Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader. Pathos, or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and.
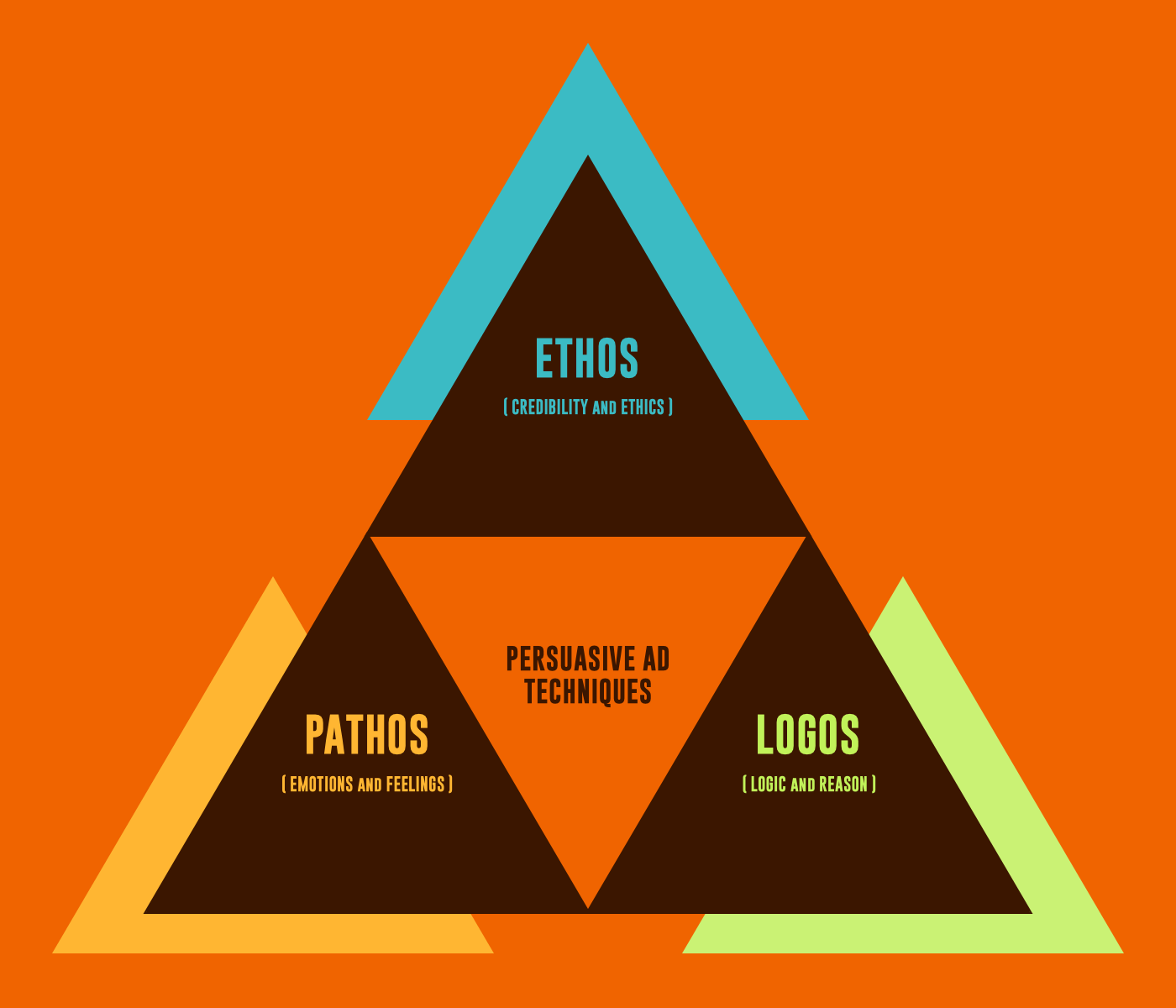
Ethos, Pathos and Logos Persuasive Advertising Techniques (2018)
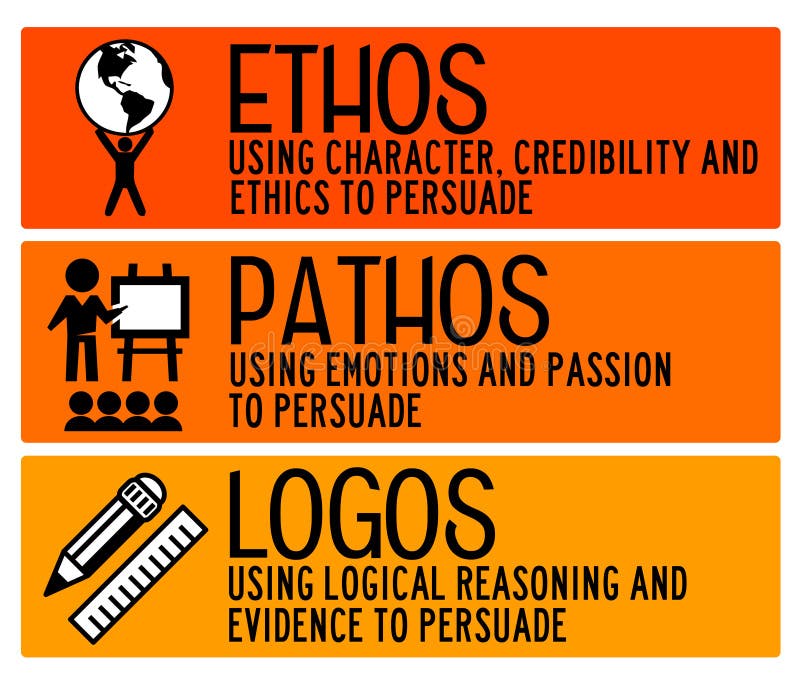
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos Definition and Examples. Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are modes of persuasion used to convince audiences. They are also referred to as the three artistic proofs (Aristotle coined the terms), and are all represented by Greek words. Ethos or the ethical appeal, means to convince an audience of the author's credibility or. These include ethos, pathos, and logos, all three of which appear in Aristotle's Rhetoric. Ethos. Ethos (plural: ethea) is an appeal to the authority or credibility of the presenter. : 41 It is how well the presenter convinces the audience that the presenter is qualified to speak on the subject. This can be done by:. Ethos is the act of appealing to the speaker's or writer's authority as a means of persuasion, Pathos is the act of evoking emotions in the audience or readers to make your point, Logos is the act of appealing to the logic of the audience or readers. Aristotle believed that logos should be the most important of the three modes of persuasion. Logos appeals to the audience's reason, building up logical arguments. Ethos appeals to the speaker's status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example. Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical.
Ethos pathos logos stock illustration. Illustration of logic 213070974
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos When being introduced to rhetorical concepts, among the first appeals students learn about are the rhetorical appeals. There are three main appeals that can be used: ethos, pathos, and logos. Although this handout does provide examples of each appeal below, it is important to note that a piece of media or text might actually contain more than one appeal. For example. Logos, ethos, and pathos are important components of all writing, whether we are aware of them or not. By learning to recognize logos, ethos, and pathos in the writing of others and in our own, we can create texts that appeal to readers on many different levels. This handout provides a brief overview of what logos, ethos, and pathos are and. Ethos, pathos and logos are rhetorical appeals. The similarity of their names can confuse their meanings, so learn what each looks like with our examples. Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but.

Set of 5 Ethos Pathos Logos Kairos Classroom Decor High Etsy
Ethos, pathos and logos are the three categories of persuasive advertising techniques. Each category invokes a different appeal between speaker and audience. Ethos calls upon the ethics, or what we'd call the values, of the speaker. Pathos elicits emotions in the audience. Finally, logos puts logic into play by using evidence and facts. Here's a quick and simple definition: Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a speaker tells a personal story, presents an audience with a powerful visual image, or appeals to an.
Conclusion. Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting. Ethos, pathos and logos are three methods of persuasion: rhetorical appeals that influence decision-making. Ethos is an appeal to the authority and reputation of the speaker (or writer). 1 For example, if your dad wants you to study business at school, he might say, "I'm older and have more life experience, therefore I know what's best.
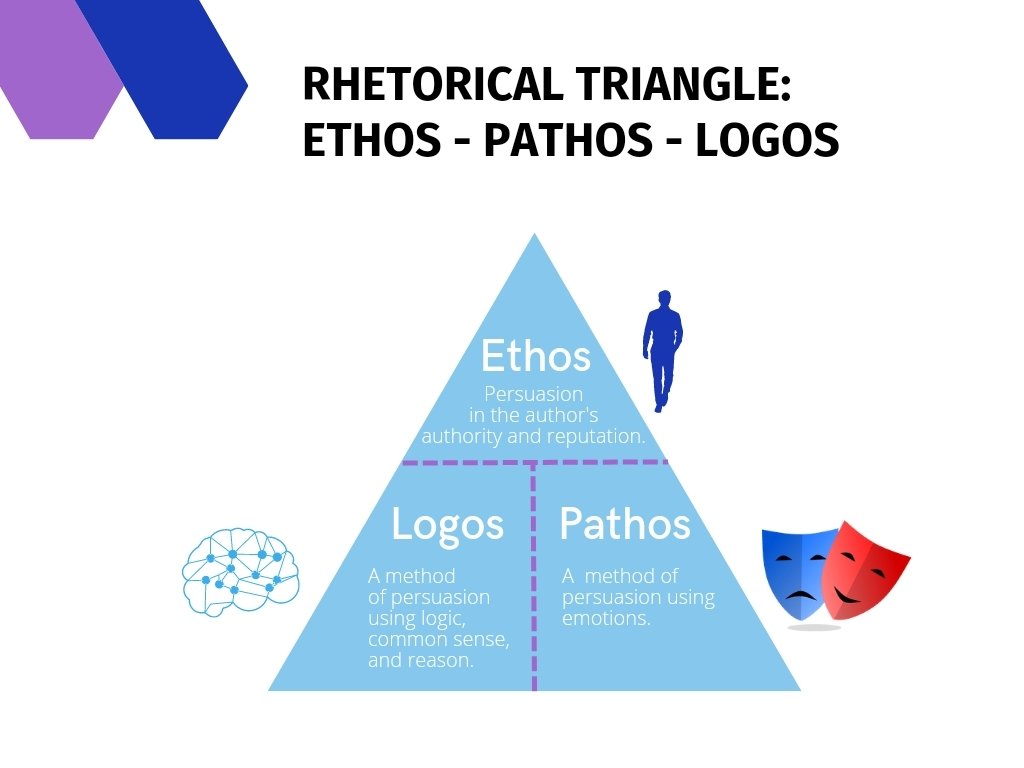
The Rhetorical Triangle Ethos, Pathos, Logos Meaning and Examples
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising. Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they're. Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the rhetorical triangle, three rhetorical appeals, or three modes of persuasion, were.




