4Ts Score for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Differentiates patients with HIT from those with other causes of thrombocytopenia. When to Use Pearls/Pitfalls Why Use Thrombocytopenia Platelet count fall >50% AND platelet nadir ≥20 +2 Platelet count fall 30-50% OR platelet nadir 10-19 +1 Platelet count fall <30% OR platelet nadir <10 0 The Reversible Causes of Cardiac Arrest: 4 Hs, 4 Ts Cardiac arrest happens when the heart stops beating. When this occurs, the heart also loses its ability to pump blood throughout the body, thus interrupting blood flow. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation are mainly the treatment for cardiac arrest.
4H's and 4T's in paediatric cardiac arrest PEM Infographics
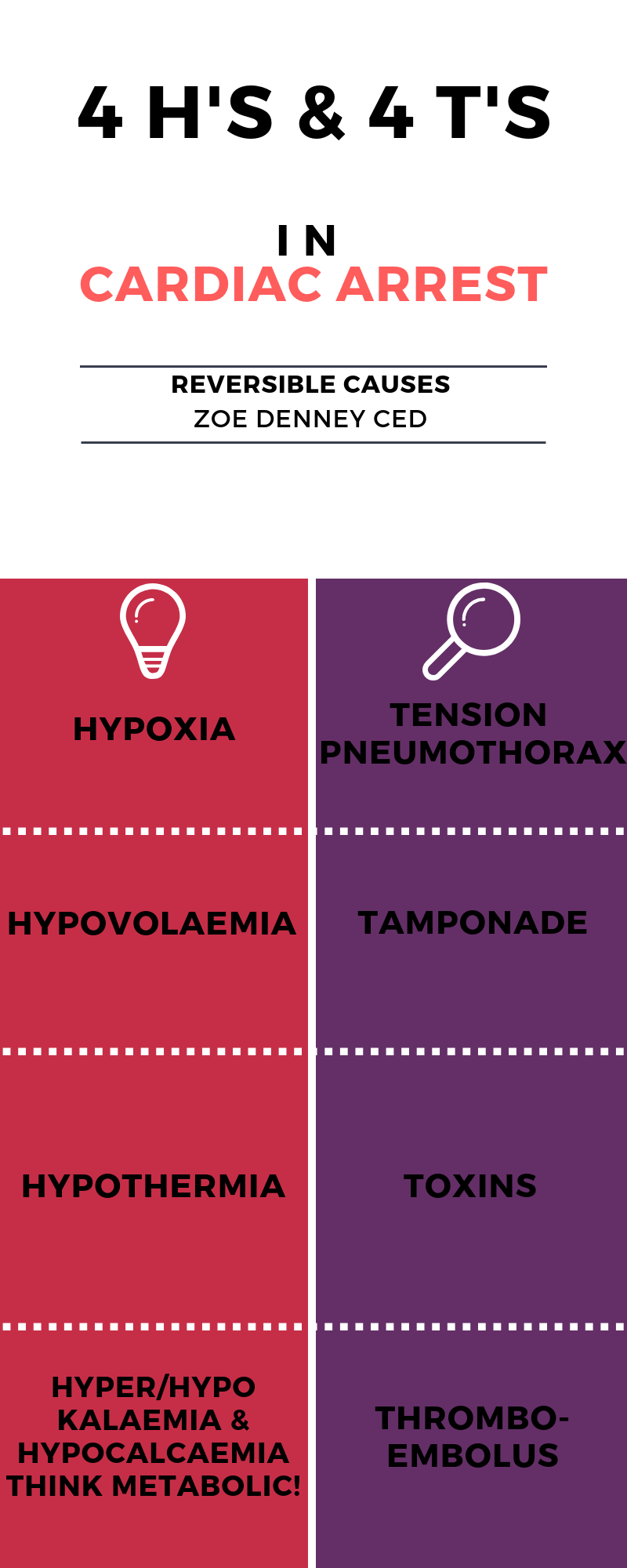
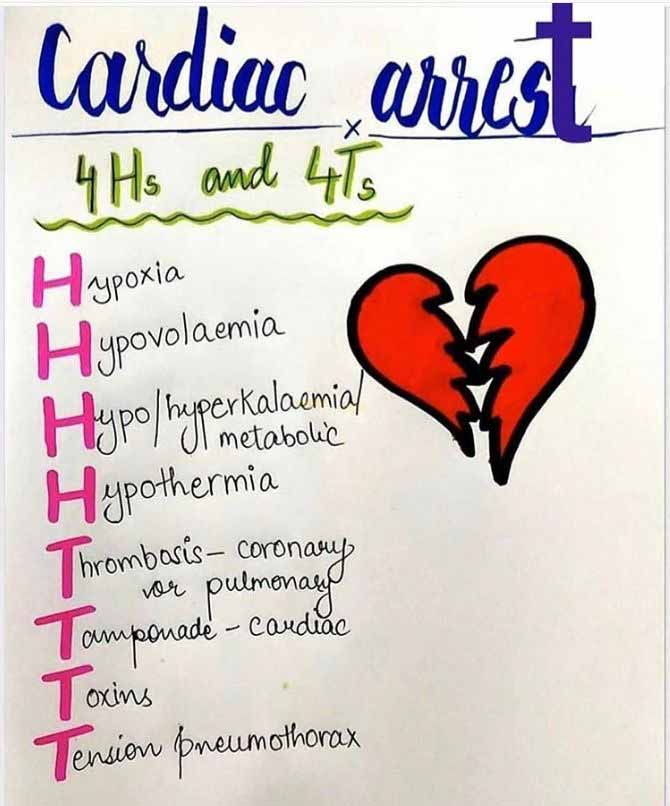
The H's and T's of ACLS is a mnemonic used to help recall the major contributing factors to pulseless arrest including PEA, Asystole, Ventricular Fibrillation, and Ventricular Tachycardia. Reversible causes of cardiac arrest 4 "Ts" and 4 "Hs" can be easily diagnosed and remembered following general ABC rule, Motol University Hospital approach Miroslav Durila Open Access Published: March 12, 2018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.03.013 Reversible causes of cardiac arrest: "4Hs and 4Ts" H ypoxia H ypokalaemia/hyperkalaemia H ypothermia/hyperthermia H ypovolaemia T ension pneumothorax T amponade T hrombosis T oxins You may also be interested in our guides to basic life support and the ABCDE approach to emergency management. Hypoxia The reversible causes of cardiac arrest can be remembered by using the "Four Hs and Four Ts": H ypoxia (low levels of oxygen) H ypovolemia (shock) H ypokalemia/Hyperkalemia/Hypoglycemia/Hypocalcemia H ypothermia T hrombosis (coronary or pulmonary) T ension pneumothorax T amponade (cardiac) T oxins Hypoxia (Low Levels of Oxygen)

(PDF) Reversible causes of cardiac arrest 4 “Ts” and 4 “Hs” can be easily diagnosed and
Reversible causes of cardiac arrest 4 "Ts and 4 Hs can be easily diagnosed and remembered following general ABC " " " rule, Motol University Hospital approach Dear editor, European Guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) re-commend treating reversible causes of cardiac arrest during CPR [1]. Reversible causes of cardiac arrest 4 "Ts" and 4 "Hs" can be easily diagnosed and remembered following general ABC rule, Motol University Hospital approach 2018 May;126:e7. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.03.013. 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.03.013 Heart Arrest / etiology* Acidosis ( h ydrogen cation excess) is an abnormal pH in the body as a result of lactic acidosis which occurs in prolonged hypoxia and in severe infection, diabetic ketoacidosis, kidney failure causing uremia, or ingestion of toxic agents or overdose of pharmacological agents, such as aspirin and other salicylates, ethanol, ethylene glycol and o. One of the recurring features in poorly managed scenarios was the failure to obtain and organise sufficient help for the tasks required. Since then we have encouraged the teaching of "four Hs and four Ts" in the initial approach to the management of life-threatening/arrest situations, i.e. "four Helpers and four Tasks".
The 4 Hs And 4 Ts In Resuscitation & Sudden Cardiac Arrest Skills Training Group
Introduction: During CPR, identification of treatable causes (H's and T's) is typically based on clinical suspicion and assumptions, while facts would allow a directed treatment of underlying causes. A blood gas (BG) is easy to obtain (e.g. Femoral Art. or Ven.), provides rapid objective information (i.e. hyperkalaemia - in relation to pH-, should be excluded in all patient with. The 4 H's and T's: How reliable is this mnemonic in classifying etiologies of in-hospital cardiac arrests? While out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCA) are predominately due to coronary artery disease and other cardiac-related conditions, 1. the etiologies of in-hospital cardiac arrests (IHCA) are often more complex.
Administer IV isotonic or hypertonic fluids (with blood sodium ≤ 130 mmol L-1 up to 3x 100 mL NaCl 3%). Consider additional electrolyte replacement with isotonic fluids. Substantial amounts of fluids may be required. In exertional heat stroke, a cooling rate faster than 0.10°C min-1 is safe and desirable. A useful mnemonic derived from the conditions shown in fig 1 causing a non-VF/VT cardiac arrest is the four Hs and the four Ts. Figure 1 Climbers in snowhole. Figure 2 Climber in spindrift. There are many cardiac and respiratory causes of severe hypoxia, which require emergency treatment of the underlying condition. Oxygen treatment in an appropriate dose should be administered where possible.

Cardiac Arrest H's and T's HYPOVOLEMIA HYPOXEMIA GrepMed
Reversible causes of cardiac arrest 4 "Ts" and 4 "Hs" can be easily diagnosed and remembered following general ABC rule, Motol hospital approach CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Authors: Miroslav Durila. Recently, we have inquired about the origins of the mnemonic '4 Hs and 4 Ts' used to recall the reversible causes of cardiac arrest (CA).




