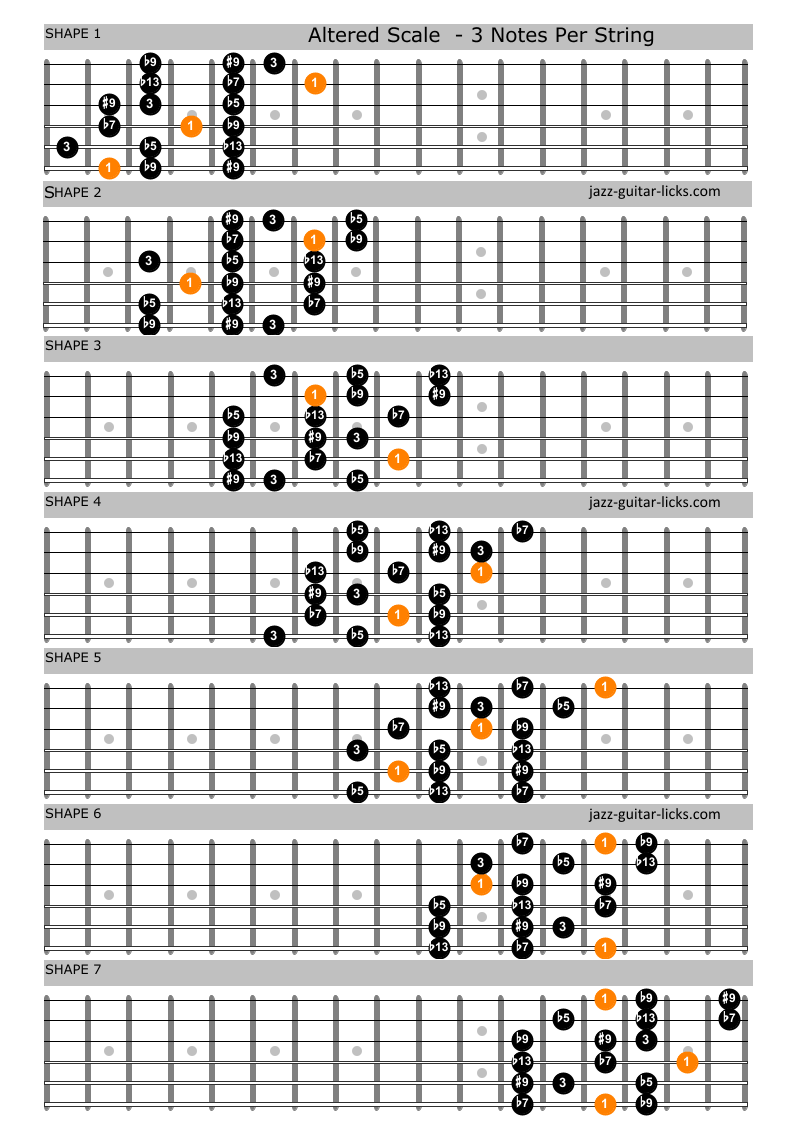
The altered scale is the 7th mode of the melodic minor scale, which means that it is like playing Ab melodic minor starting from the note G. The altered scale is used to solo over dominant 7th chords, both in major and minor keys. The Altered Scale, sometimes referred to as Super Locrian mode, Locrian b 4 or Diminished Whole-tone, is the seventh mode of the melodic minor scale. The formula is 1 (root) - b2 (minor second) - b3 (minor third) - b4 (diminished fourth) - b5 (diminished fifth) - b6 (minor sixth) and b7 (minor seventh).

Altered Scale How To Make It Sound Amazing YouTube
The Altered Scale, also known as the Super Locrian scale, allows access to the most beautiful tensions of a dominant chord in a flash. But using this scale effectively is not easy. In this lesson, we've assembled the keys to utilizing the Altered Scale to its full potential. Altered scales. What are they? Also called the altered dominant scale or the super locrian scale, the altered scale is a mode of melodic minor & awesome for improvising with over dominant chords. FREE PDF: Top 3 Pentatonic Scale Patterns for more melodic soloing Weekly Lesson #95 Altered Scale Lesson Content Outline with Timestamp Links: Altered scales. What are they? Also called the altered dominant scale or the super locrian scale, the altered scale is a mode of melodic minor & awesome for. Altered Scales in Music Theory: How to Play an Altered Scale Written by MasterClass Last updated: Nov 2, 2021 • 3 min read Have you ever wondered how jazz seems to push harmonic boundaries in a way that rock and pop rarely do? The secret lies in jazz's use of unconventional scales and modes, chief among them the altered scale. Learn From the Best

😎Altered Scale The Most Important Things to Know💥 https//www.youtube
Figures 4-10 provide just that, with a collection of fingering patterns for the A altered scale (A, Bb, C, C#, Eb, F, G) that make their way up the neck, starting with a pattern that climbs up to a 5th-fret A root on the high E string. (The A root notes are circled in red in all of these diagrams, in every octave where they occur.) #1) Master the basic scale If you ask a group of musicians about what to play over an altered dominant chord you're likely to get a number of answers. From melodic minor scales to diminished patterns, and even tritone substitutions… But what you might not realize is that most of these altered approaches are describing the same scale. The altered scale is made by the sequence: Half, Whole, Half, Whole, Whole, Whole, Whole The abbreviation "alt" (for "altered") used in chord symbols enhances readability by reducing the number of characters otherwise needed to define the chord and avoids the confusion of multiple equivalent complex names. The altered scale is a dominant scale where all the non-defining chord tones are altered. The three essential notes that define any chord are the root, the third, and the seventh (dominant chord = root, major third, flat seventh). Any note that isn't the root, the third, or the seventh can be altered.
The Altered Scale For Guitar Charts, Licks, Tabs, Theory
There is a scale called the "altered scale" which is a mode of the melodic minor and contains all these chord tones and will therefore work over any altered dominant chord. We will look at that last of all. The whole tone scale to deal with augmented chords of 7#5 chord types The whole-tone scale is a scale made up of whole tones only. The Altered Scale - The Complete Guide Get free weekly lessons, practice tips, and downloadable resources to your inbox! One of the most interesting improv scales you'll encounter in jazz theory is that of the Altered Scale. This vexing 7-note scale can be a bit confusing, but it is without question one of the hippest jazz scales you can play.
The altered scale is a set of 7 notes based on the following scale degrees related to the root note: 1, b2, b3, 3, b5, b6, and b7. An easy way to think of the notes in an altered scale is to think of the melodic minor scale a half step above. For example, for a B altered scale, think of the C melodic minor scale starting on the 7th degree. Altered scales use the same notes as jazz minor scales a semitone higher. Therefore, if you know the jazz minor scale, and encounter a dominant seven chord, play the jazz minor scale a semitone higher than the root note of the dominant chord, and you will be playing an altered scale. For example, in a song in the key of C major, a jazz.

Creating Patterns with the Altered Scale YouTube
The altered scale is used for playing on altered dominant chords such as E7#9, E7b9, E7#5, or E7b5, etc., because it contains all these alterations. The scale is easier to relate to chords if you write it out like this: 1, b9, #9, 3, b5, #5, b7 as you can instantly see how it might fit the above chords. You'll find it used mainly in jazz and. What is the Altered Scale? The Altered Scale is a Dominant scale in which all of the "non-essential" tones have been altered. There are three essential tones in the Dominant scale: the first (root) the third (mediant) the seventh (leading tone) Essential notes in a dominant scale




