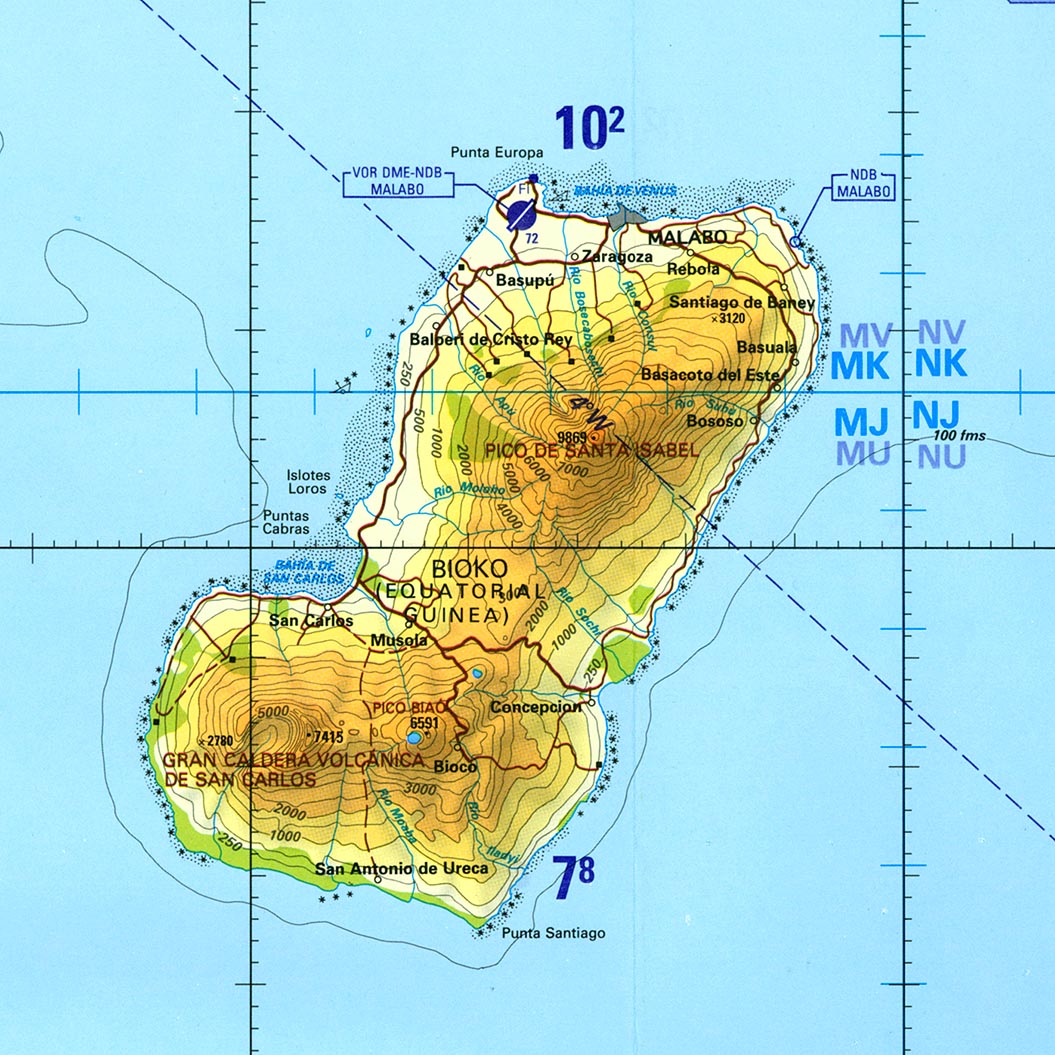
Bioko ( / biːˈoʊkoʊ /; [3] historically Fernando Po; Bube: Ëtulá a Ëri) is an island 32 km (20 mi) south of the coast of Cameroon, and 160 km (99 mi) north east of the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. B ioko Island, also known as Fernando Póo or Fernando Po, lies off the southern Nigeria coast and northwest of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Little known outside of the region, Bioko Island is a paradise waiting to be discovered.. Bioko Island was first spotted by Europeans around 1472 by a Portuguese explorer named Fernão do Pó, and was.
BiokoFernando Po island Map • mappery
Bioko, island of Equatorial Guinea, western Africa, lying in the Bight of Biafra (Gulf of Guinea) about 60 miles (100 km) off the coast of southern Nigeria and 100 miles (160 km) northwest of continental Equatorial Guinea. In 1973 the island, then called Fernando Po, was renamed Macias Nguema Biyogo Island after the first president of the country, but Bioko became the local official name after. v. t. e. Fernão do Pó ( Portuguese pronunciation: [fɨɾˈnɐ̃w du ˈpɔ]; fl. 1472), also known as Fernão Pó, Fernando Pó or Fernando Poo, was a 15th-century Portuguese navigator and explorer of the West African coast. He was the first European to see the islands in the Gulf of Guinea around 1472, one of which until the mid-1900s bore a. Fernando Po. Look up Fernando Po in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Fernando Po may refer to: Fernando Po (island) in Equatorial Guinea, now called Bioko. Fernão do Pó, Portuguese explorer. Fernando Pó, village in Palmela, Portugal. Fernando Pó halt, railway halt in Palmela, Portugal. Bioko (in Europe traditionally called Fernando Po) is an island 32 km off the west coast of Africa, specifically Cameroon, in the Gulf of Guinea. It is the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea with a population of 260,000 and an area of 2,017 km2 (779 sq mi). It is volcanic with its highest peak the Pico Basile at 3,012 m (9,882 ft).

3C7A Bioko Island Fernando Po Island News
Malabo, capital of Equatorial Guinea.It lies on the northern edge of the island of Bioko (or Fernando Po) on the rim of a sunken volcano. With an average temperature of 77 °F (25 °C) and an annual rainfall of 75 inches (1,900 mm), it has one of the more onerous climates in the Bight of Biafra (Gulf of Guinea). Malabo is the republic's commercial and financial centre. The island that came to be called Fernando Po (later Bioko) was sighted by the Portuguese explorer Fernão do Pó about 1472. At first it was called Formosa ("Beautiful"). Annobón was probably sighted by Ruy de Sequeira on a New Year's Day (hence the name, which means "Good Year") between 1472 and 1475, most likely that of 1474. By the Treaty of Tordesillas (June 7, 1494), the. Bioko ( / biːˈoʊkoʊ /; historically Fernando Po; Bube: Ëtulá a Ëri) is an island 32 km (20 mi) south of the coast of Cameroon, and 160 km (99 mi) north east of the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Its population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and. Bioko/Fernando Po Island and the Atlantic World;. Río Muni, bordering Cameroon and Gabon; the main island of Bioko, in front of the Niger Delta, with little more than 2,000 square kilometers; and several other smaller islands, such as Annobon and Corisco. With extensive coasts, the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone of the.

3C3W Bioko Island Fernando Po Island
The Krios arrived from Sierra Leone on the island of Fernando Po in 1827, a year after Great Britain leased the island for 50 years. The Krios joined an influx of several hundred freed Creole African-descended immigrants from Cape Coast and other groups from British colonies in Africa. The Krios began populating the harbor known as Clarence Cove. Spain mounted an expedition to Fernando Po, led by the Conde de Argelejos, who stayed for four months. In October 1778, Spain installed a governor on the island who stayed until 1780, when the Spanish mission left the island. Chief Molambo was succeeded by another local leader, Lorite (1760-1810), who was succeeded by Lopoa (1810-1842).
Operation Postmaster was a British special operation conducted on the Spanish island of Fernando Po, now known as Bioko, off West Africa in the Gulf of Guinea, during the Second World War.The mission was carried out by the Small Scale Raiding Force (SSRF) and the Special Operations Executive (SOE) in January 1942. Their objective was to board the Italian and German ships in the harbour and. At first, the Portuguese and then the Spanish focused primarily on the island of Fernando Po (which was named after the first Portuguese explorer to reach it), later to be known as Bioko. Unlike other Atlantic islands, however, Fernando Po remained a story of failed Portuguese and then Spanish imperialism until the early twentieth century.

The Peak Of Fernando Po. Fernando Po In Equatorial Guinea, Now Called
FERNANDO PO, or Fernando Poo, a Spanish island on the west coast of Africa, in the Bight of Biafra, about 20 m. from the mainland, in 3° 12' N. and 8° 48' E. It is of volcanic origin, related to the Cameroon system of the adjacent mainland, is the largest island in the Gulf of Guinea, is 44 m. long from N.N.E. to S.S.W., about 20 m. broad, and has an area of about 780 sq. m. Fernando Po is. Fernando Po, now called Bioko, is the island nearest the mainland. Photo by Amcaja CC BY-SA 3.0 Preparation and Politics. With the help of the Governor of Nigeria, March-Phillips obtained two tugboats and a band of local recruits to man them. Allied intelligence gathered information to help him plan, through both operatives on the ground and.




