The recurrent laryngeal nerve ( RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and left. The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) branches off the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) and has an indirect course through the neck. It supplies innervation to all of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, except for the cricothyroid muscles, as well as sensation to the larynx below the level of the vocal cords.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-laryngeus-recurrens/tV5udWXGgWcB9YRBZxJkIQ_Nervus_laryngeus_recurrens_01.png)
Nervus laryngeus recurrens Anatomie, Verlauf & Klinik Kenhub
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as the inferior laryngeal nerve, is a branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) which has a characteristic loop around the right subclavian artery on the right and the aortic arch on the left before returning up to ascend the tracheoesophageal groove and then the larynx. Summary External laryngeal nerve The external laryngeal nerve is the smaller, external branch. It descends on the larynx, beneath the sternothyroid muscle, to supply the cricothyroid muscle. The external branch functions to tense the vocal cords by activating the cricothyroid muscle, increasing pitch. The Recurrent Nerve (n. recurrens; inferior or recurrent laryngeal nerve) arises, on the right side, in front of the subclavian artery; winds from before backward around that vessel, and ascends obliquely to the side of the trachea behind the common carotid artery, and either in front of or behind the inferior thyroid artery. On the left side, it arises on the left of the arch of the aorta. The non-recurrent laryngeal nerve is an anomaly of the RLN because its origin is cervical and it runs a direct course from the vagus nerve to the larynx without looping around any of the above named structures ( 3 ). The origin of the NRLN is cervical and there are three types ( 4 ). Type 1 occurs where the NRLN arises directly from the vagus.

Recurrent laryngeal nerve Wikipedia
Nervus laryngeus recurrens Read more. Quick Facts. Origin. Course. Branches. Supplied Structures & Function. List of Clinical Correlates. Poster: "ECR 2019 / C-2121 / Nervus laryngeus recurrens anatomy and pathology " by: " V. Pesti ; Budapest/HU" Brought to you by. Browse Posters » Search result » Poster ECR 2019 / C-2121 POSTER SECTIONS Coverpage Learning objectives Background Findings and procedure details Conclusion Personal information References. ECR 2019 / C-2121. The recurrent laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and left. The right and left nerves are not symmetrical, with the left nerve looping under the aortic arch, and the right nerve looping under the right subclavian artery then traveling. 1. Introduction. The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve (CN X). It carries sensory, motor, and parasympathetic fibers to the laryngeal structures [].It is the main motor nerve of all intrinsic laryngeal muscles, except the cricothyroid, which receives its innervation via the external laryngeal nerve [].The RLN has a different course on the left and right side of the.

n.laryngeus recurrens Diagram Quizlet
The aim of this study was to define the origin, course, caliber and relations of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (N Laryngeus recurrens) in order to localize the nerve during surgery for esophageal atresia. Eighteen anatomic specimens were dissected and 12 surgical cases were analysed. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy after this. PMID: 17972539. In this study, the authors remind the readers the problem traditionally discussed in the thyroid gland surgery--protection of the nervus laryngeus recurrens (NLR) from iatrogenic damage. The aim of this study is to point out some anatomical details on the course of the recurrent nerve (Ref 4). Humans. Intraoperative Complications.
Introduction. The recurrent laryngeal nerve is a cervical branch of the vagus nerve that supplies motor, sensory and parasympathetic nerve fibers to the larynx [Citation 1, Citation 2].Non-recurrence of the nerve is a rare anatomical variant [Citation 3].The first case was reported in 1823 by Stedman [Citation 4].This variation is constantly associated with vascular malformations due to an. Nervus laryngeus recurrens 1/3. Synonyms: none. Function. Action of lateral cricoarytenoid muscle Functio musculi cricoarytenoidei lateralis 1/2. Synonyms: Adduction of vocal folds, Adductio plicae vocalis The intrinsic laryngeal muscles, of which the lateral cricoarytenoid is a part, are all involved in the production of sound (phonation).
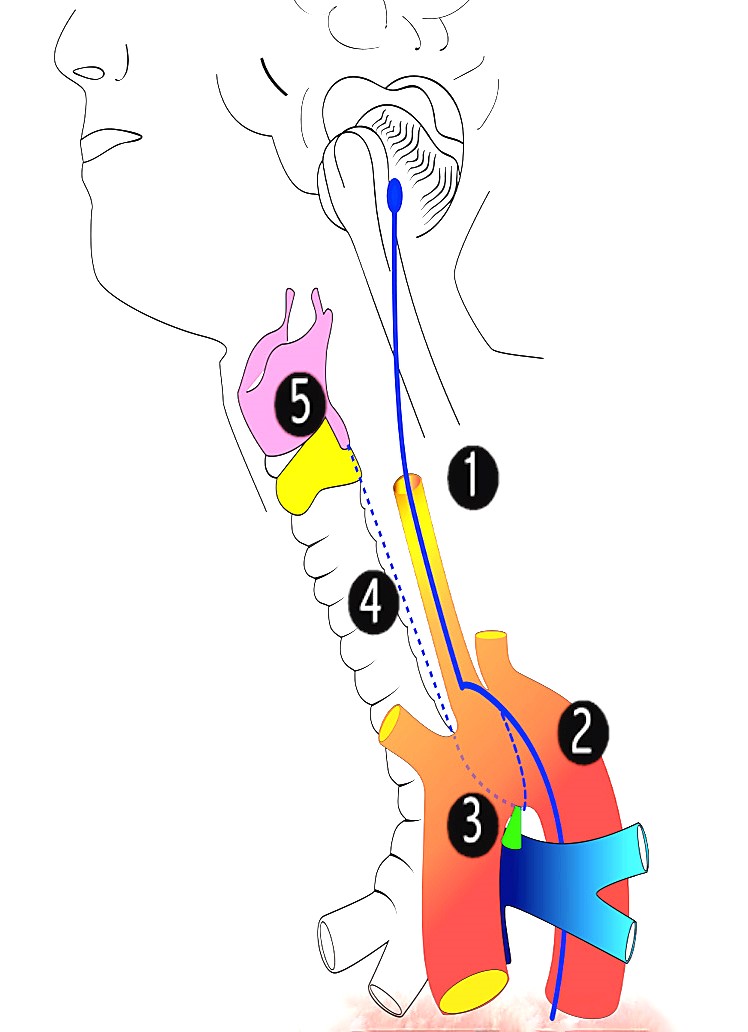
The Recurrent Laryngeal Nerves and the Thoracic Surgeon
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (n. laryngeus recurrens), which contains branchiomotor fibers. This branch arises from the trunk of the vagus nerve in the thoracic cavity, but then it returns to the neck, looping around the aortic arch (arcus aortae) inferiorly from the left, and the subclavian artery (arteria subclavia) from the right. A nonrecurrent laryngeal nerve (NRLN) is a rare anatomical variation in which the nerve enters the larynx directly from the cervical vagus nerve, without descending to the thoracic level [ 2 ]. It has been reported in 0.3-0.8% of the population on the right side, being extremely rare on the left side (0.004%) [ 3 ].
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-laryngeus-recurrens/tV5udWXGgWcB9YRBZxJkIQ_Nervus_laryngeus_recurrens_01.png)



