The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve. It begins in the posterior compartment of the jugular foramen, at the base of the skull. The internal jugular vein (IJV) is a paired vessel found within the carotid sheath on either side of the neck. It extends from the base of the skull to the sternal end of the clavicle. The internal jugular vein receives eight tributaries along its course.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/vena-jugularis-interna/cOMEyKPJ06WH227w75X4Q_qeM6C1Z6SrZvVqGFjMdPGw_Vena_jugularis_interna_sinistra_02.png)
Vena jugularis interna Anatomie und Klinik Kenhub
The internal jugular vein (IJV) is the major venous return from the brain, upper face and neck. Gross anatomy Origin and course It is formed by the union of inferior petrosal and sigmoid dural venous sinuses in or just distal to the jugular foramen (forming the jugular bulb). It descends in the carotid sheath with the internal carotid artery. The internal jugular vein is formed by the union of the sigmoid and inferior petrosal venous sinuses. Here, the internal jugular vein is dilated as the superior bulb lying in the posterior part of the tympanic floor. Course The internal jugular vein is formed by the anastomosis of blood from the sigmoid sinus of the dura mater and the inferior petrosal sinus. The internal jugular runs with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve inside the carotid sheath. It provides venous drainage for the contents of the skull . Percutaneous cannulation of the internal jugular vein uses anatomic landmarks to guide venipuncture and a Seldinger technique to thread a central venous catheter through the internal jugular vein and into the superior vena cava. Three approaches (central, anterior, and posterior) are used; the central approach is described here.
/GettyImages-530309436-cf8e158016cf4dc0a81e12ecb221d1ee.jpg)
Internal Jugular Vein Anatomy, Function, and Significance
Definition The internal jugular vein ( v. jugularis interna) collects the blood from the brain, from the superficial parts of the face, and from the neck. It is directly continuous with the transverse sinus, and begins in the posterior compartment of the jugular foramen, at the base of the skull. Background. Internal jugular (IJ) vein thrombosis refers to an intraluminal thrombus occurring anywhere from the intracranial IJ vein to the junction of the IJ and the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein. It is an underdiagnosed condition that may occur as a complication of head and neck infections, surgery, central venous access. The internal jugular vein (Latin: vena jugularis interna) is a blood vessel that arises from the junction of two intracranial venous sinuses - the inferior petrosal sinus and the sigmoid sinus.The internal jugular vein collects venous blood from the brain, skull, and superficial parts of the face and neck.. Internal jugular vein (lateral view) by Anatomy.app Introduction. Internal jugular vein (IJV) drains blood from the head and neck district. It originates from the sigmoid sinus after it exits from the cranial cavity through the jugular foramen, then descends in the carotid sheath, and unites within the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein, which enters the thorax to join vena cava superior .
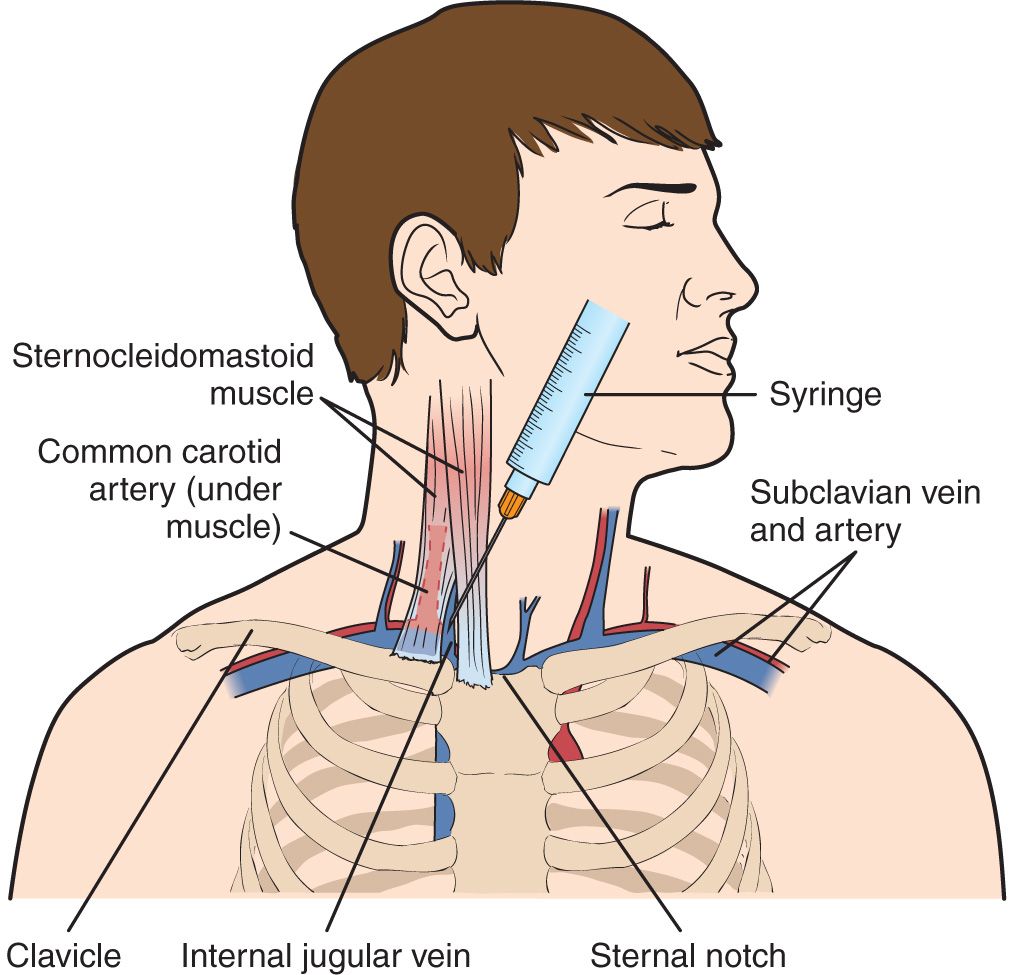
Internal Jugular Vein—Central Venous Access Anesthesia Key
C+ delayed. Comparison made to CT brain from earlier the same day. There is a filling defect in the right internal jugular vein extending from the jugular bulb 2cm inferiorly. This is consistent with thrombus. No extension above the jugular foramen. The right sigmoid and transverse sinuses opacify normally. No other filling defect identified. External jugular vein (Vena jugularis externa) The external jugular vein is a vein of the neck that arises from the union of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein and the posterior auricular vein.. The external jugular vein begins near the mandibular angle, just below or within the substance of the parotid gland.It descends obliquely along the neck, superficial to the.
Die Vena jugularis interna weist in ihrem Verlauf zwei Auftreibungen auf, die separat benannt werden: Bulbus superior venae jugularis internae: Auftreibung am Beginn der Vene im hinteren Abschnitt des Foramen jugulare Bulbus inferior venae jugularis internae: Auftreibung hinter dem Sternoklavikulargelenk Zuflüsse The V. jugularis interna reached the ventral surface of the N. vagus after a short course, and these two anatomic structures were contained within the same connective tissue sheath. Then, the V. jugularis interna united with the V. thyroidea caudalis at the subclavian artery level. Thereafter, it opened into the V. subclavian dextra as a single.

Internal Jugular Vein Anatomy ANATOMY
Clinical significance. The external jugular is a large vein used in prehospital medicine for venous access when the Paramedic is unable to find another peripheral vein [4] It is commonly used in cardiac arrest or other situations where the patient is unresponsive due to the pain associated with the procedure. Bei der perkutanen Kanülierung der V. jugularis interna werden anatomische Orientierungspunkte für die Venenpunktion verwendet und ein zentraler Venenkatheter mit der Seldinger-Technik durch die V. jugularis interna in die V. cava superior eingeführt.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/de/vena-jugularis-interna/cOMEyKPJ06WH227w75X4Q_qeM6C1Z6SrZvVqGFjMdPGw_Vena_jugularis_interna_sinistra_02.png)
/GettyImages-530309436-cf8e158016cf4dc0a81e12ecb221d1ee.jpg)


