The 8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41 is a German 88 mm anti-aircraft and anti-tank artillery gun, developed in the 1930s. It was widely used by Germany throughout World War II and is one of the most recognized German weapons of the conflict. The gun was universally known as the Acht-acht ("eight-eight") by the Germans and the "eighty-eight" by the. The 8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf Zugkraftwagen 12t (Sd.Kfz. 8), also known as the Bunkerflak or Bufla, was a German Wehrmacht half-track self-propelled gun developed before World War II and used in the first half of the war. It was used during the Invasion of Poland but is best known for its use during the Battle of France, where it was the only German self-propelled gun capable of destroying the.

8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41 Wikiwand
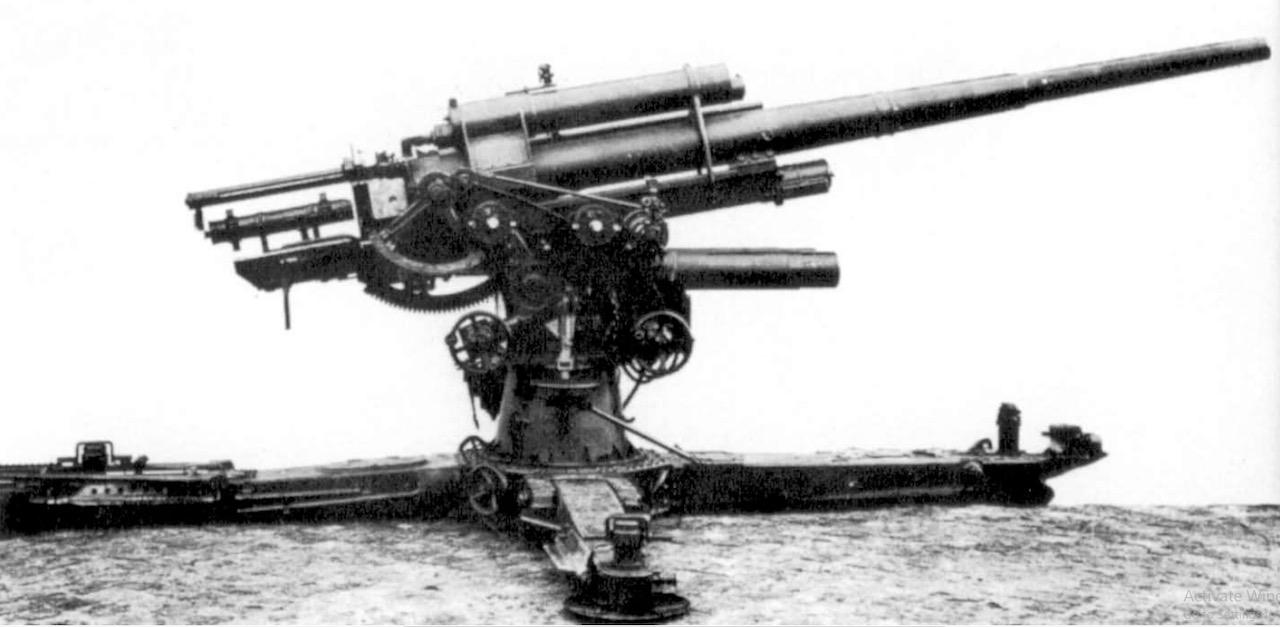
The 8.8 cm Flak 18 used a single tube barrel that was covered in a metal jacket. The barrel itself was some 4.664 meters (L/56) long. The gun recuperator was placed above the barrel, while the recoil cylinders were placed under the barrel. During firing, the longest recoil stroke was 1,050 mm, while the shortest was 700 mm.. The 8.8 cm Flak 18 used a single tube barrel which was covered in a metal jacket. The barrel itself was some 4.664 meters (L/56) long. The gun recuperator was placed above the barrel, while the recoil cylinders were placed under the barrel. During firing, the longest recoil stroke was 1,050 mm, while the shortest was 700 mm.. 8,8-cm-Flak 18/36/37 Flak 36 im Imperial War Museum. Allgemeine Angaben Entwickler/Hersteller Krupp, Essen: Entwicklungsjahr 1920er Jahre Produktionszeit 1933 bis 1945 Stückzahl 20.754 Modellvarianten Flak 18, 36, 37 Waffenkategorie Flugabwehrkanone Technische Daten Kaliber: 88 mm The 8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41 is a German 88 mm anti-aircraft and anti-tank artillery gun, developed in the 1930s. It was widely used by Germany throughout World War II and is one of the most recognized German weapons of the conflict. The gun was universally known as the Acht-acht by the Germans and the "eighty-eight" by the Allies. Due to its lethality, especially as a tank killer, the eighty.
8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37 PlaneEncyclopedia
The gun used was the 8,8 cm Flak 18, towed by the 8-ton Sd Kfz 7 prime mover. It had a cruciform gun carriage with foldable side booms, and a large gun shield. The guns were organized into platoons with two guns each, the Geschützzug 8,8 cm Flak 18 (zu 2 Geschütze) (mot Z), in accordance with K St N 447 table of organization and equipment. The 8.8 cm Flak 18 (Sfl.) auf Zugkraftwagen 12t (Sd.Kfz. 8) consisted of a 8.8cm Flak 18 gun mounted on a pedestal in the rear of a Sd.Kfz. 8 half-track heavy artillery tractor ("DB s8" or "DB 9" model). A gun shield was provided for the 88, but the gun crew was completely exposed on its sides and rea, having no other protection but the. The 8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41 is a German 88 mm anti-aircraft and anti-tank artillery gun, developed in the 1930s. It was widely used by Germany throughout World War II and is one of the most recognized German weapons of the conflict. Development of the original model led to a wide variety of guns. The name applies to a series of related guns, the first one officially called the 8.8 cm Flak 18. Contributor: C. Peter Chen ww2dbase Forbidden to produce large caliber weapons, the first German 8.8 cm FlaK anti-aircraft guns were built in partnership with the Swedish firm Bofors. The prototypes were completed in 1928, designated FlaK 18. FlaK 18 guns were designed to be mounted on cruciform gun carriages, which allowed the guns to aim at any direction.

8,8cmFlaK 18/36/37 270862 Flickr
Pages in category "8.8 cm FlaK 18/36/37/41" This category contains only the following page. 8. 88 mm gun; Media in category "8.8 cm FlaK 18/36/37/41" The following 25 files are in this category, out of 25 total. 26-G-2513 Normandy Invasion, June 1944.jpg 1,280 × 1,043; 271 KB. 8.8 cm KwK 43 L/71 - the direct successor to this gun, and the one mounted on the Tiger II; 8.8 cm Flak 18/36/37/41, the prominent anti-aircraft and anti-tank weapon the 8.8 cm KwK 36 is often confused with. Weapons of comparable role, performance, and era. British Ordnance QF 17-pounder; Soviet 85 mm D-5T/ZiS-S-53; United States 90 mm Gun M3
The modified Flak gun was mostly meant to fire high-explosive and anti-tank rounds. The 8.8 cm Sprgr Patr was a 9.4 kg high-explosive round with a 30-second timed fuze. The 8.8 cm Pzgr Patr was a 9.5 kg standard anti-tank round. With a velocity of 810 m/s, it could penetrate 95 mm of 30° angled armor at 1 km. The FlaK 18 was arguably the most famous multi-purpose artillery piece used by Germany during World War II. Since it was originally designed to bring down aircraft, the FlaK 18 could fire 88 mm shells (earning it the nickname "88") at a distance of up to 8,000 meters. In order to operate properly, it required a crew of seven to ten men and it had a maximum rate of fire of about 15 rounds per.

8,8 cm Flak 18 eastern front World War Photos
The name applies to a series of guns, the first one officially called the 8.8 cm Flak 18, the improved 8.8 cm Flak 36, and later the 8.8 cm Flak 37. Flak is a contraction of German Flugzeugabwehrkanone meaning "aircraft-defense cannon", the original purpose of the eighty-eight. In English, "flak" became a generic term for ground anti-aircraft fire. The Sonderkraftfahrzeug 8 ("special motorized vehicle 8") was a German half-track widely used during World War II, as a prime mover for heavy guns like the 21 cm Mörser 18 but also the the 15 cm Kanone 18 or the 10.5 cm FlaK 38. It was also used to carry their crews and ammunitions, but also as a standalone troop carrier.




