In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial (or fictitious) force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. Forza di Coriolis. In fisica, la forza di Coriolis è una forza apparente, a cui risulta soggetto un corpo quando si osserva il suo moto da un sistema di riferimento che sia in moto rotatorio rispetto ad un sistema di riferimento inerziale . Descritta per la prima volta in maniera dettagliata dal fisico francese Gaspard Gustave de Coriolis nel.
Paradiso delle mappe La forza di Coriolis
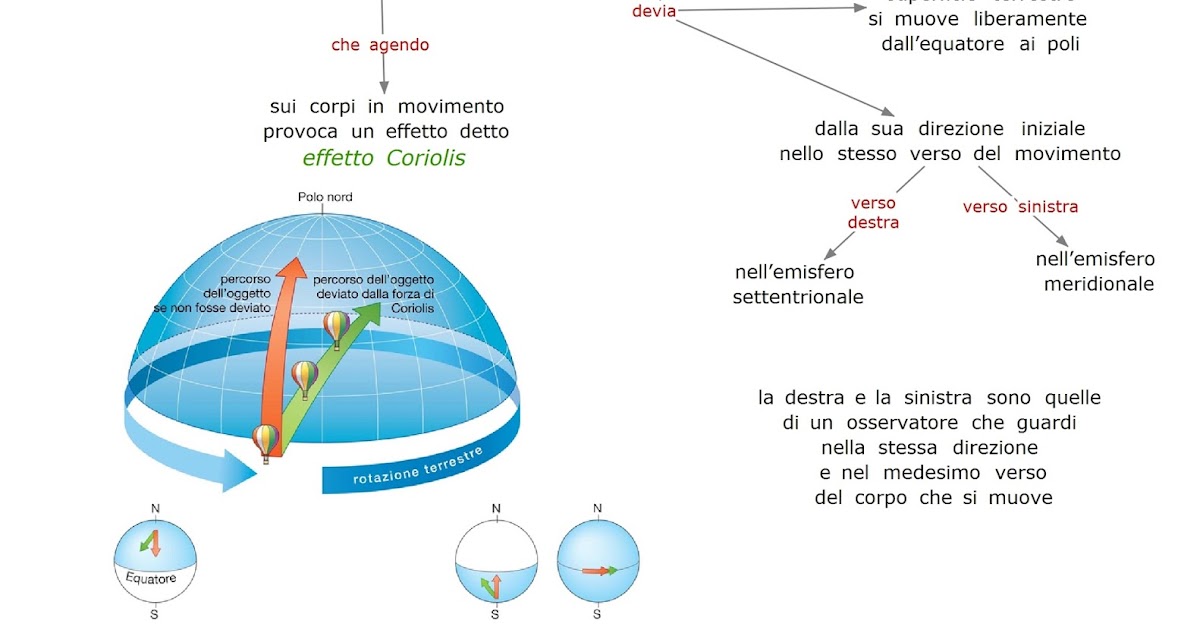
La forza di Coriolis in Fisica è una forza apparente osservata nei sistemi non inerziali in rotazione, che agisce sui corpi in moto rispetto al sistema di riferimento non inerziale e che ha l'effetto apparente di far deviare i corpi da una traiettoria rettilinea. Proseguiamo nello studio dei sistemi non inerziali e aggiungiamo un ulteriore. The Coriolis force in everyday life. The effect of the Coriolis force is an apparent deflection of the path of an object that moves within a rotating coordinate system. The object does not actually deviate from its path, but it appears to do so because of the motion of the coordinate system. The Coriolis effect is most apparent in the path of. Cos'è la forza di Coriolis? Si tratta di una forza apparente (non di una forza vera e propria) che si manifesta sui corpi che si spostano in direzione nord-sud sulla superficie della Terra. The Coriolis effect is responsible for many large-scale weather patterns. The key to the Coriolis effect lies in Earth's rotation. Specifically, Earth rotates faster at the Equator than it does at the poles. Earth is wider at the Equator, so to make a rotation in one 24-hour period, equatorial regions race nearly 1,600 kilometers (1,000 miles.

forza Coriolis YouTube
Coriolis force. English: In physics, the Coriolis effect is an inertial force first described by Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis, a French scientist, in 1835. The Earth is rotating, and therefore it is an oblate spheroid (like a football with flattned ends). The vector representing true gravity can be decomposed in a component perpendicular to the. Coriolis Force an artifact of the earth's rotation. Once air has been set in motion by the pressure gradient force, it undergoes an apparent deflection from its path, as seen by an observer on the earth. This apparent deflection is called the "Coriolis force" and is a result of the earth's rotation. As air moves from high to low pressure in the. The Coriolis force is a fictitious force exerted on a body when it moves in a rotating reference frame. It is called a fictitious force because it is a by-product of measuring coordinates with respect to a rotating coordinate system as opposed to an actual "push or pull." Coriolis, G.-G. "Sur les équations du mouvement relatif des systèmes de. However, Equation 4.9.4 also tells us that, if a particle is moving with velocity v′ with respect to Σ′, it has an additional acceleration with respect to Σ of 2ω × v′, which is at right angles to v′ and to ω. This is the Coriolis acceleration. The converse of Equation 4.9.4 is. a′ = a + ω × (r × ω) = 2vprime × ω.

13 Práctica, coriolis, Ejercicio 1 YouTube
A visual demonstration of the effects of the Coriolis and Centrifugal forces.Visit my homepage, https://www.udiprod.com/, or read about my latest book http:/. In fisica, la forza di Coriolis è una forza apparente, a cui risulta soggetto un corpo quando si osserva il suo moto da un sistema di riferimento che sia in moto rotatorio rispetto ad un sistema di riferimento inerziale.. Descritta per la prima volta in maniera dettagliata dal fisico francese Gaspard Gustave de Coriolis nel 1835, [1] [2] la forza di Coriolis dipende, anche come direzione.
Inoltre, poiché la forza di Coriolis è proporzionale anche all'intensità della velocità del corpo, il suo effetto sarà maggiormente osservabile negli oggetti con alta velocità (fu scoperto dagli artiglieri) e negli oggetti che restano in movimento per lungo tempo. La forza di Coriolis è la causa del moto rotatorio dei sistemi associati. LEGGI LA DESCRIZIONE, CHE NON FA MAI MALELe forze fittizie o apparenti sono una delle cose più strane della fisica. Ci sono e non ci sono. Ma i loro effetti.

कोरियोलिस बल कोरोयोलिस प्रभाव CORIOLIS FORCE OR CORIOLIS EFFECT
www.fisicainlaboratorio.com La forza di Coriolis e il moto di rivoluzione. La rotazione terrestre produce un'altra forza apparente, la forza di Coriolis, che agisce solo sui corpi in movimento. Infatti, a causa della sua.




