The Dutch East Indies, [3] also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( Dutch: Nederlands (ch)-Indië; Indonesian: Hindia Belanda ), was a Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which declared independence on 17 August 1945. Geography & Travel Dutch East Indies islands, Southeast Asia Cite External Websites Also known as: Nederlands Oost-Indië, Nederlandsch-Indië, Netherlands East Indies Written and fact-checked by The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica

The Dutch East Indies, 1940 Dutch east indies, East indies, History major
During the Japanese occupation and after Indonesian nationalists declared independence on 17 August 1945, the city was known as Jakarta. It remained internationally known by its Dutch name until Indonesia achieved full independence in 1949, when the city was renamed Jakarta. Dutch East India Company (1610-1799) Arrival Batavia between 1675 and 1725 It was one of the most crucial and important periods in modern Indonesian history . In May 1940, Germany occupied the Netherlands, and martial law was declared in the Dutch East Indies. Following the failure of negotiations between the Dutch authorities and the Japanese, Japanese assets in the archipelago were frozen. The most restrictive and best-known use is as a synonym for the islands that now constitute the Republic of Indonesia (formerly known as the Netherlands Indies, or Dutch East Indies); these include the Greater Sunda Islands (Borneo, Celebes, Java, and Sumatra), the Lesser Sunda Islands (stretching eastward from Bali to Timor), the Moluccas, and. Dutch East India Company, trading company founded in the Dutch Republic (present-day Netherlands) in 1602 to protect that state's trade in the Indian Ocean and to assist in the Dutch war of independence from Spain.

History of the Dutch East Indies Every Year YouTube
The Dutch East Indies (c. 1600 - 1942) was part of a vast Dutch trading empire ( Nederlands-koloniale Rijk) which stretched across the world. THE EAST INDIES In the context of the Eighty Years' War (Dutch Revolt), the general expansion of trade and shipping, and to a lesser extent, the missionary impulse of Calvinism, Dutch overseas expansion was spurred by a powerful combination of politico-economic, commercial, and religious motivations. The "first shipping" to Asia of 1595 was followed by the creation of "precompanies" in various. Published January 8, 2022 Updated January 10, 2022 Batavia thrived as the spice market at the center of Dutch East India company — at the expense of its native population. Wikimedia Commons The Dutch controlled Batavia, in present day Indonesia, from 1619 to 1942. Today, Batavia is no more. Watch the rise and fall of the Dutch East Indies, as the single most valuable company in human history, the Dutch East India company, laid its claim in the Malay Archipelago and permanently.

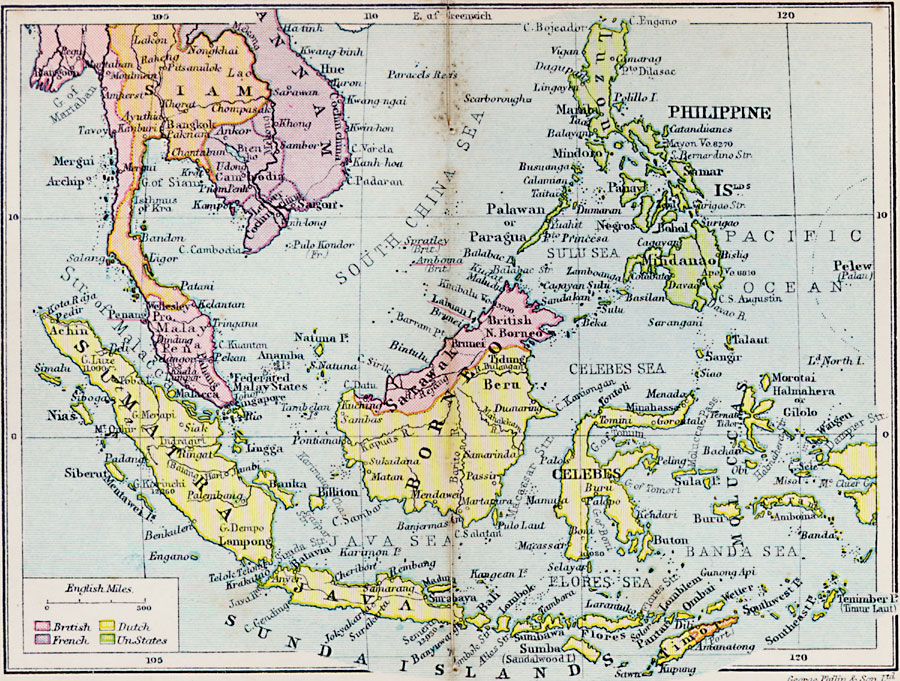
Netherlands East Indies Map Memories Of The Dutch East Indies From Plantation Society To
By the mid-1600s, the Dutch East India Company had approximately 50,000 employees working in both Asia and the Netherlands. Between 1602 and 1799, when the company was formally dissolved, its ships made nearly 5,000 voyages from the Netherlands to the East Indies in search of sought-after spices and carried over one million people to Asia. Declaration of war In late November, the Netherlands government in the East Indies under the Dutch government-in-exile (already at war with Imperial Japan's Axis power ally Germany in Europe) began preparing for war against Japan itself: ships of the Royal Netherlands Navy were sent to sea and the KNIL Air Force was mobilised. [22]
Dutch and Indonesian nationalist representatives formally signed the Linggadjati Agreement in Batavia (Jakarta) on March 25, 1947, which provided for a cessation of military hostilities and the establishment of the United States of Indonesia consisting of the Republic of Indonesia (Java, Madura, Sumatra) and Borneo. published on 26 January 2022 Listen to this article Available in other languages: French 17th-century Dutch East India Company ( Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie or VOC) navigators were the first Europeans to set foot on Australian soil.
Dutch East Indies Wiki
In his five-volume magnum opus on the Dutch East Indies, Oud en Nieuw Oost-Indiën (1724-26), Calvinist minister François Valentijn appropriately called the enslavement of human beings "the world's oldest trade" (den oudsten handel in de wereld).[1]. Finally, studies of the Dutch East India Company period (1602-1799) concentrate. The English East India Company was incorporated by royal charter on December 31, 1600 and went on to act as a part-trade organization, part-nation-state and reap vast profits from overseas trade.




