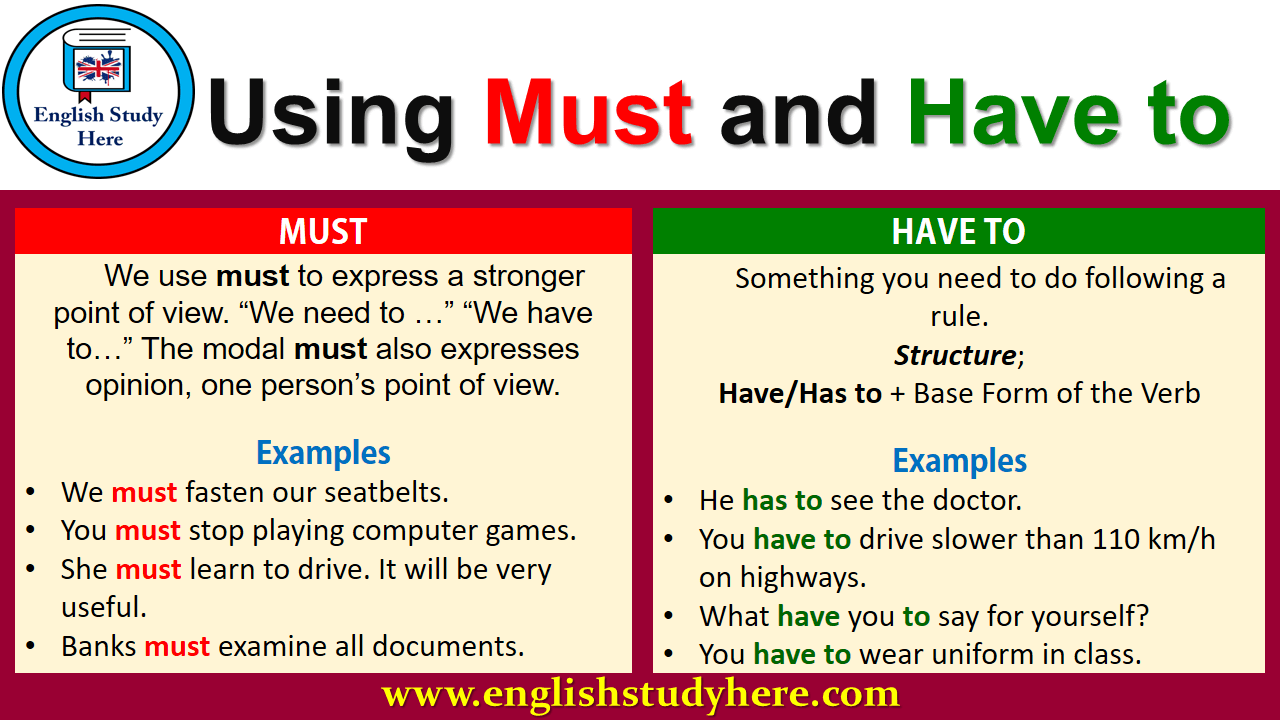
Both Must and have to express obligation or necessity, but there are some small differences: • Must expresses the speaker's feelings, whereas have to expresses, above all, an impersonal idea: You must come. You are obliged to come (I require that you come) You have to come. You are obliged to come. (There's a rule requiring you to come) EnglishClub: Learn English: Grammar: Verbs: Modals: have to, must have to, must. Have to is NOT an auxiliary verb (it uses the verb have as a main verb). We include have to here for convenience.. Must is a modal auxiliary verb.. In this lesson we look at have to, must and must not, followed by a quiz to check your understanding.. have to for objective obligation. We often use have to to say.

Educational infographic Must vs Have to Your
Questions - Must or Have to? For questions it is much more common to use Have to instead of Must (Must sounds very formal): When do you have to finish the report?; Normally, you will not hear someone say "When must you finish the report?" as it doesn't sound natural.. Note however that you may still hear MUST used in questions, though mainly in British English. must visit. had to visit. 10. I __________ (get up) every morning at six o'clock, so I can make it to work on time. need to get up. have to get up. both are correct. Must, need to, and have to are similar modal forms in English. Learn the differences and when to use each, and then test your knowledge. Have To: 7 Questions to Help You Figure It Out. It can be tricky to know when to use must and when to use have to . Both terms have a similar meaning: to express a need or obligation. However, must and have to also have their own meanings. Must is a modal verb, whereas have to is an auxiliary verb. In this blog post, we'll solve the mystery. We use have to / must / should + infinitive to talk about obligation, things that are necessary to do, or to give advice about things that are a good idea to do. Mus t and have to are both used for obligation and are often quite similar. They are both followed by the infinitive. I must go now. / I have to go now.
Using Must and Have to in English English Study Here
Must Obligation from Within. We can use must when the obligation comes from the speaker themselves rather than from an external source.. Examples: I must study more if I want to pass the exam. I must stop eating so much sugar. Future Obligation/Orders. Must doesn't have a future form.Use will have to to talk about future obligations.. Example: She ' ll must have to study more, if she wants. Must / mustn't - quiz 1. I have to walk the dog. Have to, don't have to, must, mustn't. Modal verbs of obligation. Modals of probability: must / can't. Must not / don't have to 1. Modals of necessity : must / have to. Must and have to have similar meanings in English. Both are used to express necessity. However, there are a few important differences between them. Must is a modal verb. Modal verbs do not take any endings like -s, -ed or -ing (never 'musts' or 'musted') Modal verbs are followed by the base form of another verb (must do, must be) If you are learning English online, you probably already know there are many modal verbs in the English language. In this article, we'll look at English grammar rules governing the use of the modal verbs must, have to, may, and might.. The first thing to remember about modal verbs is that, unlike ordinary verbs, they don't change according to time (they have "substitutes" for this.

Must vs Have To Easy English Conversation Practice Learn English
Obligations are things that are needed to be done. We use ' have to ' and ' must ' to express such actions and events. There is a distinction that requires attention: ' Must ' is used for obligations and needs that are external. By external, we mean that they have been motivated and assigned by someone else. Not fulfilling such actions may also. It means you have no choice but to do (or not do) an action. We can only use 'must' in the present form to describe a general or permanent obligation, or an obligation in the near future. The structure of 'must' is easy because it is the same for every subject: When you drive you must wear a seatbelt.
This video explains when to use 'must' and when to use 'have to'.We use 'must' to express a necessity or requirement, a strong recommendation or order, or a. Must vs Have To / Has To. Must and have to express obligation or necessity: The main differences between must and have to are: Must means "really should or else it will be bad for you", it expresses an obligation forced by the speaker. Have / Has to expresses general obligations. When we are talking about another person's obligation we use have.

Modals Must vs. Have to in English englishacademy101
PART 1: CHOICES / OBLIGATIONS. We use "must" and "have to" when we do not have a choice. We are speaking about obligations like laws and rules. These two verbs mean the same thing. Citizens must pay tax. Citizens have to pay tax. Citizens have got to pay tax. (informal) All students must wear a school uniform. Learn how to use the verbs MUST and HAVE TO in today's lesson. Part 1: choice / obligationsPart 2: probability / deductions We'll look at the structures: mus.




