A hand X-ray (radiograph) is a test that creates a picture of the inside of your hand. The picture shows the inner structure ( anatomy) of your hand in black and white. Calcium in your bones absorbs more radiation, so your bones appear white on the X-ray. A hand X-ray is a black and white image that shows the inner structures of your hand, such as your bones and soft tissues. This diagnostic tool can help your doctor locate and understand.
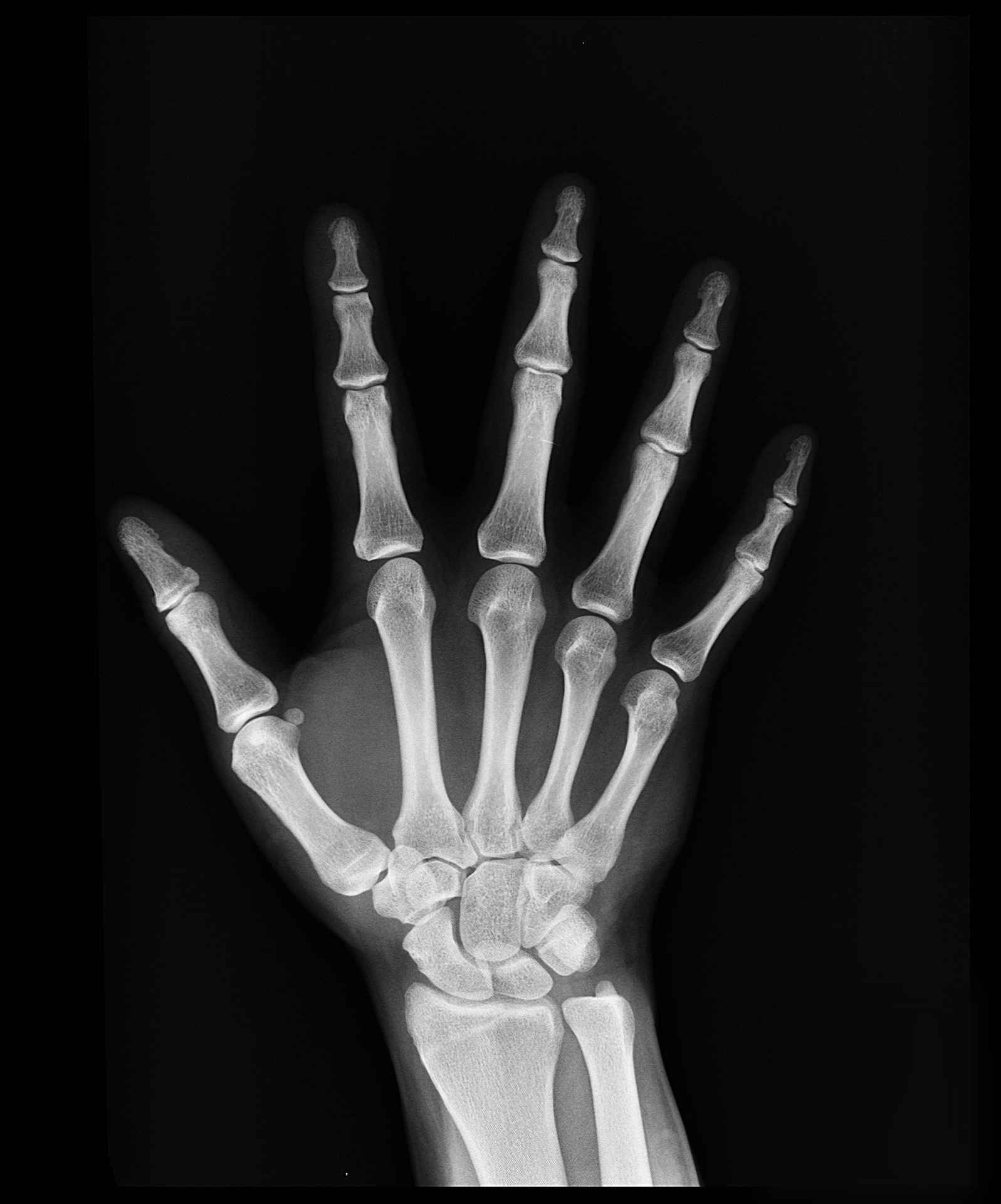
Hand XRay
Hand x-rays are indicated for a variety of settings, including: trauma with suspected fracture suspected metacarpal dislocation foreign body detection and localization investigation of joint pain and/or deformity rheumatoid arthritis osteoarthrosis Projections Standard projections PA view Medical Encyclopedia → Hand x-ray Hand x-ray This test is an x-ray of one or both hands. How the Test is Performed A hand x-ray is taken in a hospital radiology department or your health care provider's office by an x-ray technician. You will be asked to place your hand on the x-ray table, and keep it very still as the picture is being taken. Access my FREE Online Membership today → https://www.thenotedanatomist.com___Unlock my Premium Tutoring Memberships → https://www.thenotedanatomist.com/premi. A hand x-ray is an imaging technique used to take pictures of hand bones using radiological waves known as "x" rays for medical purposes. Who do I need to see to get an x ray? If you have experienced an acute trauma to your hand, finger or wrist and think you may have an injury you should see your doctor.

Hand xray. Causes, symptoms, treatment Hand xray
Key points. Finger injuries visible on X-ray include bone fractures, dislocations and avulsions. The hand comprises the metacarpal and phalangeal bones. Fractures and dislocations are usually straightforward to identify, so long as the potentially injured bone is fully visible in 2 planes. Finger joints commonly dislocate and are susceptible to. Hand series (summary) Last revised by Andrew Murphy on 23 Aug 2019 Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data This is a basic article for medical students and other non-radiologists A hand series (or hand x-ray) may be performed for a multitude of reasons. Hand x-ray is used to detect fractures, tumors, foreign objects, or degenerative conditions of the hand. Hand x-rays may also be done to find out a child's "bone age." This can help determine if a health problem is preventing the child from growing properly or how much growth is left. What Abnormal Results Mean Abnormal results may include: Hand X-ray Guideline. Routine: 3 views • PA • PA OBLIQUE • LATERAL - Separate fingers to prevent overlapping (Fan lateral) Foreign Body: 2 views • PA. • PA view both hands and wrists (position hands as close together as possible to minimize the necessary field of view) • Oblique AP view (Ball catcher's view) with same bilateral.
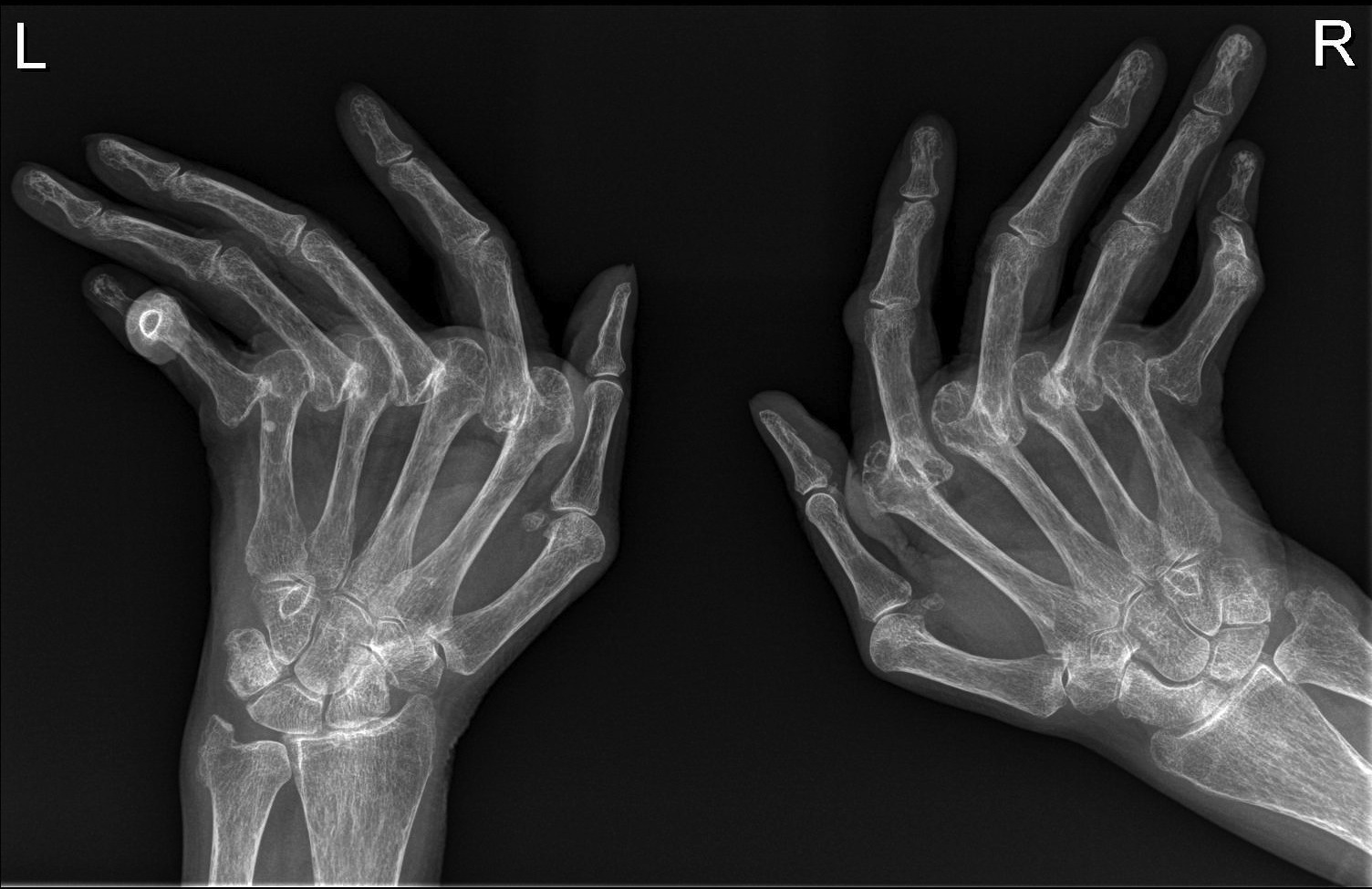
Rheumatoid arthritis hands Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital
Hand radiograph (an approach) Last revised by Mostafa El-Feky on 1 Oct 2020 Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data Hand radiographs are commonplace in the Emergency Department or the trauma reporting list. Systematic review X-ray - hand. How the Test is Performed. A hand x-ray is taken in a hospital radiology department or your health care provider's office by an x-ray technician. You will be asked to place your hand on the x-ray table, and keep it very still as the picture is being taken. You may need to change the position of your hand, so more images can be taken.
Hands Last revised by David Carroll on 4 Dec 2022 Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data The hand is part of the upper limb below the forearm and wrist . In the supinated anatomical position, the palm is facing anteriorly and the dorsum posteriorly. The bones of the hand are: carpals (8) scaphoid lunate triquetrum pisiform Shaft of third metacarpal. Neck of fifth metacarpal. Head of forth metacarpal. Metacarpophalangeal joint. Proximal phalanx. Middle phalanx. Distal phalanx. Sesamoid bones (flexor pollicis brevis, adductor pollicis). Terminal tuft.

XRay Open Air MRI of CenLa
1. Introduction Hand radiographs are frequently ordered as the first imaging modality in the assessment of patients presenting with peripheral arthritis. They can provide invaluable information about the bones, joints, mineralization, soft tissues and the distribution of abnormalities. POSTERIOR-ANTERIOR VIEW. This is the most commonly used view for interpretation. Finger deformities may not be noticed as patients are required to press their hands down firmly against the plate, while the X-Rays are shot from above.




