Cold section: Air intake (inlet) — For subsonic aircraft, the inlet is a duct which is required to ensure smooth airflow into the engine despite air approaching the inlet from directions other than straight ahead. This occurs on the ground from cross winds and in flight with aircraft pitch and yaw motions. g GE Aviation GE Aircraft Engines The Aircraft Engine Design Project Fundamentals of Engine Cycles Ken Gould Spring 2009 Phil Weed 1.. Augmented Turbofan Engine Cross-Section 16 General Electric Aircraft Engines. g GE Aircraft Engines Design Considerations- Process Centering and Variation Off-Target Variation XX X
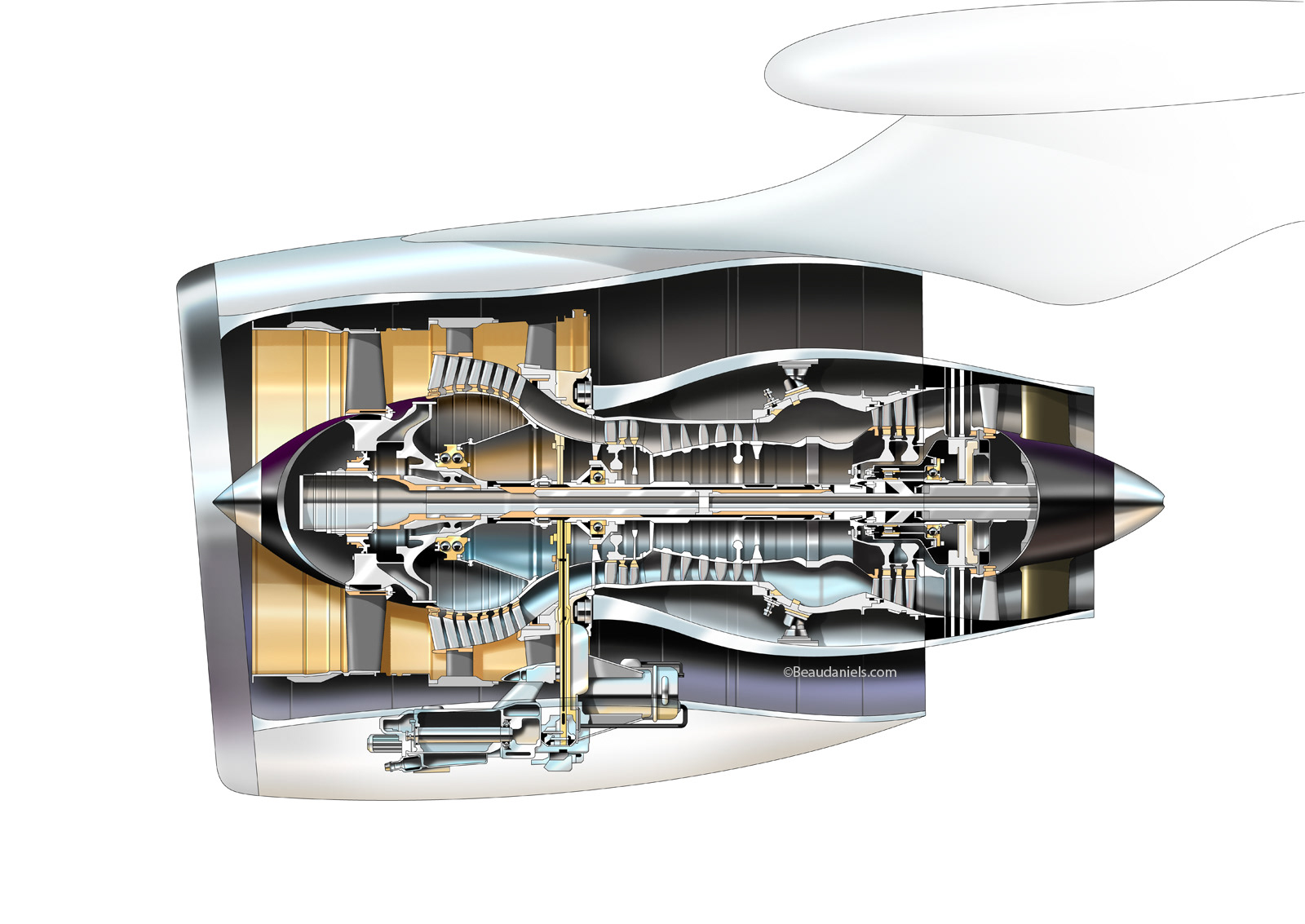
Technical illustration, Beau and Alan Daniels. Aviation technical
Because weight and volume are at a premium in the overall design of an aircraft and because the power plant represents a large fraction of any aircraft's total weight and volume, these parameters must be minimized in the engine design. The airflow that passes through an engine is a representative measure of the engine's cross-sectional area and hence its weight and volume. Jet engines generate thrust by harnessing the principles of jet propulsion, expelling large volumes of fluid in one direction to propel a vehicle in the opposite direction. In aircraft, this forward motion creates a flow of air over the wings that produces lift to keep the airplane in the sky. The thrust generation is accomplished by exploiting. A Boeing 747 aircraft has a PW4000 engine with a 94 inch inlet diameter. Find the radius, circumference, and area of this inlet. A DC-10 has a JT9D engine with a 46.7 inch inlet radius.. The Airbus 318 has a Pratt & Whitney 6000 engine with a cross-sectional circular inlet area of 2508.5774 square inches. What is the circumference of this inlet? This made the engine narrower, giving it a smaller cross section, and easier to shoehorn into airframes. The engine weighed 2 lb/hp, making it far more powerful than other mass-produced engines of.

Air Progress The Jet Engine, July 1951 Air Trails Airplanes and Rockets
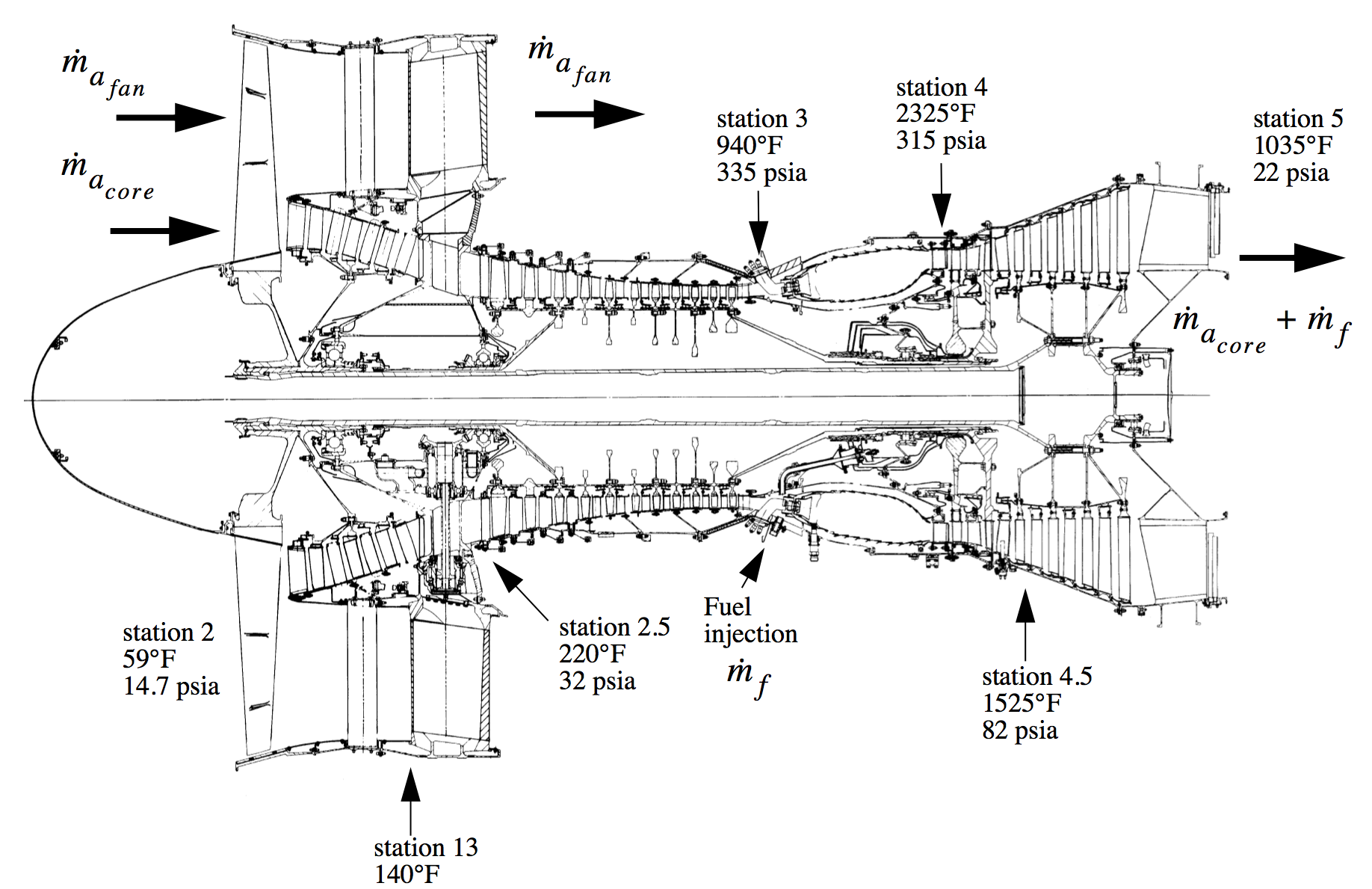
This cross-section of a turbofan jet engine shows the components of the HyTEC project's smaller engine core, with the compressor, combustor, and turbine noted. By shrinking the engine core, better fuel efficiency can be achieved.. developing methods to pull more electrical power from this engine to power other systems aboard the aircraft,. g GE Aviation GE Aircraft Engines The Aircraft Engine Design Project Fundamentals of Engine Cycles Peter Rock Spring 2008 Earl "Will" DeShazer 1. Augmented Turbofan Engine Cross-Section 17 General Electric Aircraft Engines. g GE Aircraft Engines Design Considerations- Process Centering and Variation Off-Target Variation XX X INTRODUCTION. This chapter looks at the layout of some jet engines, using cross-sectional drawings, beginning with relatively simple ones and leading up to the large engines for one of the most recent aircraft, the Boeing 777. Two concepts are introduced. One is the multi-shaft engine with separate low-pressure and high-pressure spools. The cross-section of aircraft engine. 3D transonic flow of an inviscid non-heat con- ductive gas through axial 5.5 compressor stages in an SO-3 aircraft engine ( Fig. 1) was considered. The.
How does a jet engine work? GlobalSpec
From 1903, the year of the Wright Brothers first flight, to the late 1930s the gas powered reciprocating internal-combustion engine with a propeller was the sole means used to propel aircraft. It was Frank Whittle , a British pilot, who designed and patented the first turbo jet engine in 1930. cross section of a jet engine - airplane cross section stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images.. aircraft windows - airplane cross section stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. Plane spraying delta area w. Dioxin-tainted herbicide/defoliant Agent Orange, in Vietnam war defensive measure. 20 MI SE OF SAIGON.
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft propulsion.The word "turbofan" is a combination of the preceding generation engine technology of the turbojet, and a reference to the additional fan stage added.It consists of a gas turbine engine which achieves mechanical energy from combustion, and a ducted fan that uses the mechanical energy from the. The F100 engine picture does not show the aircraft inlet because the inlet is part of the airframe and changes from aircraft to aircraft. The F100 is an afterburning turbofan engine and the flame holders for the afterburner are shown in orange in the nozzle of the drawing. The front section of the F100 is the fan section which is not modeled on.

Cross section of a radial engine, used in aircraft. interestingasfuck
In this animation, we pull the engine apart to see how the parts go together. A graphical version of this slide is also available. Most modern passenger and military aircraft are powered by gas turbine engines, which are also called jet engines. Jet engines come in a variety of shapes and sizes but all jet engines have certain parts in common. On this page we have a computer model of a basic. Unheated engine bypass air is then diverted through nozzles mounted on the wings of the aircraft, called roll posts, in order to allow roll control. The system is capable of handling 18,000lbf of dry thrust through the 3BSM, 20,000lbf through the lift fan and a further 3,900lbf through both roll posts, totalling 41,900lbs of thrust.




