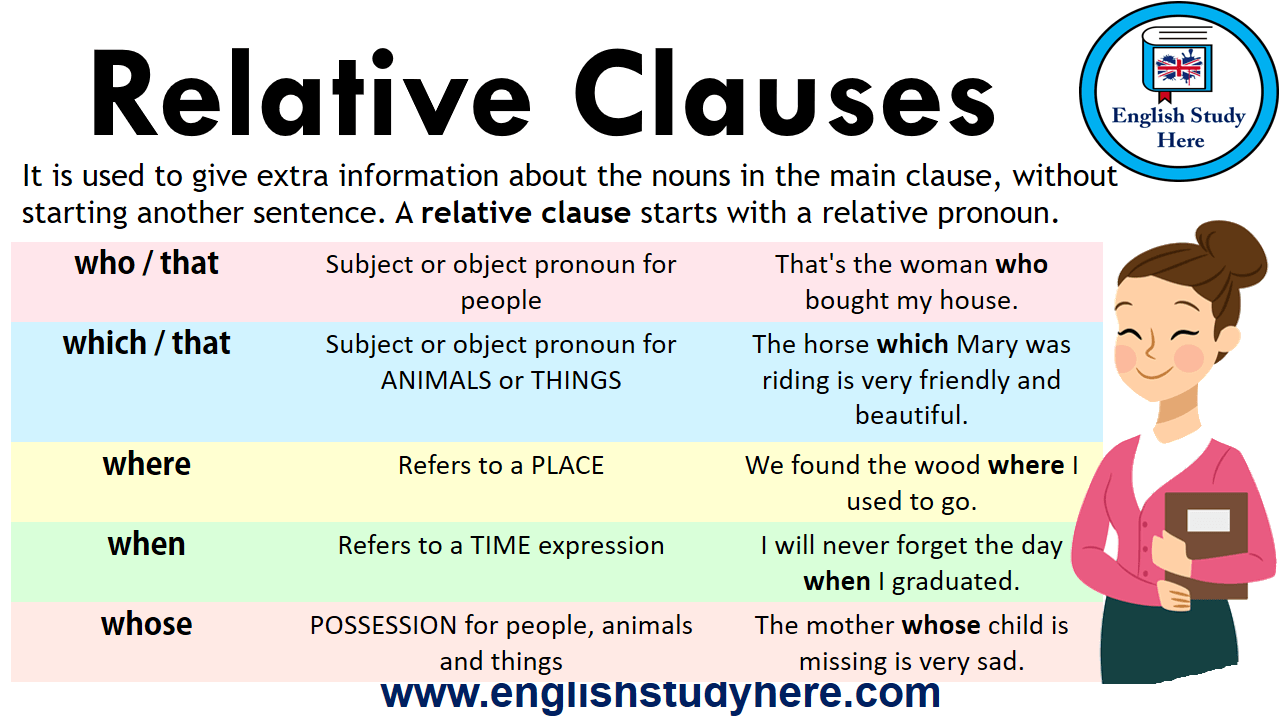
Relative clauses Grammar > Words, sentences and clauses > Relative clauses Relative clauses give us more information about someone or something. We can use relative clauses to combine clauses without repeating information. Defining relative clauses give us essential information - information that tells us who or what we are talking about. The woman who lives next door works in a bank. These are the flights that have been cancelled. We usually use a relative pronoun or adverb to start a defining relative clause: who, which, that, when, where or whose. who / that Definition of "Relative Clause" (with Examples) A relative clause is a multi-word adjective that includes a subject and a verb. For example: The nightingale that we fed last year has returned. (The relative clause "that we fed last year" is functioning as an adjective describing "the nightingale." Grammar Relative clauses Relative clauses give us more information about someone or something. We can use relative clauses to combine clauses without repeating information.. Types of relative clause

relative clause Google Search Relative clauses, English grammar
Defining relative clauses We use defining relative clauses to give essential information about someone or something - information that we need in order to understand what or who is being referred to. A defining relative clause usually comes immediately after the noun it describes. A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phrase [1] and uses some grammatical device to indicate that one of the arguments in the relative clause refers to the noun or noun phrase. Defining relative clauses: 1: The relative pronoun is the subject: First, let's consider when the relative pronoun is the subject of a defining relative clause. We can use 'who', 'which' or 'that'. We use 'who' for people and 'which' for things. We can use 'that' for people or things. What is a relative clause? A relative clause can be used to give additional information about a noun. They are introduced by a relative pronoun like 'that', 'which', 'who', 'whose',.

Relative clauses online presentation
What is a relative clause? A relative clause is one kind of dependent clause. It has a subject and verb, but can't stand alone as a sentence. It is sometimes called an "adjective clause" because it functions like an adjective—it gives more information about a noun. Relative clauses are dependent clauses that give the reader more information about another noun in the sentence. For example: The unicorn possessed magical powers, which could heal the sick. In this sentence, the relative clause which could heal the sick modifies the subject, unicorn, by identifying which magical powers it possessed.
Relative clauses. A relative pronoun is a word like "that" or "which" or "who", so a relative clause is a clause that begins with a relative pronoun. In the sentence "The dragon who breathed blue fire has retired," "who breathed blue fire" is a relative clause. Learn more about these constructions by watching the video! Relative Clauses. Relative clauses, also known as adjective or attributive clauses, are a type of complex sentence in English grammar. The two main types are defining and non-defining relative clauses. They will start with a relative pronoun or a relative adverb. We can also reduce relative clauses into present or past participle phrases.

Relative Clause Definition and Examples of Relative Clauses
A relative clause is a type of subordinate clause, it is used in order to modify or adapt or describe a noun or a pronoun. Relative clauses are always dependant. Relative clauses must contain both a verb and a subject and always being with the words who, whom, that, which, when, whose, why or where or any variation of these words. part of a sentence that cannot exist independently and describes a noun that comes before it in the main part of the sentence: In the sentence "The woman whom I met was wearing a brown hat ," "whom I met " is a relative clause. Fewer examples In the sentence 'The restaurant that we went to has closed ', 'that we went to' is a relative clause.




