Get thousands of teacher-crafted activities that sync up with the school year. Access the most comprehensive library of K-8 resources for learning at school and at home. Is your child overwhelmed from online learning? Take a brain-break and make learning fun! Science, math, writing, and more key subjects brought to life through immersive gameplay.
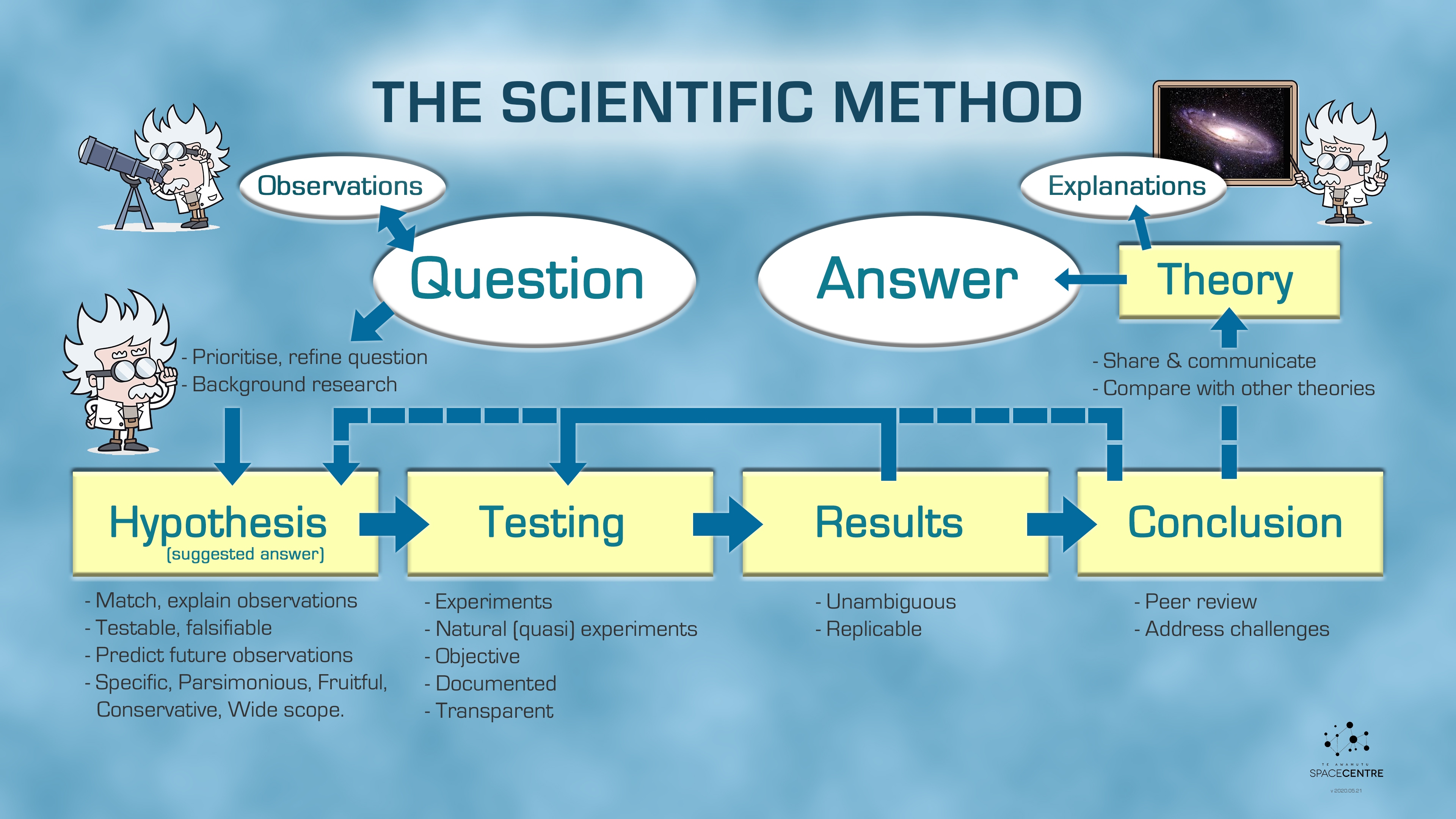
The Scientific Method
Science and method by Poincaré, Henri, 1854-1912. Publication date 1914 Topics Science -- Methodology Publisher London : T. Nelson Collection gerstein; biodiversity; toronto Contributor Gerstein - University of Toronto Language English. 14 35 Addeddate 2008-02-29 19:25:04 Bookplateleaf 0002 Call number AIC-3013 1 Science and the Scientific Method Science is with us everywhere. Advances in technology and science are rapidly transforming our world - from growing food, developing medicines, making exercise regimes, recycling and presenting the daily weather report, to reading a map and using our mobile phones and computers. The scientific method is critical to the development of scientific theories, which explain empirical (experiential) laws in a scientifically rational manner. In a typical application of the scientific method, a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the. The scientific method When conducting research, scientists use the scientific method to collect measurable, empirical evidence in an experiment related to a hypothesis (often in the form of.

Formula for Using the Scientific Method Owlcation
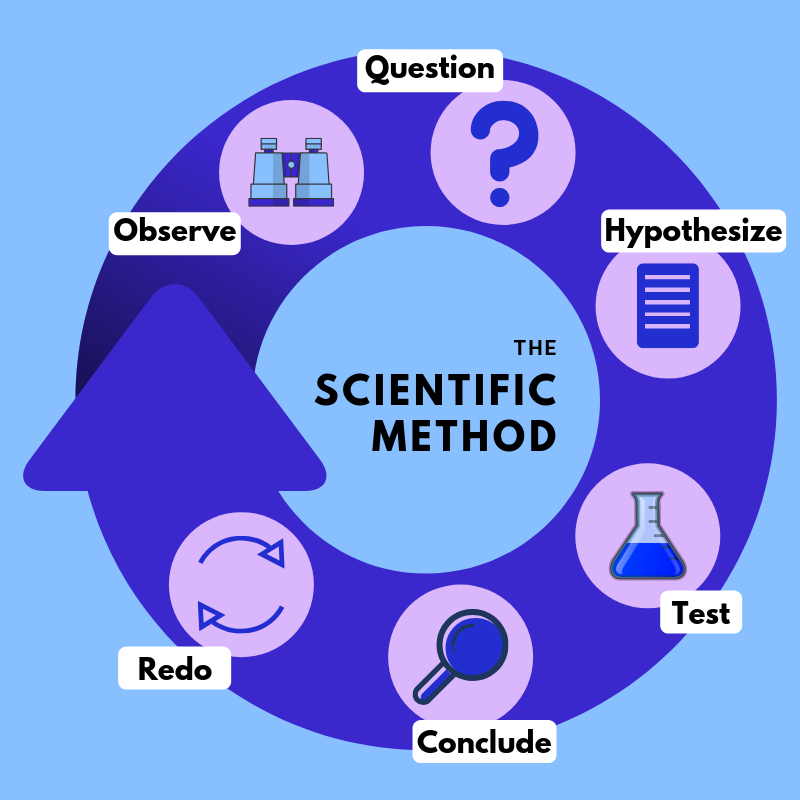
Science and Method, written in 1908, has been appreciated by a wide audience of nonprofessionals and translated into many languages. It defines the basic methodology and psychology of scientific discovery, particularly in regard to mathematics and mathematical physics. Though scientific investigation can loosely follow the steps of the scientific method, it doesn't have to. The scientific method isn't an unbreakable law that defines what is and isn't science. The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific method for additional detail.) It involves careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is. The scientific method has five basic steps, plus one feedback step: Make an observation. Ask a question. Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation. Make a prediction based on the hypothesis. Test the prediction. Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.

Explaining the Scientific Process NOVA PBS
Science and Method Henri Poincaré Cosimo, Inc., Jan 1, 2010 - Science - 292 pages Henri Poincare's Science and Method is an examination of the process scientists go through when determining. Science and Method. "Still a joy to read." — Mathematical Gazette This classic by the famous mathematician defines the basic methodology and psychology of scientific discovery, particularly regarding mathematics and mathematical physics. Drawing on examples from many fields, it explains how scientists analyze and choose their working facts.
What is the Scientific Method? The scientific method is a process for experimentation that is used to explore observations and answer questions. Do all scientists follow the scientific method exactly? No. Some areas of science can be more easily tested than others. Scientific Methods and Knowledge. The specific questions posed about reproducibility and replicability in the committee's statement of task are part of the broader question of how scientific knowledge is gained, questioned, and modified. In this chapter, we introduce concepts central to scientific inquiry by discussing the nature of science and.
Scientists Use the Scientific Method to Ensure Which Two Things MarilynkruwSuarez
Scientific method should also be distinguished from meta-methodology, which includes the values and justifications behind a particular characterization of scientific method (i.e., a methodology) — values such as objectivity, reproducibility, simplicity, or past successes. Science and Scientific Method Authors: J.G.C. da Silva Universidade Federal de Pelotas (retired). Abstract The roots of science go back to the contributions of Greek philosophers some 2,500.




