How sounds make their way from the source to the human brain. An ear is the organ that enables hearing and (in mammals) body balance using the vestibular system.In mammals the ear is usually described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal.Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most. The occipital lobe is the smallest lobe in the cerebrum cortex. It is located in the most posterior region of the brain, posterior to the parietal lobe and temporal lobe. The role of this lobe is visual processing and interpretation. Typically based on the function and structure, the visual cortex is divided into five areas (v1-v5).
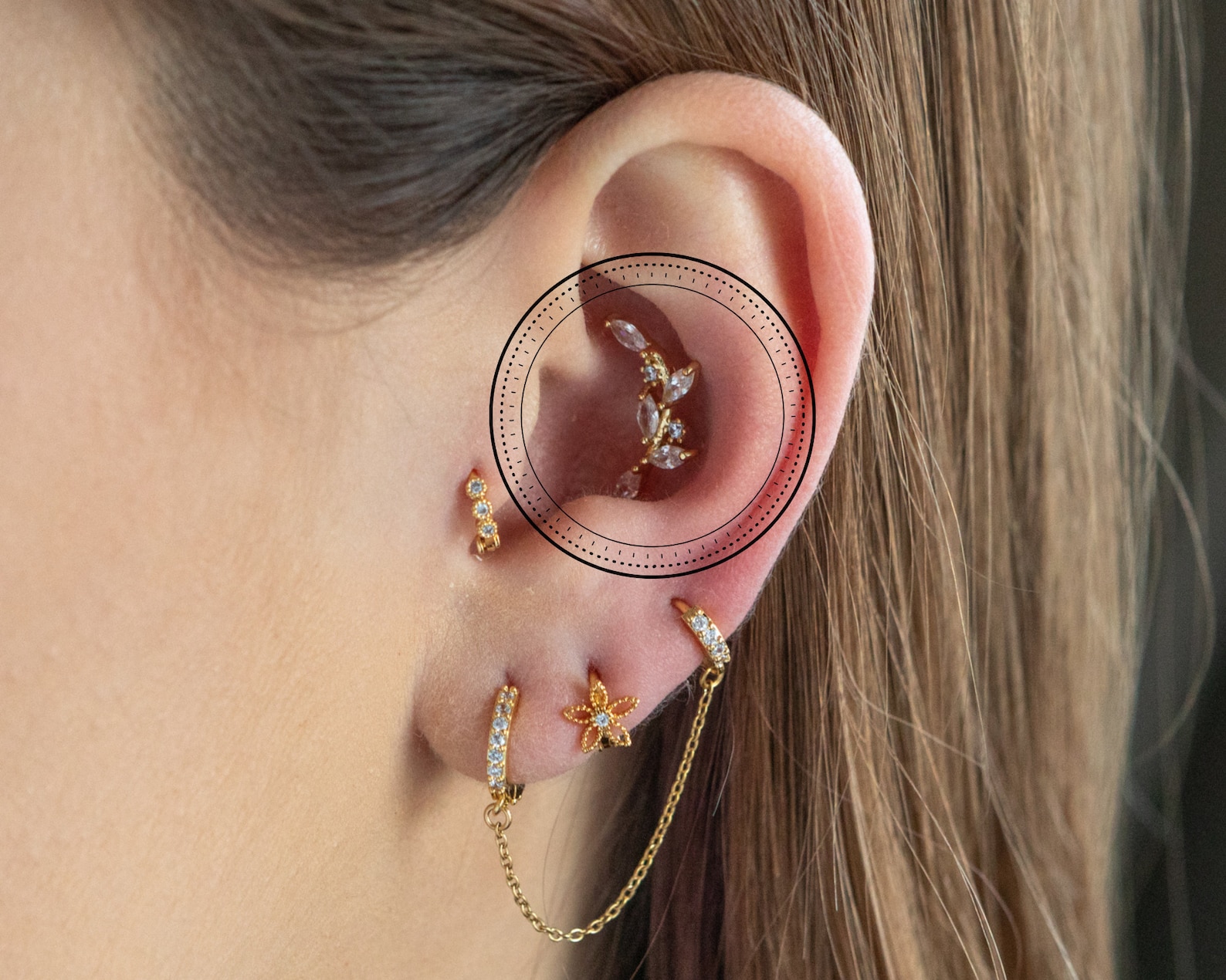

Floral CZ Oorbel Crawler Stack Lobe Piercing Helix CZ Etsy
Vestibular system anatomy. The vestibular system is a somatosensory portion of the nervous system that provides us with the awareness of the spatial position of our head and body ( proprioception) and self-motion ( kinesthesia ). It is composed of central and peripheral portions. The peripheral portion of the vestibular system consists of the. The cerebellum makes up approximately 10% of the brain's total size, but it accounts for more than 50% of the total number of neurons located in the entire brain. The cerebellum is comprised of small lobes and serves several functions. It receives information from the inner ear's balance system, sensory nerves, and auditory and visual systems. The vestibular system is an essential function of the body that helps humans maintain postural balance and spatial orientation in response to changes in the environment. Starting from the inner ear, a complex interplay among constituents in the vestibular pathway allows sensory information to reach multiple destinations in the body and make simultaneous outputs. Any disruption along the. Auditory pathway Author: Shahab Shahid MBBS • Reviewer: Jerome Goffin Last reviewed: July 27, 2023 Reading time: 15 minutes Hearing is an essential process. It enables us to understand and communicate with our fellow human beings using our ears, and also experience the outside world.The auditory pathway is more complex than the visual and the olfactory pathways.
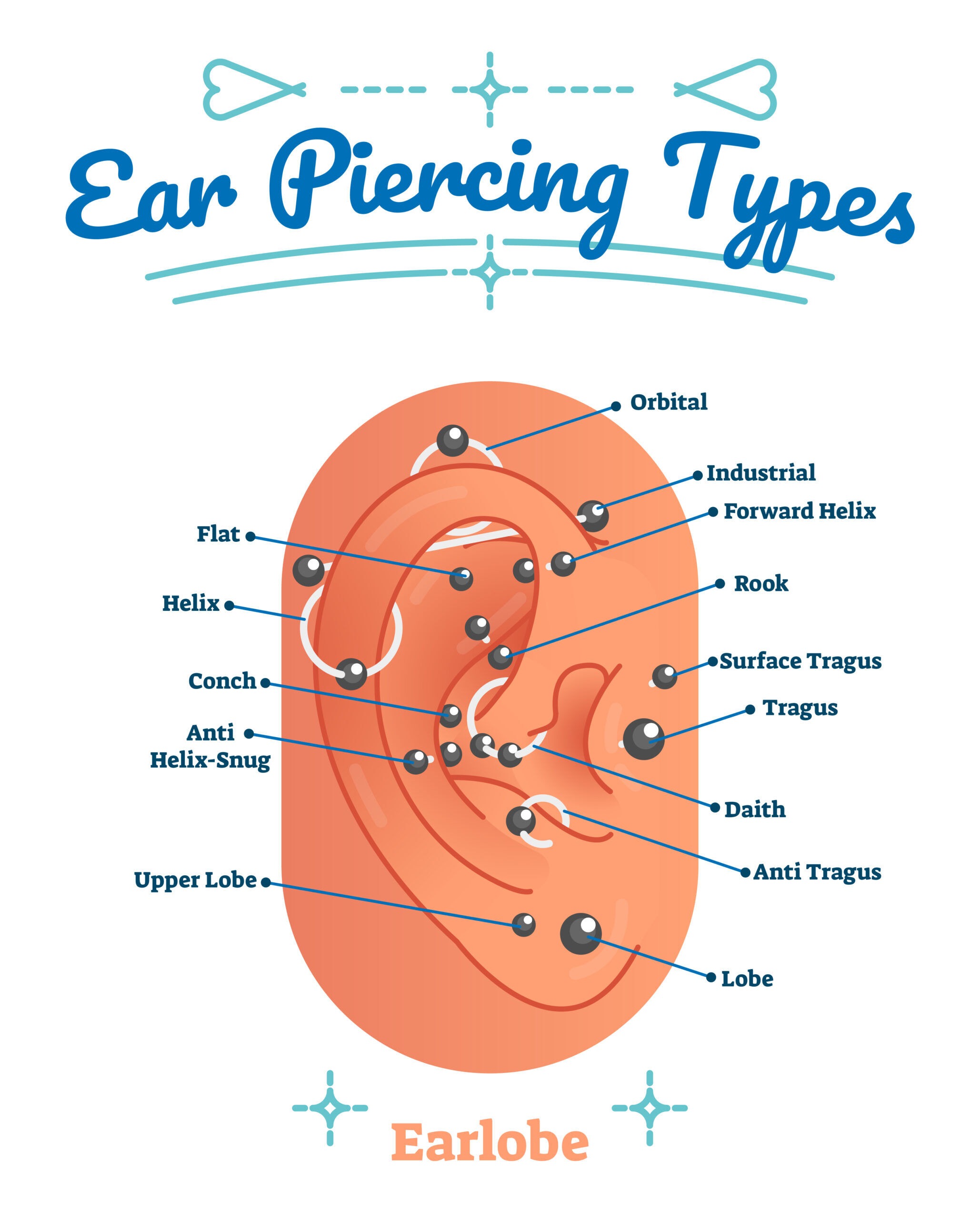
Das RookPiercing Alles, was Sie über das Ohrpiercing wissen müssen
Key Terms. frontal lobe: The frontal lobe is an area in the brain of mammals, located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned anterior to the parietal lobe and superior and anterior to the temporal lobes.In humans, it contributes to a number of higher cognitive functions including attention, planning, and motivation. temporal lobe: A region of the cerebral cortex that is. The frontal lobe is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned in front of the parietal lobe and above and in front of the temporal lobe.It is separated from the parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by a deep fold called the lateral sulcus also called the Sylvian fissure. . The precentral gyrus, which forms the. Lobe (anatomy) In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension [1] of an organ (as seen for example in the brain, lung, liver, or kidney) that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to the much smaller lobule, which is a clear division only visible under the microscope. [2] The cochlea of the inner ear is the most critical structure in the auditory pathway, for it is there that the energy from sonically generated pressure waves is transformed into neural impulses. The cochlea not only amplifies sound waves and converts them into neural signals, but it also acts as a mechanical frequency analyzer, decomposing complex acoustical waveforms into simpler elements.

The Lobe Piercing Everything You Need to Know (2022)
The occipital bone (/ ˌ ɒ k ˈ s ɪ p ɪ t əl /) is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull).It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum.At the base of the skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows. Figure 12.3.3 12.3. 3: Coronal Section of the Brain. The coronal section shows the layers of the cerebrum. The superficial gray matter is called cerebral cortex, while the deep gray matter is organized in basal nuclei. The superficial and deep regions are connected by myelinated axons (white matter) called tracts.
The human earlobe (lobulus auriculae), the lower portion of the outer ear, is composed of tough areolar and adipose connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the auricle (the external structure of the ear). In some cases the lower lobe is connected to the side of the face. Since the earlobe does not contain cartilage it has a large blood supply and may help to warm. In mammals, sound waves are collected by the external, cartilaginous part of the ear called the pinna, then travel through the auditory canal and cause vibration of the thin diaphragm called the tympanum or ear drum, the innermost part of the outer ear (illustrated in Figure 17.13).Interior to the tympanum is the middle ear.The middle ear holds three small bones called the ossicles, which.
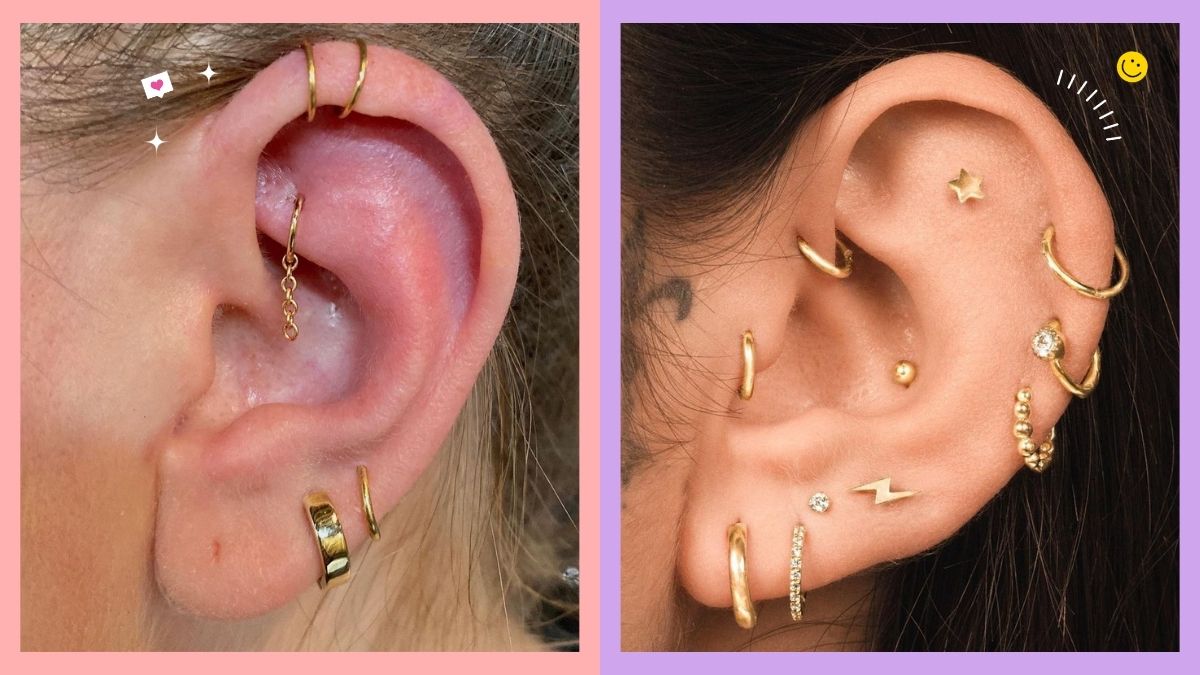
Cartilage Ear Piercings All The Best Piercings To Get
The inferior parietal lobe (IPL) is a key neural substrate underlying diverse mental processes, from basic attention to language and social cognition, that define human interactions. Its putative domain-global role appears to tie into poorly understood differences between cognitive domains in both hemispheres. Across attentional, semantic, and. The cerebral cortex is a highly convoluted gray matter structure consisting of many gyri and sulci. The lobes of the cerebrum are actually divisions of the cerebral cortex based on the locations of the major gyri and sulci. The cerebral cortex is divided into six lobes: the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital , insular and limbic lobes.




