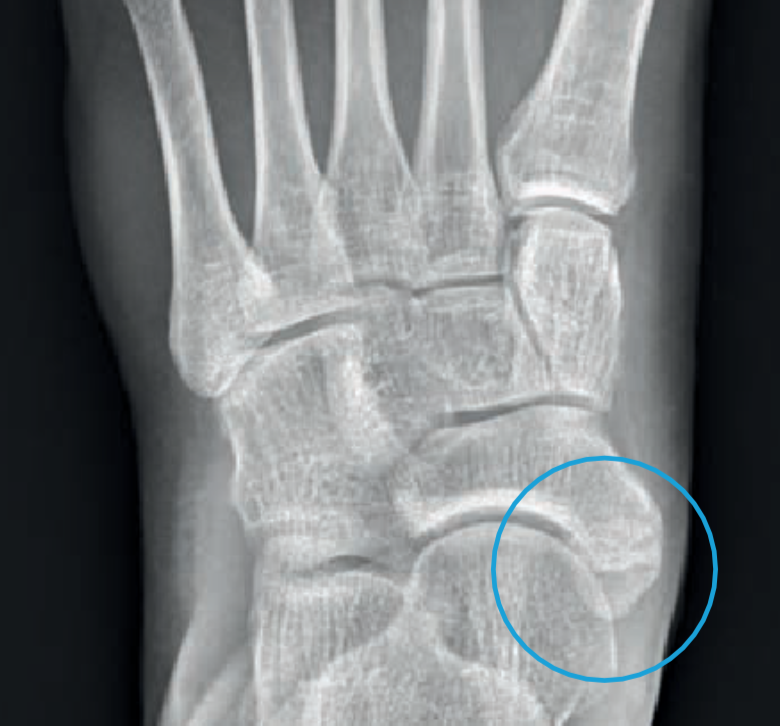
The accessory navicular (os navicularum or os tibiale externum) is an extra bone or piece of cartilage located on the inner side of the foot just above the arch. It is incorporated within the posterior tibial tendon, which attaches in this area and can lead to Accessory Navicular Syndrome. An accessory navicular is congenital (present at birth). An accessory navicular is a large accessory ossicle that can be present adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone. The tibialis posterior tendon often inserts with a broad attachment into the ossicle. Most cases are asymptomatic but in a small proportion, it may cause painful tendinosis due to traction between the ossicle and the navicular.

Os tibiale externum Image
Type 1: An os tibiale externum is a 2-3 mm sesamoid bone in the distal posterior tibialis tendon. Usually asymptomatic. Type 2: Triangular or heart-shaped ossicle measuring up to 12 mm, which represents a secondary ossification center connected to the navicular tuberosity by a 1-2 mm layer of fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage. Os tibiale externum (accessory navicular) is a large ossicle adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone. The tibialis posterior tendon often inserts with a broad attachment onto the ossicle, which may cause a painful tendinosis due traction between the ossicle and the navicular. Such changes are best seen on MRI. Credit: Dr Donna D'Souza. Definition accessory ossicles secondary ossification centers that remain separated from the normal bon sesamoids are bones that are incorporated into tendons and move with normal and abnormal tendon motion Most common ossicles os trigonum accessory navicular (os tibiale externum) os intermetatarseum Most common sesamoids os peroneum Some of the more common include 1-4: os peroneum os subfibulare os subtibiale os tibiale externum (accessory navicular) os trigonum os calcaneus secundaris os calcanei accessorium 6 os intermetatarseum pars peronea metatarsalis primi (pars peronea metatarsalia) os supratalare bipartite hallux sesamoid os supranaviculare

Os tibiale externum type II Image
The accessory navicular syndrome , also known as os naviculare syndrome occurs when a type II accessory navicular becomes painful due to movement across the pseudo-joint between the ossicle and the navicular bone. Radiographic features Ultrasound Also known as os naviculare or os tibiale externum, an accessory navicular is an extra bone on the inside of the navicular (the bone in the middle of the arch of the foot) and within the posterior tibial tendon that attaches to the navicular bone. Top-view of accessory navicular in the right foot Types of accessory navicular The os tibiale externum is also known as accessory navicular bone, os naviculare secundarium, accessory (tarsal) scaphoid, or prehallux. It is found within the tibialis posterior tendon near its insertion on the navicular bone. The os peroneum is a small sesamoid bone located within the peroneus longus tendon, adjacent to the cuboid. Characteristics and articulations The navicular is a boat-shaped bone, which has an important role in the maintenance of the medial longitundinal arch of the foot. Proximally, the navicular bone consists of a concave surface with an ovoid shape that articulates with the head of the talus.

Os tibiale externum sagittal T2 YouTube
Acessory Navicular is a common idiopathic condition of the foot that presents with an enlargement of the navicular bone. Diagnosis is made with plain radiographs of the foot showing a plantar medial enlargement of the navicular bone. The accessory navicular bone is a surplus piece of cartilage or bone fragment. It usually forms in the inner part of the foot, right above the arch. It's called the accessory navicular since it.
In rare cases, the accessory navicular bone creates a bony prominence in the midfoot that causes pain, redness and swelling in the medial arch area, plantar fasciitis, bunions and heel spurs. When this happens, the condition is called accessory navicular syndrome. ANS can arise from a number of things, including foot trauma like ankle sprains. also known as os tibiale externum 2-3 mm sesamoid bone embedded within the distal portion of the posterior tibial tendon no cartilaginous connection to the naviculam tuberosity and may be separated from it by up to 5 mm accounts for 30% of accessory navicular bones usually asymptomatic type 2 accessory navicular bone
Knickfuss Leonardo
Accessory ossicles usually remain asymptomatic, but can become painful due to fractures, dislocations, degenerative changes, osteonecrosis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrial lesions, avascular necrosis, tumors, and irritation or impingement of adjacent soft tissues. An accessory navicular is a large accessory ossicle that can be present adjacent to the medial side of the navicular bone. The accessory navicular bone presents as a sesamoid in the posterior tibial tendon, in articulation with the navicular [1] or as an enlargement of the navicular itself. Epidemiology Navicular bone green




