How does the Silverman score calculator work? This health tool is used to evaluate the pediatric patient's work of breathing. It allows clinicians to quickly recognize respiratory distress or its impending presence. Also known as the Silverman-Anderson Index, the score supports the evaluation of 5 breathing parameters: 29426853 PMC5998375 10.1038/s41372-018-0049-3 To determine if the Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score, which is assessed by physical exam, within 1 h of birth is associated with elevated carbon dioxide level and/or the need for increased respiratory support. Prospective cohort study including 140 neonates scored within 1 h of birth.

The SilvermanAnderson index is used to score an infant's degree of
38 Citations 3 Altmetric Metrics Abstract Objective: To determine if the Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score, which is assessed by physical exam, within 1 h of birth is associated with. Journal of Perinatology J Perinatol. 2018; 38 (5): 505-511. Published online 2018 Feb 9. doi: 10.1038/s41372-018-0049-3 PMCID: PMC5998375 PMID: 29426853 Performance of the Silverman Andersen Respiratory Severity Score in predicting PCO 2 and respiratory support in newborns: a prospective cohort study The Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score can be simplified and still predicts increased neonatal respiratory support Acta Paediatr. 2020 Jun;109 (6):1273-1275. doi: 10.1111/apa.15142. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Authors Shubha G Setty 1 , Maneesh Batra 1 2 , Anna B Hedstrom 1 2 Affiliations Silverman Anderson Score and Downe's Score | Pediatrics Learning Pediatrics 84.6K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 709 Share 81K views 5 years ago Neonatal Conditions This video describes how.
PPT Respiratory Distress Syndrome PowerPoint Presentation, free
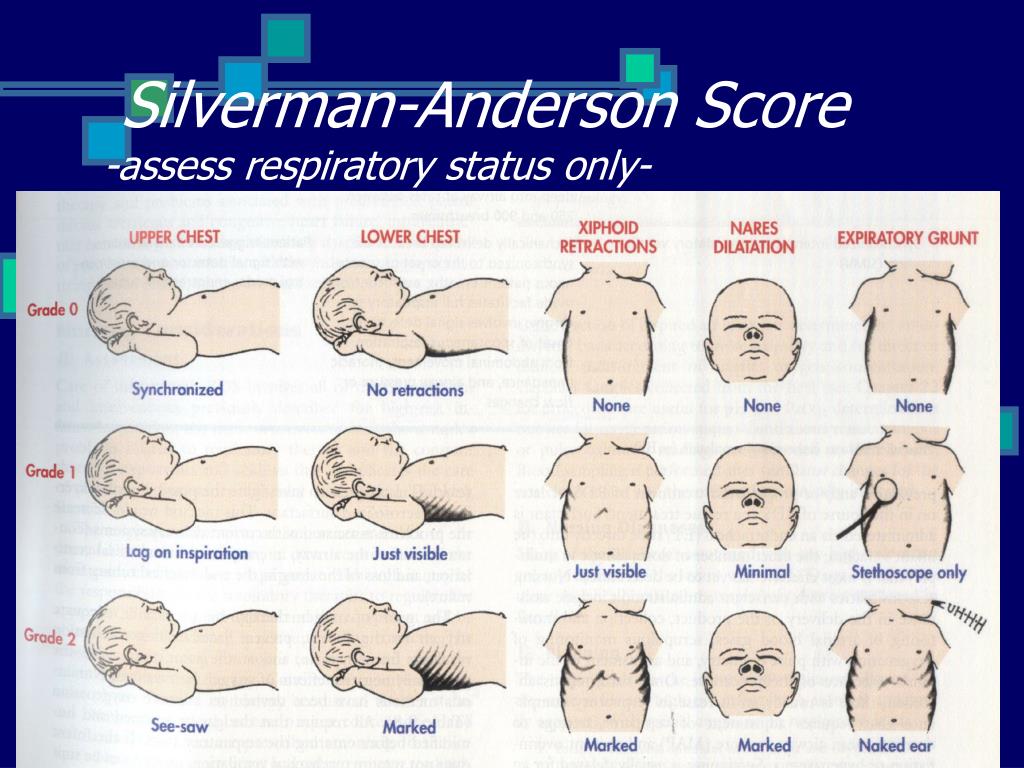
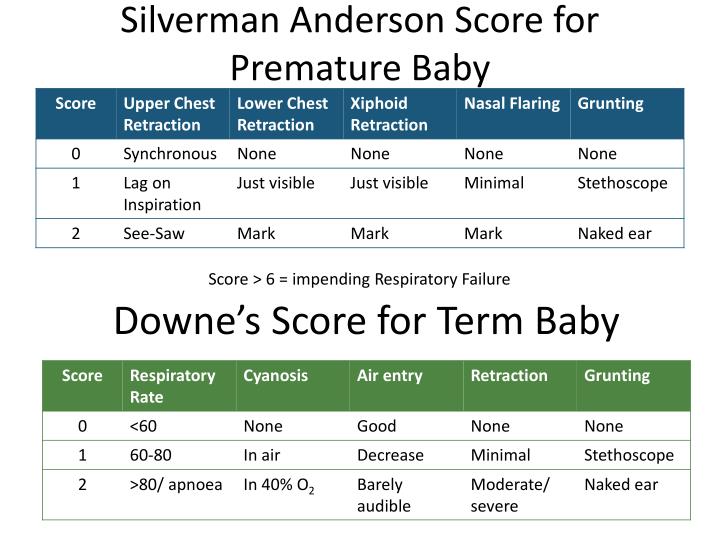
The Silverman Andersen Respiratory Severity Score (RSS) evaluates five parameters of work of breathing and assigns an overall score with a patient breathing comfortably a "0" and a patient in. Downes and Silverman Anderson Score (SAS) on the clinical evaluation, oxygen saturation (SpO 2) Objective: To determine if the Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score, which is assessed by physical exam, within 1 h of birth is associated with elevated carbon dioxide level and/or the. Silverman and Anderson developed a simple score for grading the severity of neonatal respiratory distress. Parameters: (1) chest movements (2) retractions of the intercostals muscles (3) retractions at the xyphoid (4) nares flaring/dilatation (5) expiratory grunt total score = = SUM (points for all 5 parameters) Interpretation: • minimum score: 0

Escala de SilvermanAnderson para dificultad respiratoria del recién
The Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score in the delivery room predicts subsequent intubation in very preterm neonates Acta Paediatr. 2020 Nov 18. doi: 10.1111/apa.15671. Online ahead of print. Authors Anna B Hedstrom 1. Respiratory distress in the neonate is diagnosed when one or more of the following is present; tachypnoea or respiratory rate of more than 60/minute, retractions or increased chest in drawings on respirations (subcostal, intercostal, sternal, suprasternal) and noisy respiration in the form of a grunt, stridor or wheeze [ 1 ].
Downes` score (DS) (3) and Silverman Anderson score (SAS) (4) are commonly used for quick diagnosis of distress and assessment of its severity. This grading is crucial in decision making for further management which might include mechanical ventilation for severe distress. The Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score in the delivery room predicts subsequent intubation in very preterm neonates
PPT An approach to Respiratory Distress in Newborn PowerPoint
For example, increases in FiO 2 and respiratory severity scores like the Silverman Anderson score (SAS) often occur following changes in lung aeration [4][5] [6]. Moreover, blood gas analysis. The Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score may be valuable for predicting need for escalation of respiratory support and facilitate decision making for transfer in low-resource settings. Objective:To determine if the Silverman Andersen respiratory severity score, which is assessed by physical exam, within 1 h of birth is associated with elevated carbon dioxide level and/or the need for.




