Prime Try Before You Buy is now available for eligible Prime members! Explore men's & women's new arrivals, shop latest sales & deals, and everyday essentials Instant-Address, Phone, Age & More A Jolly- Search Now. Get A Jolly's Phone, Email, Social Profiles - No Hit No Fee!

HowellJolly Bodies A Laboratory Guide to Clinical Hematology
A Howell-Jolly body is a cytopathological finding of basophilic nuclear remnants (clusters of DNA) in circulating erythrocytes. During maturation in the bone marrow, late erythroblasts normally expel their nuclei; but, in some cases, a small portion of DNA remains. Howell-Jolly bodies occur where there is no spleen or an non-functioning spleen, referred to as asplenia. They are usually one of these at most in a red cell, round, dark purple to red in color and often located peripherally on the red blood cell. If a patient comes in with sepsis, fever, headache and myalgias, meningitis is very likely. Howell-Jolly bodies are DNA-containing inclusions found after erythrocyte maturation. The composition of the DNA is still unknown to this day. However, studies show that they are of centromeric origin. Howell-Jolly Bodies. Howell-Jolly bodies are seen in significant numbers in patients with splenic atrophy or who have undergone splenectomy. Vitamin B12 deficiency may also result in small numbers of RBCs containing Howell-Jolly bodies, mainly if the deficiency is chronic or severe and megaloblastosis has occurred.
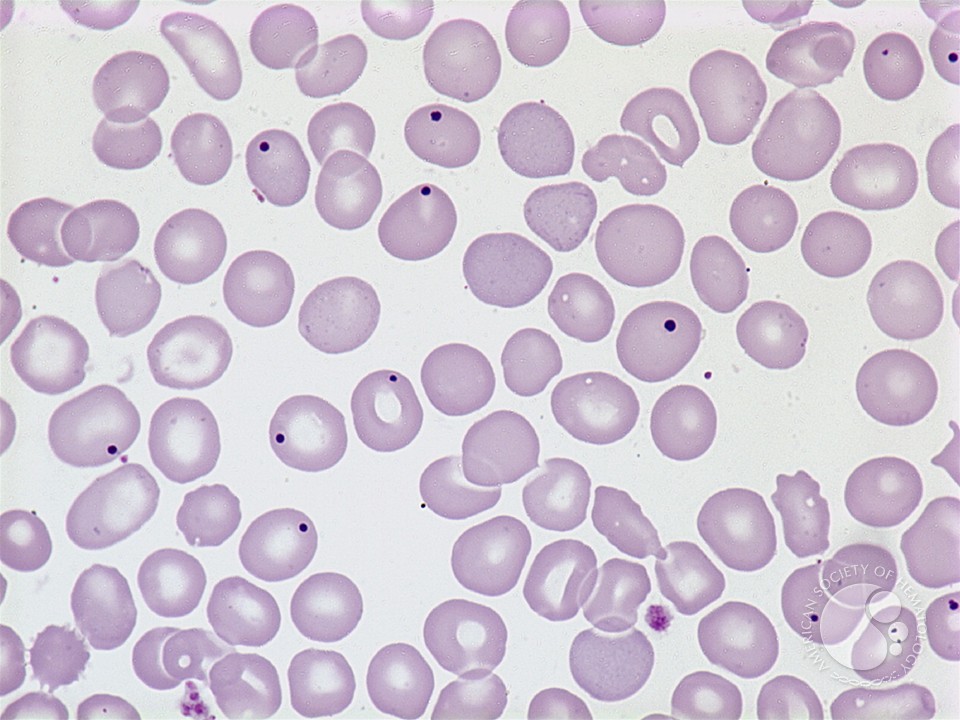
HowellJolly bodies 1.
Howell-Jolly bodies are small (0.5-1 micron) purple inclusions that contain DNA. They are thought to represent chromosomes that have separated from the mitotic spindle that are left behind when the red cell nucleus is extruded. These inclusions are generally removed by the spleen. Howell-Jolly bodies are nuclear remnants. They are small, round cytoplasmic inclusions that stain purple on a Romanowsky stain. They are regularly present after splenectomy and when there is splenic atrophy ( Fig. 5-57 ). They may be seen in a small percentage of red cells in pernicious anaemia. Howell-Jolly bodies are nuclear remnants found in red blood cells (erythrocytes) under various pathological states. They most commonly present in patients with absent or impaired function of the spleen; this is because one of the spleen's functions is to filter deranged blood cells and remove the in. Objectives: Identify the etiology of functional asplenism. Describe the presentation of a patient with functional asplenism. Review the treatment and management options available for functional asplenism.
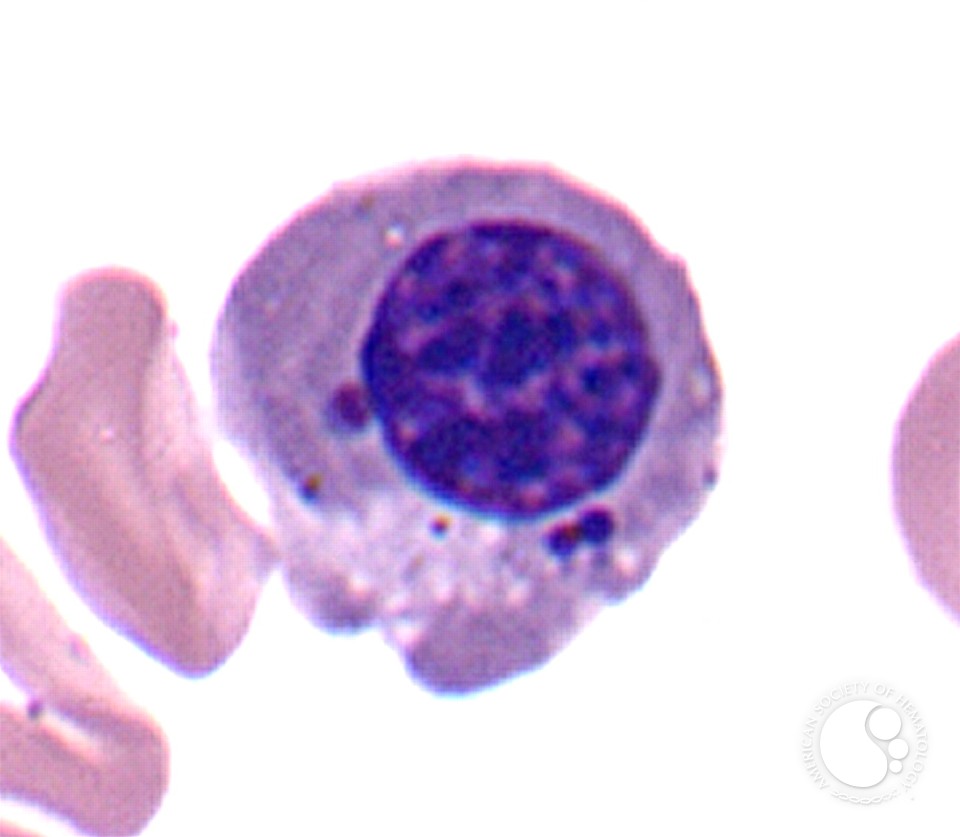
HowellJolly Bodies 1.
Introduction Erythrocytes, red blood cells (RBC), are the functional component of blood responsible for the transportation of gases and nutrients throughout the human body. Their unique shape and composition allow for these specialized cells to carry out their essential functions. Under Wright/Romanowksy stains, Howell-Jolly Bodies appear as dark blue/purple round inclusions located at the periphery of the RBC. They usually present as a single inclusion inside the cell. Howell-Jolly Bodies are also visible under supravital stains. 1-4. Inclusion composition: 2,3. Nuclear fragments/remnants made up of DNA 1-4
David S Rosenthal, MD Section Editor: Robert A Brodsky, MD Deputy Editor: Jennifer S Tirnauer, MD Literature review current through: Nov 2023. This topic last updated: Oct 05, 2023. INTRODUCTION Examination of the peripheral blood smear is an inexpensive but powerful diagnostic tool in both children and adults. Definition Howell-Jolly bodies are small, intra-erythrocytic remnants of erythrocyte nuclei. These inclusions are solitary in each erythrocyte and strongly basophilic. These are often confused with overlying platelets, but can be distinguished by the presence of a halo around overlying platelets. [from HPO] Term Hierarchy GTR MeSH
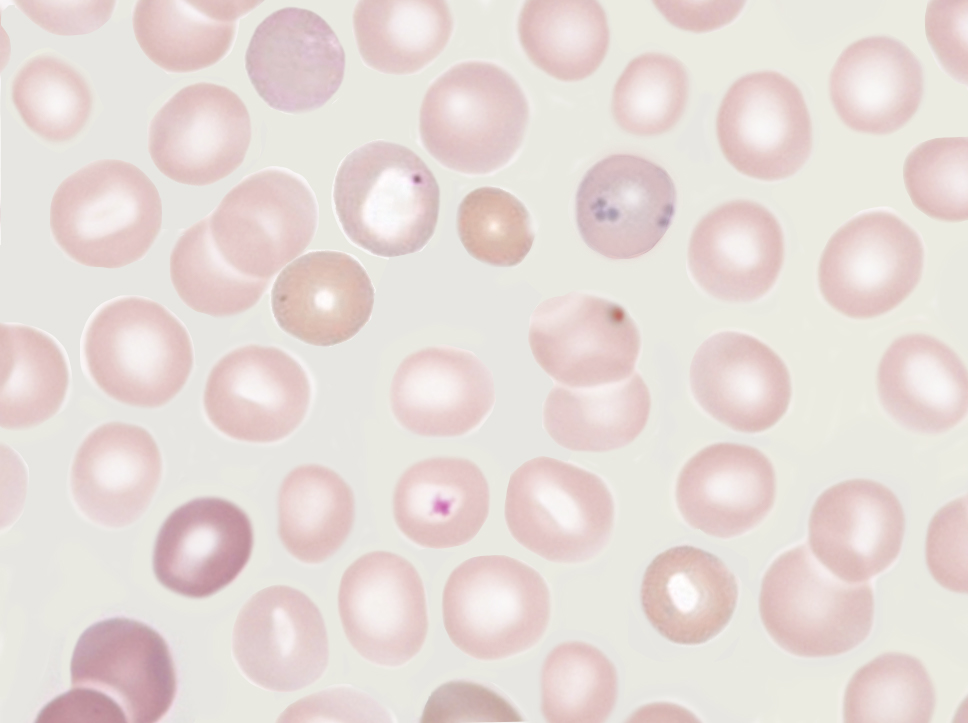
Histology, Howell Jolly Bodies Article StatPearls
Howell-Jolly Body . On these Wright-stained peripheral blood smears the small dark spheres within red cells are Howell-Jolly bodies. Note the variation. in size. These bodies represent residual nuclear DNA which, under normal circumstances, is removed by the spleen. There can . be more than one H-J body within a red cell. The inclusions persisted at stable frequency after treatment. Howell-Jolly-like bodies in granulocytes arise secondary to stressed granulopoiesis induced by immunosuppressive drugs, viral infection, or chemotherapy, and must be differentiated from other neutrophil inclusions such as those observed in intracellular bacterial infections.


