A Lancet Editorial1 in 1977, referring to an article entitled "Clinical use of the anion gap"2 opined: "In an age when all too often plasma-electrolyte measurements are ordered without any deliberate judgment being made as to the likely usefulness of the result, it is refreshing to have a reminder of the subtleties involved in the interpretation of this commonest set of clinical. GOLD MARK is a new mnemonic recommended to replace MUDPILES for causes of anion-gap metabolic acidosis. GOLD MARK. G lycols (propylene glycol and ethylene glycol); O xoproline - 5-oxoproline (or pyroglutamic acid) is associated with chronic acetaminophen use, often by malnourished women.; L-lactate,; D-lactate - D-lactic acid can occur in some patients with short bowel syndromes
ABG Interpretation The Anion Gap (Lesson 5) YouTube
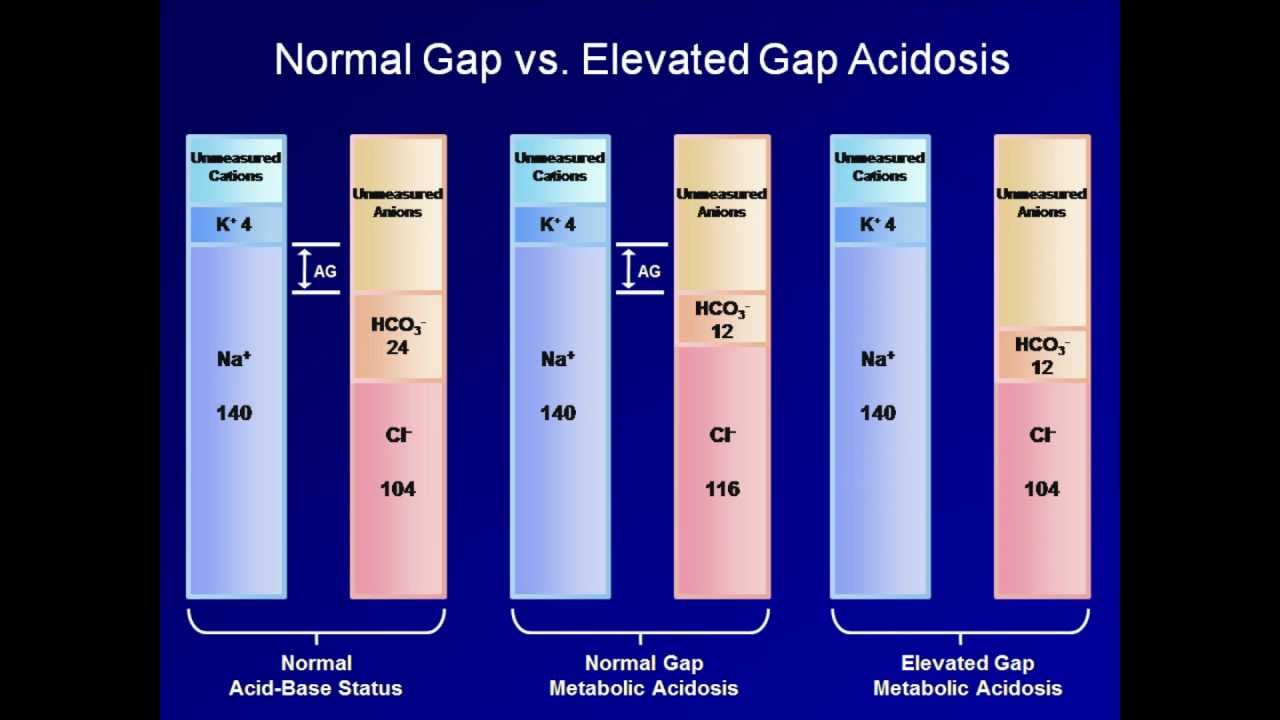
the basis of an anion gap calculation (Na+[Cl-HCO 3 -]): the high-anion-gap metabolic acidoses, and the normal-anion-gap, or hyperchloraemic, metabolic acidoses. Two popular mnemonics are often used to remember the major causes of the high-gap metabolic acidoses. The fi rst is KUSMALE (a useful misspelling of Adolph Kussmaul's name), which Mnemonic for causes: the mnemonic GOLDMARK replaces the older MUDPILERS and is a more accurate reflection of common modern causes of anion gap acidosis. The starred conditions are the most common causes.. Serum anion gap: its uses and limitations in clinical medicine. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;2(1):162-74. Kraut JA, Mullins ME. Toxic. Anion gap is calculated as (Na - Cl - Bicarb). Nothing fancy, no corrections for anything (glucose, albumin, potassium, etc.). More discussion of the anion gap in the chapter on diagnosing acid/base problems here. Elevated anion gap is concerning, because many causes of this are immediately life-threatening. (Unlike, for example, non-anion. GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for the 21st century. GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for the 21st century. GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for the 21st century Lancet. 2008 Sep 13;372(9642):892. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61398-7. Authors Ankit N Mehta, Joshua B Emmett, Michael Emmett. PMID:.

Anion gap calculation, anion gap blood test & causes of high or low anion gap
GOLDMARK mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis Glycols (ethylene glycol & propylene glycol) Oxoproline (metabolite of acetaminophen) L-lactate D-lactate (acetaminophen, short bowel syndrome, propylene glycol infusions for lorazepam and phenobarbital) Methanol ASA Renal Failure A mnemonic to remember the commonest causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis is: GOLDMARK Mnemonic G: glycols (ethylene glycol and propylene glycol) O: oxoproline L: L-lactate D: D-lactate M: methanol A: aspirin R: renal failure K: ketoa. The most common causes of high anion gap metabolic acidosis (HAGMA) are listed in Table 1. They are arranged as the mnemonic "GOLDMARK" (Glycols [ethylene, pro-pylene, and diethylene], 5-Oxoproline [acetaminophen], L-Lactic Acid, D-Lactic acid, Methanol, Aspirin, Renal fail-ure, Ketoacidosis). In contrast, when metabolic acidosis is due to. A useful mnemonic for the differential diagnosis of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis is GOLDMARK (glycols [ethylene glycol and propylene glycol], oxoproline, L-lactate, D-lactate, methanol, aspirin, renal failure, and ketoacidosis) (Table 21-13). + + Table 21-13. Common causes and therapy for increased anion gap metabolic acidosis..

Anion gap calculation, anion gap blood test & causes of high or low anion gap
The acronym GOLDMARK, which was proposed in 2008, is the most frequently used . Based on the clinical presentation and initial laboratory results at time of admission and using the GOLDMARK-acronym, 5-oxoproline and D-lactate were considered as potential causes of the raised anion gap metabolic acidosis. More recently a new mnemonic has been suggested to update new our understanding of anion-gap generating acids. The updated mnemonic "GOLD MARK" was proposed in a 2008 article in The Lancet. G - Glycols (ethylene glycol and propylene glycol) O - Oxoproline; L - L-Lactate; D - D-Lactate; M - Methanol; A - Aspirin; R - Renal Failure
The concepts underlying the clinical use of the anion gap (AG) and those disorders associated with its alteration are reviewed and stress is placed upon the utility of the AG in defining the cause of the acidosis, and as a guide to therapy in certain organic acidoses. 377. Semantic Scholar extracted view of "GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for. A helpful mnemonic called "GOLDMARK" can be used when evaluating causes of elevated anion gap metabolic acidoses such as in this case [5]. These include glycols (ethylene and propylene.

Medical Mnemonics
High-Anion-Gap Metabolic Acidosis During a Prolonged Hospitalization Following Perforated Diverticulitis: An Educational Case Report. Cecilia Farfan Ruiz A , Sriperumbuduri S , Shaw JLV , Clark EG. Can J Kidney Health Dis, 9:20543581221129753, 28 Oct 2022. Cited by: 0 articles | PMID: 36325264 | PMCID: PMC9619282. Free to read & use. The GOLDMARK mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis is more useful. GOLDMARK mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis; Glycols (ethylene glycol & propylene glycol) Oxoproline (metabolite of acetaminophen) L-lactate. D-lactate (acetaminophen, short bowel syndrome, propylene glycol infusions for lorazepam and phenobarbital)




