De taxonomie van Bloom is een van de meest gebruikte manieren om verschillende kennisniveaus in te delen. De onderwijspsycholoog Benjamin Bloom bedacht deze taxonomie als algemeen model voor de doelstellingen van het leerproces. De taxonomie van Bloom onderscheidt zes niveaus, die oplopen in moeilijkheidsgraad: Onthouden Begrijpen Toepassen Bloom's taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used for classification of educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains.

De Taxonomie van Bloom l Blog l September Onderwijs
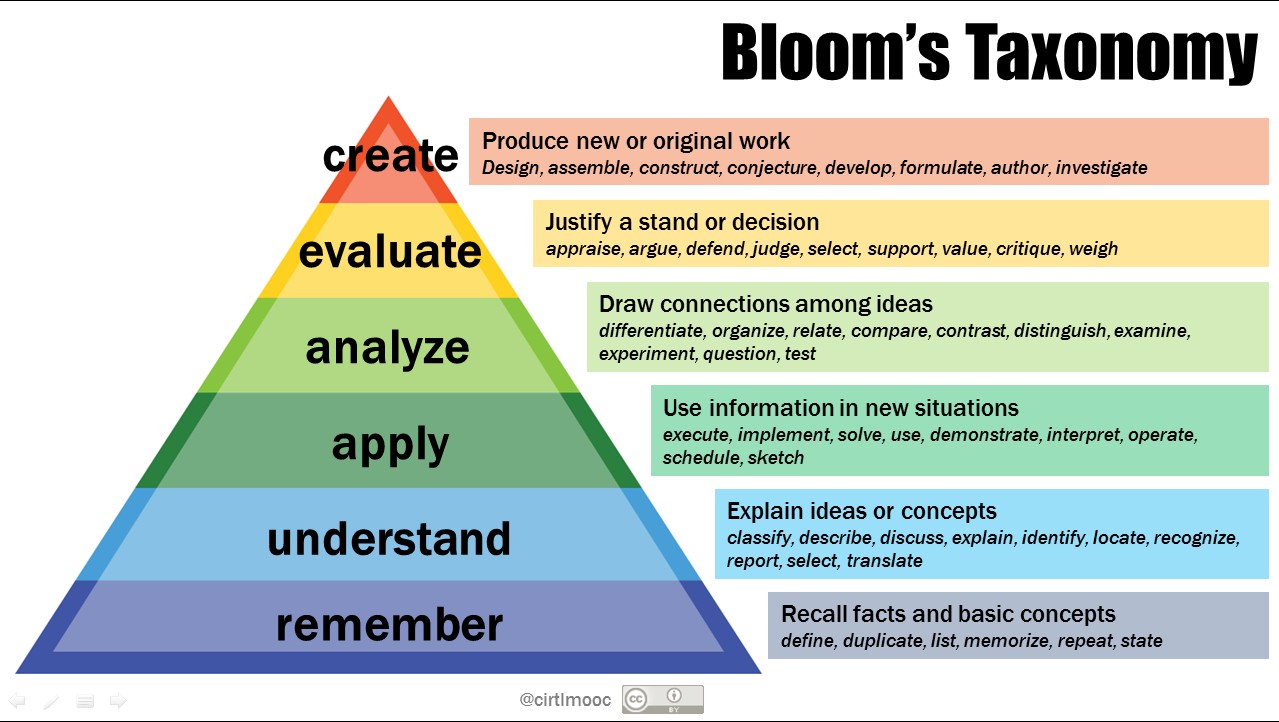
Bloom's Taxonomy is a hierarchical classification of the different levels of thinking, and should be applied when creating course objectives. Course objectives are brief statements that describe what students will be expected to learn by the end of the course. Many instructors have learning objectives when developing a course. De taxonomie van Bloom heeft denkvaardigheden geclassificeerd. De taxonomie kent een kennis- en een handelingsdimensie. De taxonomie ordent de denkvaardigheden naar lagere en hogere denkvaardigheden. Elk volgend (denk)niveau waarop gehandeld moet worden, is complexer. De (enigszins aangepaste) taxonomie van Bloom onderscheidt twee dimensies. 7 november 2023 De taxonomie van Bloom geeft mogelijkheden om activiteiten rijker te maken. In de taxonomie worden zes denkniveaus onderscheiden: onthouden, begrijpen, toepassen, analyseren, evalueren en creëren. De niveaus dienen om een onderscheid te maken in de complexiteit van het denkniveau waar een beroep op wordt gedaan. A group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Bloom's Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment.

Wat is de taxonomie van Bloom? agile4all
A group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published in 2001 a revision of Bloom's Taxonomy with the title A Taxonomy for Teaching, Learning, and Assessment. This title draws attention away from the somewhat static notion of "educational objectives" (in. Bloom's Taxonomy is actually a set of three different models, exploring three separate aspects (or "domains") of thinking and learning. These domains are: Cognitive - knowledge-based learning. Affective - emotional learning, including how we handle feelings and develop attitudes. Sensory - physical learning: sensing, moving and manipulating. Bloom's Taxonomy. Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes skills that students are expected to attain as learning progresses. Originally published in 1956, the tool is named after Benjamin Bloom, who was the Associate Director of the Board of Examinations at the University of Chicago. Now a classic arrangement of intellectual skills, the taxonomy and. Bloom's taxonomy differentiates between cognitive skill levels and calls attention to learning objectives that require higher levels of cognitive skills and, therefore, lead to deeper learning and transfer of knowledge and skills to a greater variety of tasks and contexts.

Leerdoelen en de taxonomie van Bloom over leren en ICT
Bloom's taxonomy is divided into six levels: remembering, understanding, applying, analysing, evaluating, and creating. The levels serve to differentiate in complexity of the knowledge level required. It does not describe an order in which certain levels should be addressed. Rich learning activities should address multiple levels. Bloom's taxonomy fostered a common vocabulary for thinking about learning goals. It engendered a means of aligning educational goals, curricula, and assessments, and it provided a structure for instructional activities and curriculum. Bloom and a group of assessment experts he had assembled began their work in 1949 and completed their efforts.
What is Bloom's Taxonomy? Bloom distinguishes between six levels of thinking. The first two levels, remembering and understanding,tend to stimulate superficial learning. Students take in information and are capable of reproducing this information. A drawback of this type of learning is that new information is easily forgotten again. De taxonomie van Bloom drukt het cognitieve leerproces uit in een reeks werkwoorden en wordt gebruikt om uitgebreidere vormen van denken te stimuleren zoals het analyseren en evalueren van procedures, processen, principes en concepten. Het raamwerk is bijzonder effectief bij het ontwerpen van educatieve modules.
10. Blooms taxonomy Andrea´s Portfolio
People also read lists articles that other readers of this article have read.. Recommended articles lists articles that we recommend and is powered by our AI driven recommendation engine.. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations. Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. 2.1.5. Atheoretical Levels Bloom's taxonomy is almost 50 years old. It was developed before we understood the cognitive processes involved in learning and performance.




