Finally, the magic mirror flight has lifted the ban on face mosaics! It will be the long-awaited full-length appearance! !! This memorable work, which will be the first work of the face moza ban, is a local expedition special of the No. 1 blockbuster popular project "School girls until 3 minutes ago" in the mirror flight! 29 real school girls right after the graduation ceremony in the Kansai. A Japanese magic mirror does not reflect the relief design cast on the back. Nor does it have any obvious irregularities on its reflecting surface. So how does a magic mirror work? The secret image is actually cast into the design on the back of the mirror's reflecting surface. The secret image areas are made to be thicker than the rest of the.

Magic mirror Lizz+Lopez
In Japan, bronze mirrors are known as magic mirrors, or makkyo (魔鏡). One side is brightly polished, while an embossed design decorates the reverse side. Remarkably, when light is directed onto the face of the mirror, and reflected to a flat surface, an image magically appears (usually the one featured on its back). Researchers discover a small, bronze Japanese "magic mirror" in the collections of the Cincinnati Art Museum. The hidden image. (Photo: Rob Deslongchamps/Cincinnati Art Museum) The glass is subtly sculpted to reflect an image of the Buddha. The face of the mirror. (Photo: Rob Deslongchamps/Cincinnati Art Museum) A Shinjū-kyō (神獣鏡, "deity and beast mirror") is an ancient type of Japanese round bronze mirror decorated with images of gods and animals from Chinese mythology. The obverse side has a polished mirror and the reverse has relief representations of legendary Chinese shén ( 神 "spirit; god"), xiān ( 仙 "transcendent; immortal"), and legendary creatures. Published Jul 14, 2022, 7:00:48 AM (CNN) — Amid the thousands of treasures in the Cincinnati Art Museum's East Asian art collection, a small bronze mirror dating back to the 15th or 16th century.
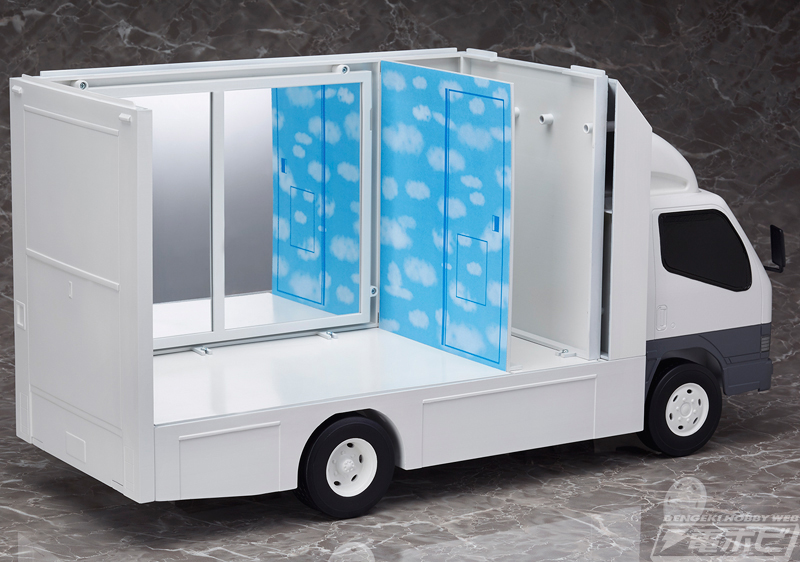

全国の男子が憧れる夢の乗り物があなたの手に!!あのマジックミラー号がネイティブからまさかの立体化! 電撃ホビーウェブ
The Japanese Magic Mirror An Object of Art and of Scientific Study Masao Watanabe Professor of History of Science, School of Science and Engineering, Chuo University, Tokyo Important articles were published on the Japanese magic mirror by Mr. Herbert Maryon and by Dr. Cyril Stanley Smith, respectively, in a recent issue of the present The Japanese Magic Mirror, Watanabe Masao, 1965 5. Recent Advances in Understanding the Mystery of Ancient Chinese Magic Mirrors, Jan. 1987 6. A Magic Mirror Trick (pp. 142~149), Lost Knowledge, Benjamin B. Olshin, 2019 Plate 1 Plate 2 7. Chinese "magic" mirrors, Derek B. Swinson, 1992 8.. March 24, 2022 at 07:50 JST Akihisa Yamamoto introduces "magic mirrors" (The Asahi Shimbun) Akihisa Yamamoto poses for the camera, with a "magic mirror" in his hands, in Kyoto's Shimogyo. Magic mirrors (in Japanese: Makyoh) are ancient artefacts originating from China and Japan. Such mirrors are metallic mirrors with a backside relief pattern. If a light beam falls on the mirror.
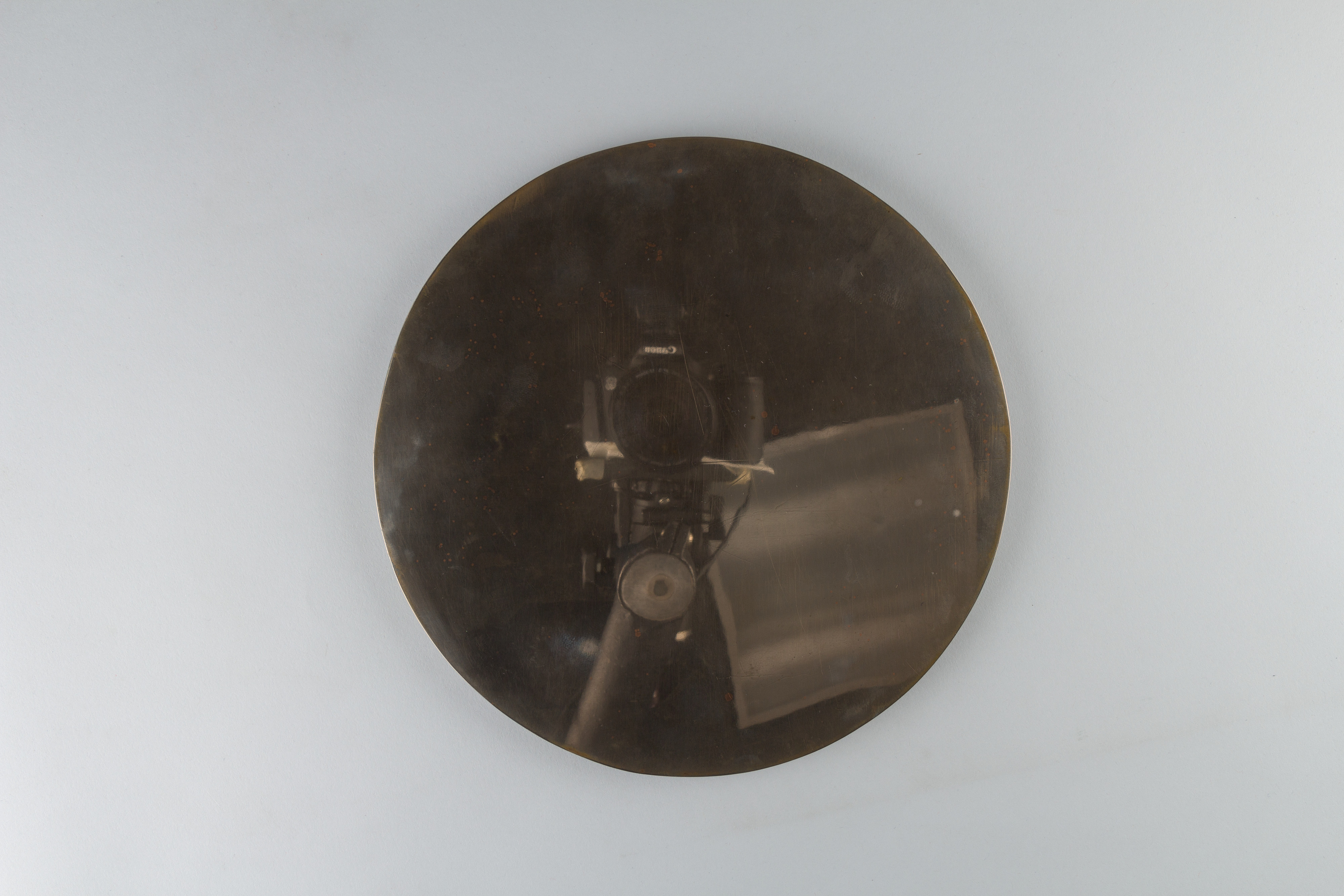

Magic Mirror with Image of the Buddha Amida Japan Edo (16151868
In Japan, some bronze mirrors are known as magic mirrors, or makkyo (魔鏡). One side is brightly polished, while an embossed design decorates the reverse side. Remarkably, when light is directed onto the face of the mirror, and reflected to a flat surface, an image magically appears (usually the one featured on its back). A magic mirror flight carrying everyone's dreams has been dispatched nationwide this year as well! !! The destination is the graduation ceremony of the school, which has a reputation for cute uniforms in the Kanto, Kansai, and Tokai regions!
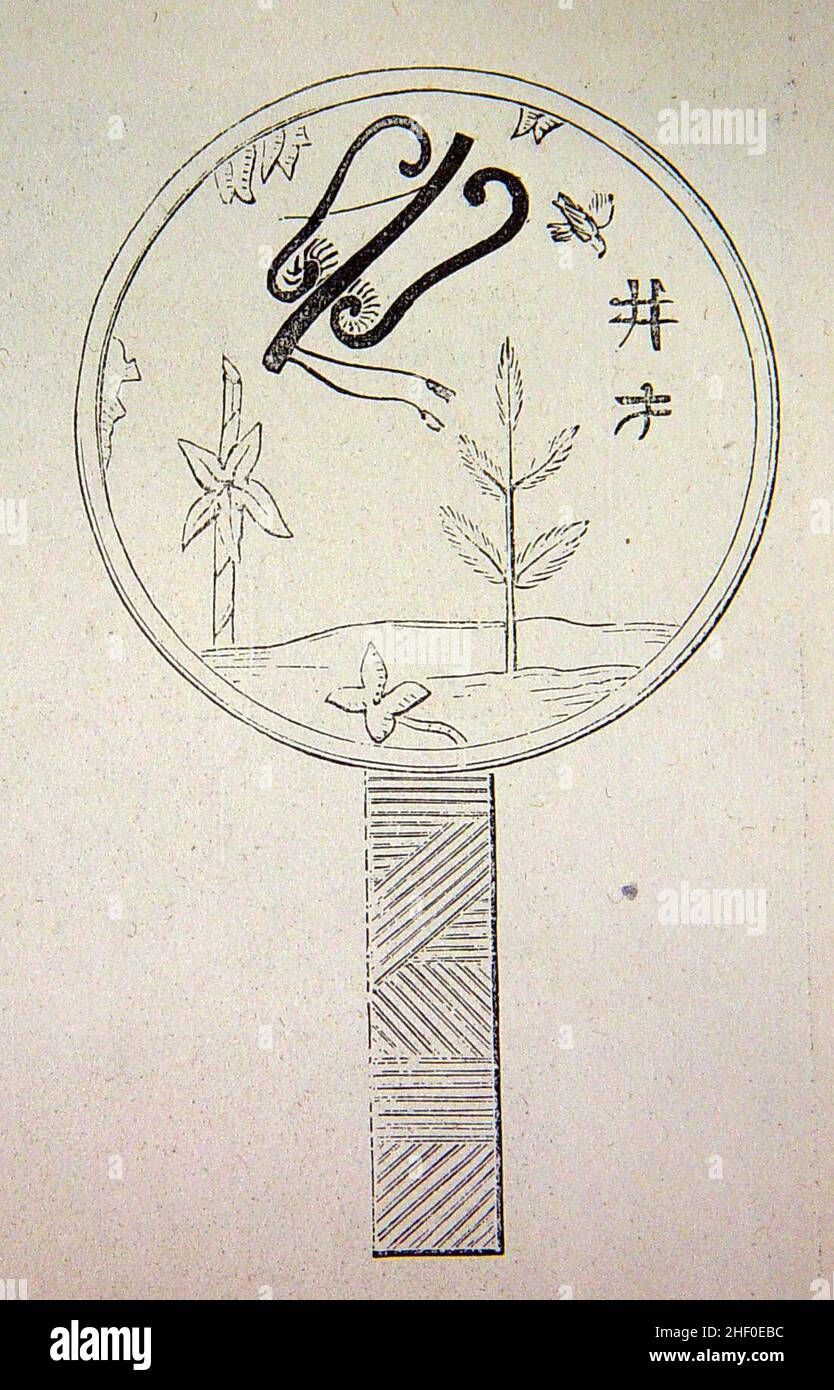
JAPANESE MAGIC MIRROR.*. The interesting apparatus, familiarly known by this name, is a circular, metallic, hand-mirror, having figures in relief upon its back. The reflecting surface is highly polished, and reflects the face as well apparently as mirrors of silvered glass; but when it is used to reflect the direct rays of a powerful light upon. Yamamoto Shinji, or Oryu, the third generation, grandfather of Akihisa found the method to create Christian magic mirrors in 1974. The term "magic mirror" refers to a mirror that projects the design applied to its back in its reflected light. In Japan, they began appearing in historical documents around the middle of the Edo period.
"Japanese magic mirror Stock Photo Alamy
Many critics have explored Carter's use of mirrors, particularly in relation to Japan. 11 Murai argues that Carter represents Japan as "the exact mirror image of the West" ("Passion" 9), and Takahashi similarly argues, "For Carter, Japan was almost like a looking-glass, or to be more exact, an incessantly changing image that appears on the surface of a mirror" (2). Yet, as. Some bronze mirrors give a curious effect. When a light is shone on the apparently smooth mirror surface, an image of the design on the back is seen reflecte.




