Today, the most common versions of these abbreviations are "sin" for sine, "cos" for cosine, "tan" or "tg" for tangent, "sec" for secant, "csc" or "cosec" for cosecant, and "cot" or "ctg" for cotangent. Sine, Cosine and Tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is To calculate them: Divide the length of one side by another side Example: What is the sine of 35°?

Sin,Cos,Tan adjacent, cos, en, geometry, hypotenuse, math, sin, tan, trigonometry Glogster
Sines Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Sin Cos Tan Values In trigonometry, sin cos and tan values are the primary functions we consider while solving trigonometric problems. These trigonometry values are used to measure the angles and sides of a right-angle triangle. Apart from sine, cosine and tangent values, the other three major values are cotangent, secant and cosecant. 42,598 🔎 Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) are all ratios. Therefore, you can find the missing terms using nothing else but our ratio calculator! Trigonometry has plenty of applications: from everyday life problems such as calculating the height or distance between objects to the satellite navigation system, astronomy, and geography. Sin, cos, and tan are trigonometric ratios that relate the angles and sides of right triangles. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. They are often written as sin (x), cos (x), and tan (x), where x is an.
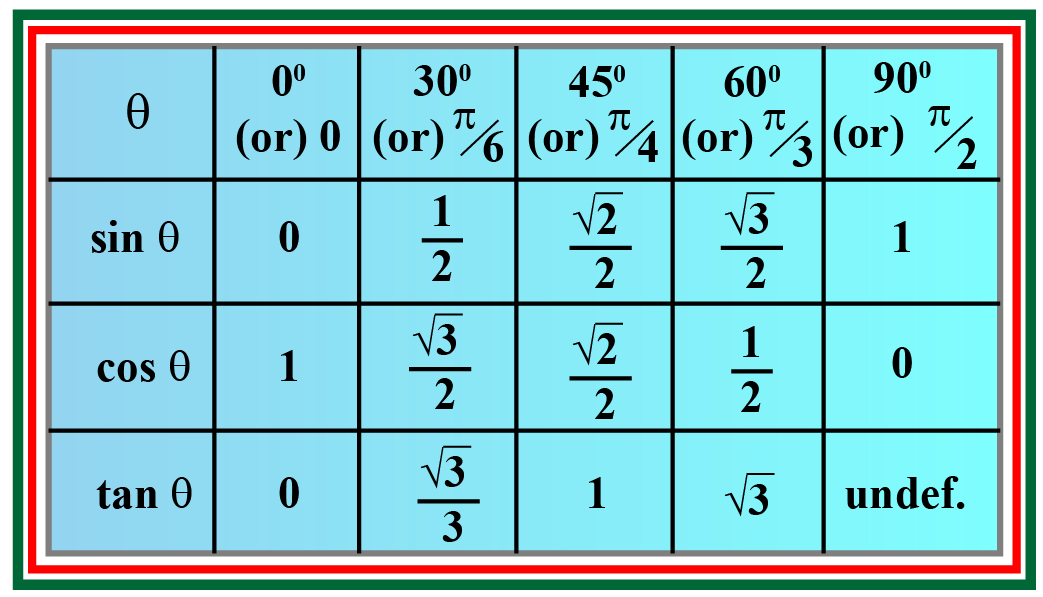
sin cos tan definitions, facts and solved examples Cuemath
Solving for an angle in a right triangle using the trigonometric ratios Sine and cosine of complementary angles Modeling with right triangles The reciprocal trigonometric ratios Unit 2: Trigonometric functions 0/1900 Mastery points Sine, Cosine and Tangent The three main functions in trigonometry are Sine, Cosine and Tangent. They are just the length of one side divided by another For a right triangle with an angle θ : For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is When we divide Sine by Cosine we get: Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and ratios of lengths. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. The Greeks focused on the calculation of chords, while mathematicians in India created the earliest-known tables of. Sine is the ratio of Opposite / Hypotenuse: sin (45°) = Opposite Hypotenuse Get a calculator, type in "45", then the "sin" key: sin (45°) = 0.7071.

What are sin cos tan? SOHCAHTOA With Examples Teachoo
About Transcript Trigonometric identities like sin²θ+cos²θ=1 can be used to rewrite expressions in a different, more convenient way. For example, (1-sin²θ) (cos²θ) can be rewritten as (cos²θ) (cos²θ), and then as cos⁴θ. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted E Man 9 years ago What is Sin Cos Tan in Trigonometry? Sin, cos, and tan are the three primary trigonometric ratios, namely, sine, cosine, and tangent respectively, where each of which gives the ratio of two sides of a right-angled triangle.
This page explains the sine, cosine, tangent ratio, gives on an overview of their range of values and provides practice problems on identifying the sides that are opposite and adjacent to a given angle. The Sine, Cosine and Tangent functions express the ratios of sides of a right triangle. tan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) . sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos ^2 (x) - sin ^2 (x) = 2 cos ^2 (x) - 1 = 1 - 2 sin ^2 (x) . tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1.
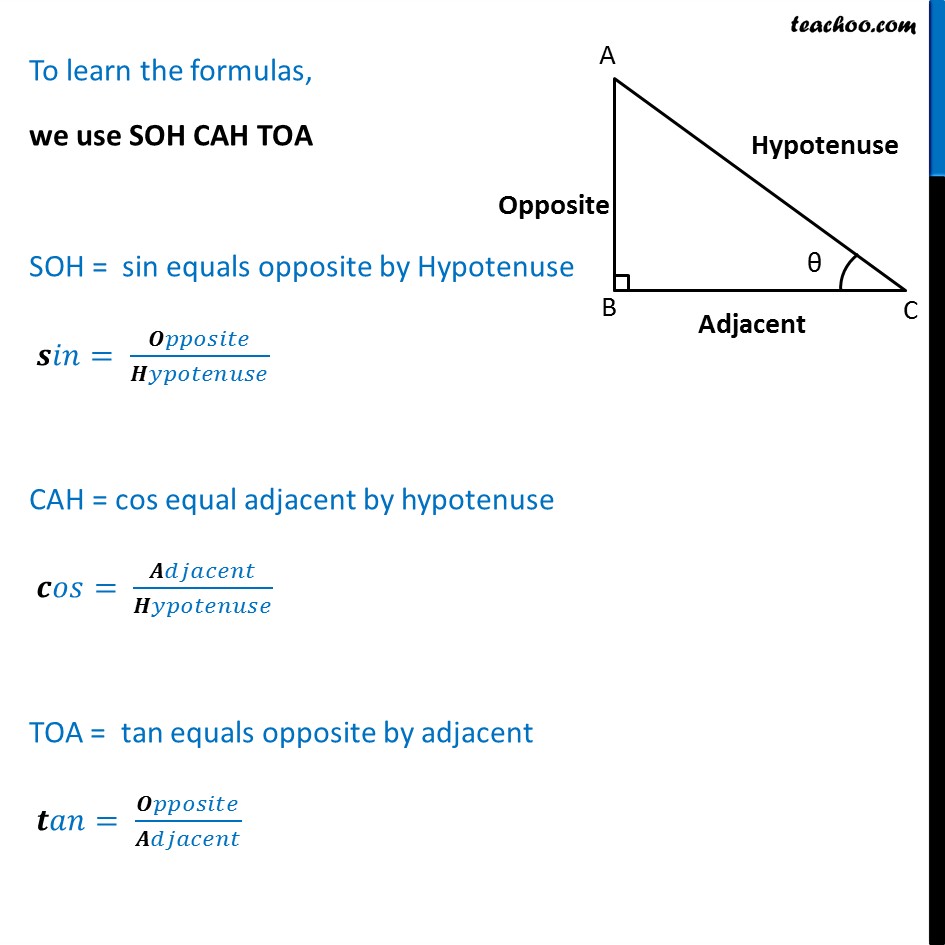
What are sin cos tan? SOHCAHTOA With Examples Teachoo Finding
1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider the unit circle, where the angle is t, the "opposite" side is sin (t) = y, the "adjacent" side is cos (t) = x, and the hypotenuse is 1. Sine and cosine are written using functional notation with the abbreviations sin and cos.. Often, if the argument is simple enough, the function value will be written without parentheses, as sin θ rather than as sin(θ).. Each of sine and cosine is a function of an angle, which is usually expressed in terms of radians or degrees.Except where explicitly stated otherwise, this article assumes.




