The primary rule of fractions states that the value of a fraction does not change when its numerator and denominator are multiplied by the same non-zero number. It can be applied to add or subtract two fractions. Basic rules for fraction to add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions are given below. Algebra rules for combining fractions. These rules apply for both proper fractions and improper fractions. They apply for all rational expressions as well. See also Distributing rules ---

Printable Fraction Rules Cheat Sheet Printable Word Searches
By understanding how the numerator and denominator work together, you'll be able to break down numbers into smaller parts, compare different fractions, and get a grasp on concepts like equivalent fractions. Fractions intro Learn FRACTION RULES Adding and Subtracting Fractions: 1. Common (like) denominators are necessary, so change all unlike fractions to equivalent fractions with like denominators. To make equivalent fractions, multiply the numerator and denominator by the same number. 2. Keep mixed numbers; DO NOT change mixed numbers into improper fractions. 3. Rules For Fractions As we already mentioned above, as long as you are aware and understand the rules for fractions, you shouldn't have any problems solving a problem with fractions. So, today, we are going to take a look at these rules. As you know, a fraction is just a part of a whole and it consists of a numerator and a denominator. Converting Fractions: Mixed to Improper: Multiply the whole number by the denominator (bottom number) Add the numerator (top number) This number becomes the new numerator The denominator stays the same Example: 5 3 × 5 = 15 15 + 2 = 17 17 5 2. Improper to Mixed: Divide the numerator by the denominator

Multiplying Fractions The Complete Guide — Mashup Math
Deb Russell Updated on October 20, 2019 Here is a cheat sheet, a basic outline of what you need to know about fractions when you are required to perform computations that involve fractions. In a nonscientific sense, the word computations refers to problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Fraction rules are a set of algebraic rules for working with fractions . A fraction has a numerator and a denominator . A fraction represents a division operation. The numerator is the dividend. The denominator is the divisor . References McAdams, David E.. All Math Words Dictionary, fraction rules. 2nd Classroom edition 20150108-4799968. pg 82. Rule #2: When we multiply two fractions, then the numerators are multiplied as well as the denominators are multiplied. Later simplify the fraction. Rule #3: When we divide a fraction from another fraction, we have to find the reciprocal of another fraction and then multiply with the first one to get the answer. Adding Fractions. The addition. Dividing fractions: 3/5 ÷ 1/2. Dividing two fractions is the same as multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. The first step to dividing fractions is to find the reciprocal (reverse the numerator and denominator) of the second fraction. Next, multiply the two numerators. Then, multiply the two denominators.
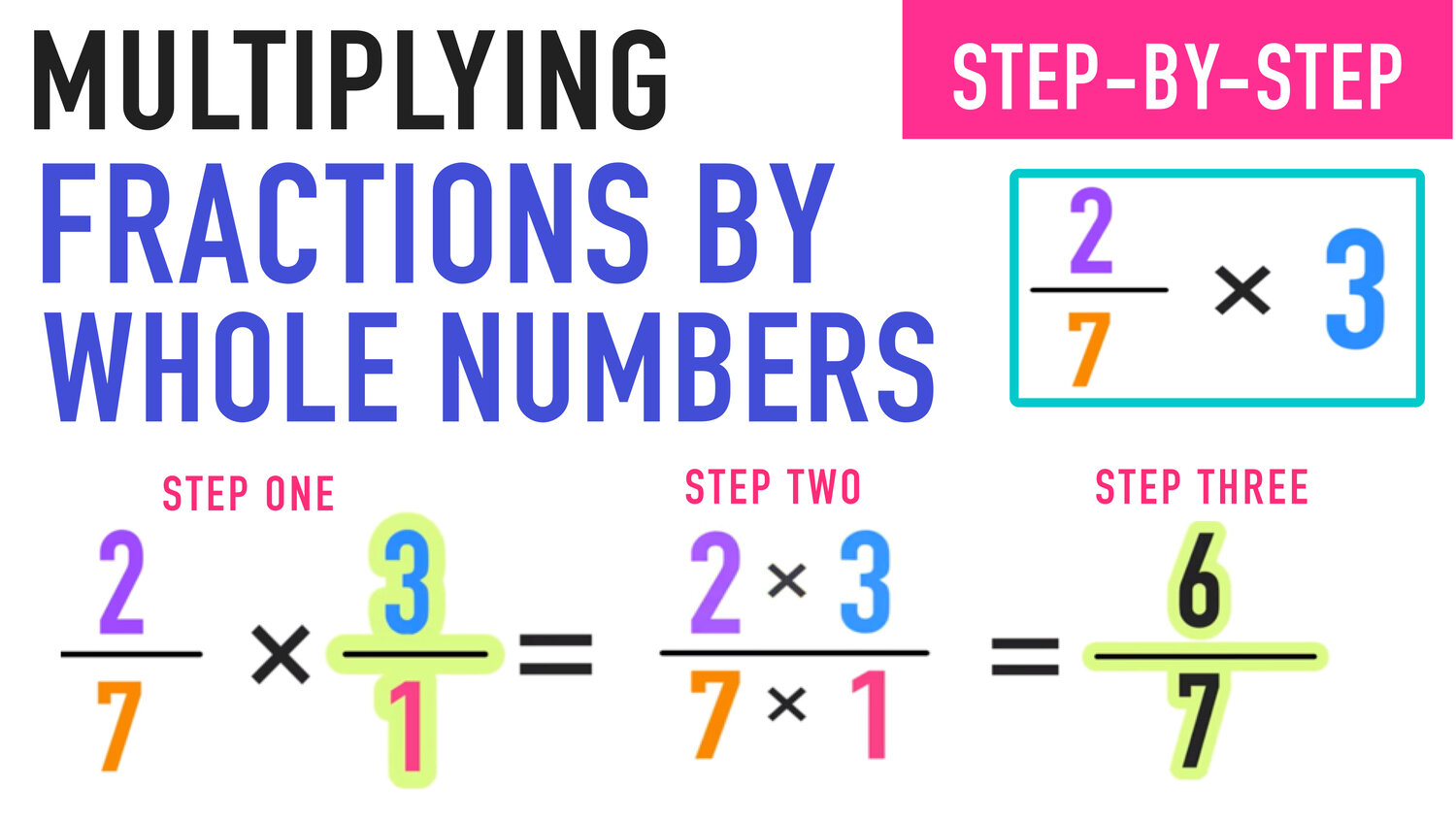
Multiplying Fractions by Whole Numbers Your Complete Guide — Mashup Math
Part 1. Fraction as a share Let's imagine a whole pie divided into 4 equal parts. One part is shaded red. image of a circle with one quarter shaded red One red part out of four equal parts means 1/4 of a whole is shaded. If we think of equal parts of a whole as shares, one share of a pie here is shaded red. What are Fraction Rules? A fraction represents a part-to-whole relationship. A fraction consists of two main components: the numerator and denominator. The numerator signifies the number of parts we have, while the denominator represents the total number of equal parts that make up a whole.
Suppose we have to divide 3/2 by 5/4. Step 1: Changing the sign to multiplication from division and writing the reciprocal of the second term ÷5/4 = ×4/5 ÷ 5 / 4 = × 4 / 5. Step 2: Multiplying the first with the reciprocal of the second fraction. Step 3: Getting the simplified result of the expression. Adding Fractions A fraction like 3 4 says we have 3 out of the 4 parts the whole is divided into. To add fractions there are Three Simple Steps: Step 1: Make sure the bottom numbers (the denominators) are the same Step 2: Add the top numbers (the numerators ), put that answer over the denominator Step 3: Simplify the fraction (if possible) Example:

Fraction rules
Divisibility Rules; Divisibility by 2; Divisibility by 5; Divisibility by 4; Divisibility by 25; Divisibility by 3 and 9; Fractions; Fractions. Fractions; Examples of Fractions; Reduction of Fractions; Addition of Fractions; Subtraction of Fractions; Multiplication of Fractions; Division of Fractions; Fraction Rules; Percents; Polynomial. An improper fraction is when the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator, like 7/3 or 5/5. A mixed number consists of a whole number and a proper fraction, such as 2 1/2. Understanding these different types of fractions is essential to apply the various rules of fractions effectively. What Are Fraction Rules?




