The accessory navicular (os navicularum or os tibiale externum) is an extra bone or piece of cartilage located on the inner side of the foot just above the arch. It is incorporated within the posterior tibial tendon, which attaches in this area and can lead to Accessory Navicular Syndrome. An accessory navicular is congenital (present at birth. Os tibiale externum; Pirie's bone; Talonaviculare ossicle; Os scaphoideum accessorium; URL of Article. An accessory navicular is a large accessory ossicle that can be present adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone. The tibialis posterior tendon often inserts with a broad attachment into the ossicle. Most cases are asymptomatic but.

Treating The Accessory Navicular In Young Athletes
accessory navicular (os tibiale externum) os intermetatarseum. Most common sesamoids. os peroneum. located in the peroneus longus tendon. hallux sesamoids. located in the flexor hallucis brevis tendon at the base of the 1st metatarsal head. Classification. Accessory Ossicles and Sesamoids of the Foot and Ankle. Os tibiale externum (accessory navicular) is a large ossicle adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone. The tibialis posterior tendon often inserts with a broad attachment onto the ossicle, which may cause a painful tendinosis due traction between the ossicle and the navicular. Such changes are best seen on MRI. Classification. The Geist classification divides the accessory navicular bones into three types. Type 1: An os tibiale externum is a 2-3 mm sesamoid bone in the distal posterior tibialis tendon.Usually asymptomatic. Type 2: Triangular or heart-shaped ossicle measuring up to 12 mm, which represents a secondary ossification center connected to the navicular tuberosity by a 1-2 mm layer of. Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Accessory ossicles of the feet are common developmental variants with almost 40 having been described. Some of the more common include 1-4: os peroneum. os subfibulare. os subtibiale. os tibiale externum (accessory navicular) os trigonum. os calcaneus secundaris.

Os tibiale externum Geist classification Radiology Case
Accessory Navicular. Acessory Navicular is a common idiopathic condition of the foot that presents with an enlargement of the navicular bone. Diagnosis is made with plain radiographs of the foot showing a plantar medial enlargement of the navicular bone. Treatment is generally conservative with shoe modifications and a short period of cast. The accessory navicular syndrome, also known as os naviculare syndrome occurs when a type II accessory navicular becomes painful due to movement across the pseudo-joint between the ossicle and the navicular bone.. Radiographic features Ultrasound. It can be inferred on musculoskeletal ultrasound if a patient's pain is located at a type II accessory navicular and the patient is tender to. Also known as os naviculare or os tibiale externum, an accessory navicular is an extra bone on the inside of the navicular (the bone in the middle of the arch of the foot) and within the posterior tibial tendon that attaches to the navicular bone. Top-view of accessory navicular in the right foot. The os tibiale externum is also known as accessory navicular bone, os naviculare secundarium, accessory (tarsal) scaphoid, or prehallux. It is found within the tibialis posterior tendon near its insertion on the navicular bone. The os peroneum is a small sesamoid bone located within the peroneus longus tendon, adjacent to the cuboid.

Surgery Assistant
The accessory navicular (os navicularum or os tibiale externum) is an extra bone or piece of cartilage located on the inner side of the foot just above the arch. It is incorporated within the posterior tibial tendon, which attaches in this area. An accessory navicular is congenital (present at birth). In rare cases, the accessory navicular bone creates a bony prominence in the midfoot that causes pain, redness and swelling in the medial arch area, plantar fasciitis, bunions and heel spurs. When this happens, the condition is called accessory navicular syndrome. ANS can arise from a number of things, including foot trauma like ankle sprains.
The Geist1 classification divides accessory navicular bones into three types: type 1 accessory navicular bone. also known as os tibiale externum. 2-3 mm sesamoid bone embedded within the distal portion of the posterior tibial tendon. no cartilaginous connection to the naviculam tuberosity and may be separated from it by up to 5 mm. An accessory navicular bone is located posterior to the posteromedial tuberosity of the tarsal navicular bone. The tibialis posterior tendon inserts into the navicular bone. Tibialis posterior is an inverter of the foot, assists in the plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle and also has a major role in supporting the medial arch of the foot.
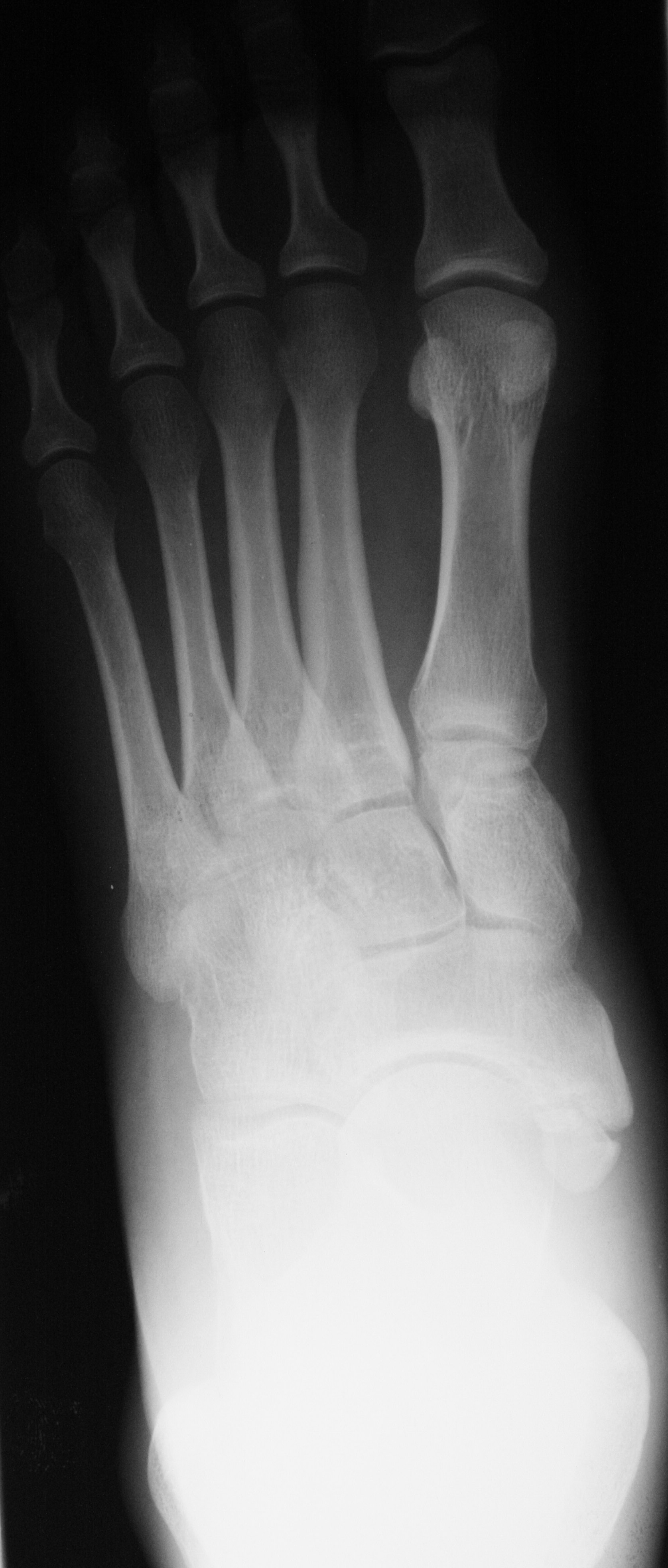
UCSD Musculoskeletal Radiology
The accessory navicular, or os tibiale externum, is an accessory bone on the medial side of the navicular of the foot at the insertion of the posterior tibial tendon (PTT). It can cause obvious hyperpronation, medial foot pain, and a limited and painful relevé in dancers. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the operative. The os intermetatarseum is less common than the os tibiale externum, os trigonum, and os peroneum. The estimated prevalence is 1.2%-10% [ 2 , 9 ]. Reichmister, et al. reported three cases of painful os intermetatarseum, and described compression of the deep peroneal nerve by the os intermetatarseum [ 23 ].




