Animal Cell: Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram June 6, 2023 by Faith Mokobi Edited By: Sagar Aryal An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Animal Cell Diagram The diagram given below depicts the structural organization of the animal cell. The various cell organelles present in an animal cell are clearly marked in the animal cell diagram provided below. Animal cell diagram detailing the various organelles

What is a cell? Facts
Cell diagrams showing a typical animal cell and plant cell. Image created with Biorender.com. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted lillianjohnson a year ago has there ever been anything that had both animal and plant cells? • 12 comments ( 65 votes) Upvote Barrs Julianna a year ago Definition Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Animal Cell - Diagram, Organelles, and Characteristics This entry was posted on May 9, 2023 by Anne Helmenstine (updated on December 26, 2023) An animal cell lacks a cell wall or chloroplasts. Its outer coating is a semipermeable cell membrane. Animal cells are the fundamental units of life in protozoa and multicellular animals. Unit 1 Intro to biology Unit 2 Chemistry of life Unit 3 Water, acids, and bases Unit 4 Properties of carbon Unit 5 Macromolecules Unit 6 Elements of life Unit 7 Energy and enzymes Unit 8 Structure of a cell Unit 9 More about cells Unit 10 Membranes and transport Unit 11 More about membranes Unit 12 Cellular respiration Unit 13 Photosynthesis

What Is An Animal Cell? Facts, Pictures & Info For Kids & Students.
Animal Cell Anatomy The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; in fact, most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. The contents of a cell are called the protoplasm. Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall. This feature was lost in the distant past by the single-celled organisms that gave rise to the kingdom Animalia. Overview of animal and plant cells Google Classroom About Transcript Animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes, cytoskeletons, and mitochondria. However, they differ in certain aspects. For example, plant cells have a cell wall and a central vacuole, while animal cells contain centrosomes. How are cells structured? Learn about the size and function of plant and animal cells for GCSE Combined Science, AQA.

The animal cell diagram. Vector illustration on white Etsy in 2021 Animal cell, Cell diagram
Cilia and mucous cells of rat oviduct. Micro Discovery / Getty Images. In the hierarchical structure of life, cells are the simplest living units.Animal organisms can be composed of trillions of cells.In the human body, there are hundreds of different types of cells.These cells come in all shapes and sizes and their structure suits their function. cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed.A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast.Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become the building blocks of large multicellular organisms.
Animal Cell Diagram 1) Centrioles They are paired tube-like organelle composed of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are about 500nm long and 200nm in width that are found close to the nucleus and helps in cell division. They are also found in cilia and flagella. Functions Helping in cell division by allowing separation of chromosomes The cells that make up animals, plants and fungi are eukaryotic cells. Therefore, animals, plants and fungi can be described as being 'eukaryotic'. Although animals and plants are both eukaryotic, there are differences between animal and plant cells. We'll learn about these differences further down the page. Prokaryotic Cells
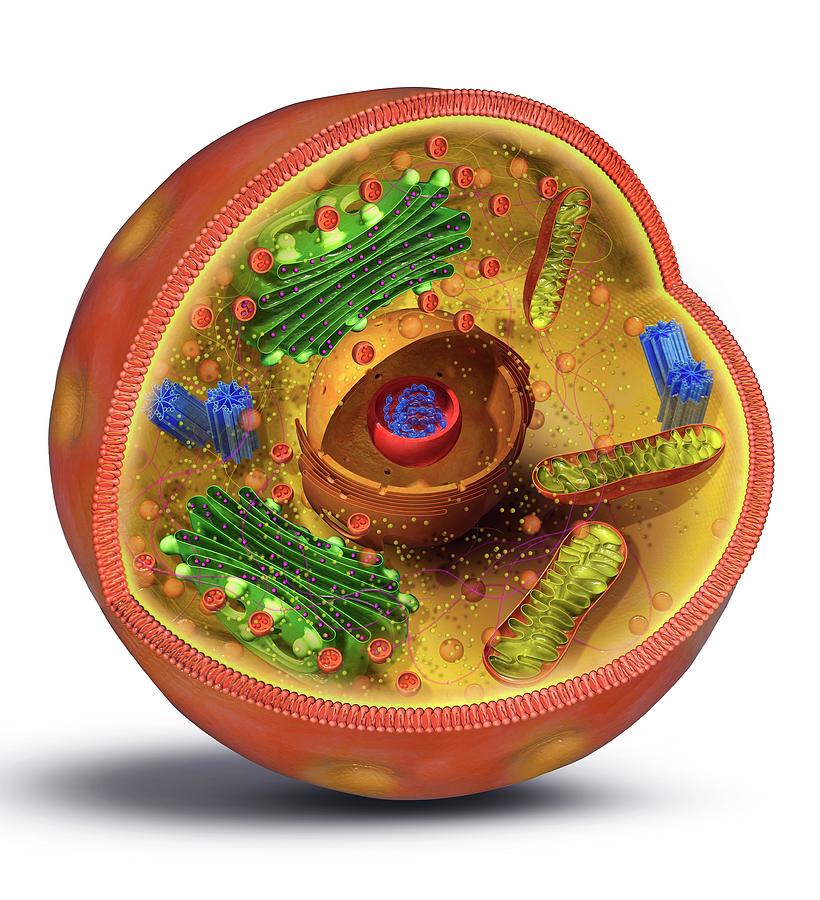
Animal Cell Structure Photograph by Claus Lunau/science Photo Library Pixels
The animal cell diagram is a visual representation of the different parts of an animal cell and their respective functions. This diagram is often used in examinations as a way to understand the structure and functions of an animal cell. The different parts of an animal cell include centrioles, cilia, and flagella, endoplasmic reticulum. The animal cell structure is composed of the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and cell organelles. The organelles are covered with a plasma membrane . The nucleus is the control center of the cell and.




