Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds, thus reducing or compressing an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is commonly used in sound recording and reproduction, broadcasting, live sound reinforcement and some instrument. 'Dynamic Range' Compression vs Regular compression. Dynamic range compression (DRC) is a specific type of audio signal processing technique that is used to reduce the dynamic range of an audio signal. Compression, on the other hand, is a more general term that refers to any technique that reduces the dynamic range of an audio signal.
Dynamic Range Compression and Noise Innovation in Augmented Listening
Dynamic Range Processing and Digital Effects Dynamic Range Compression Compression is a reduction of the dynamic range of a signal, meaning that the ratio of the loudest to the softest levels of a signal is reduced. This is accomplished using an amplifier with variable gain that can be controlled Dynamic range is good because it adds flair, nuance, and color to audio. Compression is used to illustrate that where musicians want it to be, and that's done by reducing variation elsewhere. On the other hand, compression can add its own effect to audio. Dynamic range compression (often shortened to just "compression") is a process that limits the volume range of a piece of music. This means that rather than have passages that are almost inaudibly quiet of ear-splittingly loud, a piece of music will slot entirely into a preset volume range. Many people believe that an audio compressor both. For dynamic range compression, a ratio of 2:1 means that for every 2 dB the signal exceeds the threshold, it will be reduced to 1 dB above the threshold. The higher the ratio, the more severe the compression or limiting effect. In dynamic range compression, the ratio setting allows control over the amount of compression applied to the signal.

Madamwar Dynamic Range Compression Image
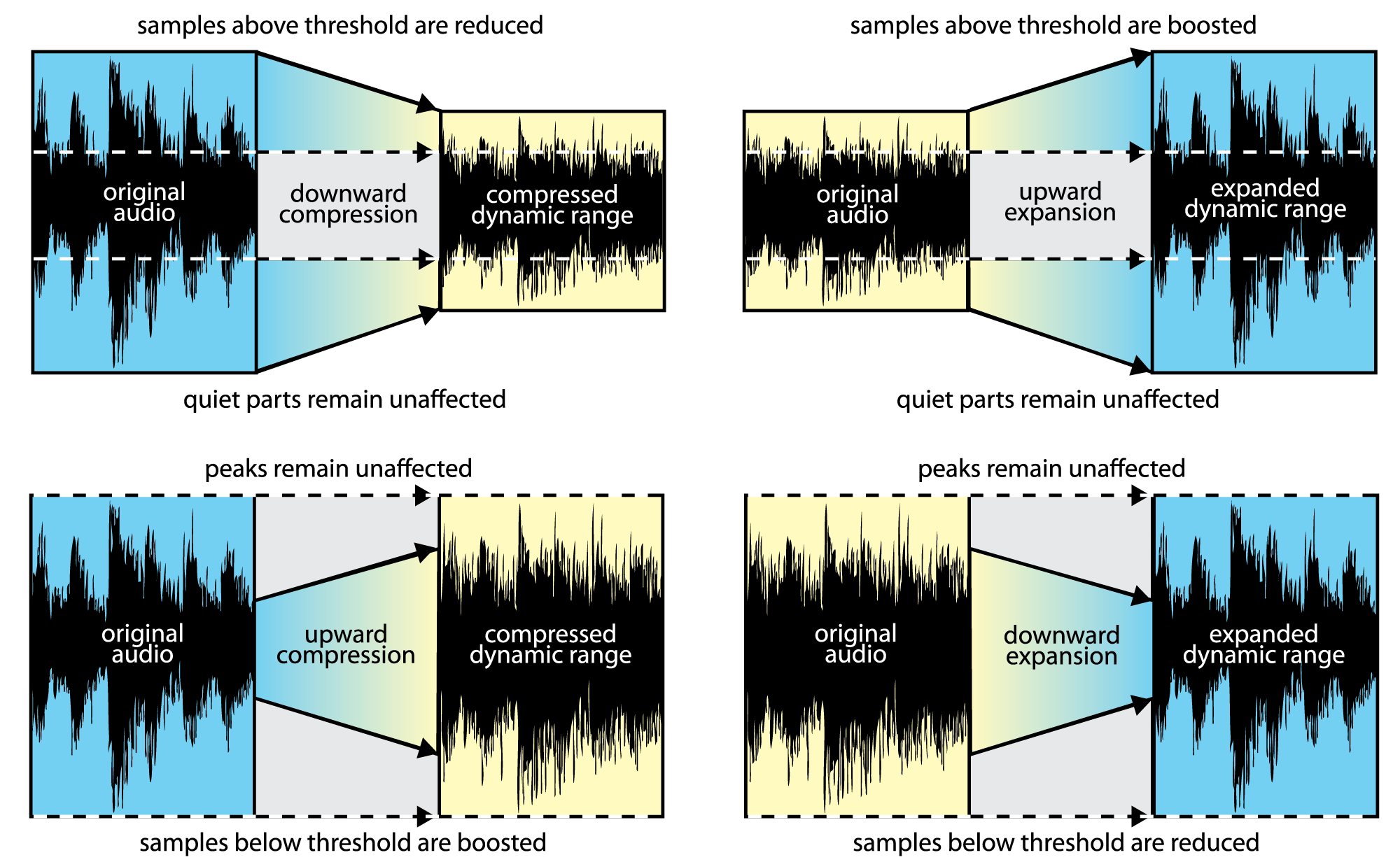
Dynamic range compression is a set of techniques used in audio recording and communication to put high-dynamic-range material through channels or media of lower dynamic range. Optionally, dynamic range expansion is used to restore the original high dynamic range on playback. Dynamic range compression is a critical tool in audio production, used to balance the loud and quiet parts of an audio signal. It has a wide range of applications, from music production and voice recordings to broadcasting and live sound reinforcement. As illustrated by the 'loudness wars' of the 1980s to 2000s, however, overuse of. Static compression characteristic with make-up gain and hard or soft knee. Threshold defines the level above which compression starts. Any signal overshooting the threshold will be re-duced in level. Ratio controls the input/output ratio for signals over-shooting the threshold level. Dynamic range compression or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds, thus reducing or compressing an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is commonly used in sound recording and reproduction, broadcasting, live sound reinforcement and some instrument amplifiers.

Dynamic range compression
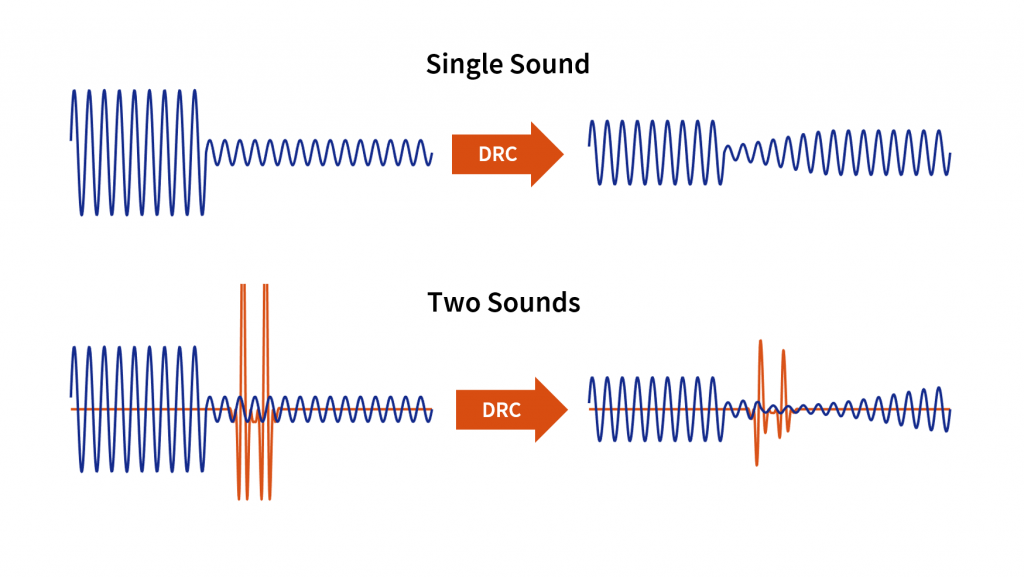
Dynamic range compression and noise. Because DRC is a nonlinear algorithm — it processes the signal differently depending on the signal's level — it can cause distortion when used on multiple sounds at once. Nonlinear distortion from DRC sounds cool in Daft Punk songs, but it's less welcome for a hearing aid user trying to have a. Audio engineers use audio compression to control dynamic range in the music production process. A compressor reduces the peaks of the signal, thus lowering the dynamic range and making it possible to turn up the entire song without peaks causing distortion. With peaks removed, a song can be turned up a lot louder without distortion.
Audio Compression is the most used tool in audio production. In this quick informative episode, you'll learn the basics of how a compressor works and some s. Dynamic range compression is a crucial tool in audio and music production that can be used to control the dynamics of a recording or mix. By understanding the different types of compressors and how to use them effectively, you can improve the overall quality of your sound and bring your recordings to the next level. Every signal is unique; it.
7.1.10 Dynamics Processing Digital Sound & Music
Dynamic Range Compression (DRC), also referred to simply as "compression," is a procedure in which an audio signal's dynamic range is lessened. Compression can be used in many different situations, including broadcasting, live sound reinforcement, and sound recording to helps control audio levels. For input levels between the kneepoints, the system provides dynamic-range compression. The output level increases by 1/CR dB for each dB increase in the input level, where CR is the compression ratio. Figure 5. Input/output relationship for a typical hearing-aid compression amplifier.




