NAND XNOR NOT Logic Gates in Computer Code Wrapping up Logic gate: a cool term, but what does it mean? This article will introduce the concept of a logic gate as well as describe how each specific logic gate (OR, AND, XOR, NOR, NAND, XNOR, and NOT) works. What Is a Logic Gate? First, it's important to realize that logic gates take many forms. Logic Symbol of XOR Gate Truth Table for XOR Gate NOR Gate Logic Symbol of NOR Gate Truth Table for NOR gate XNOR Gate Logic Symbol for XNOR Gate NAND Gate Logic Symbol for NAND Gate Truth Table for NAND Gate FAQ What are Logic Gates? Basic Gates Basic gates are defined as gates very basic and are not complicated. These are of three types AND gate
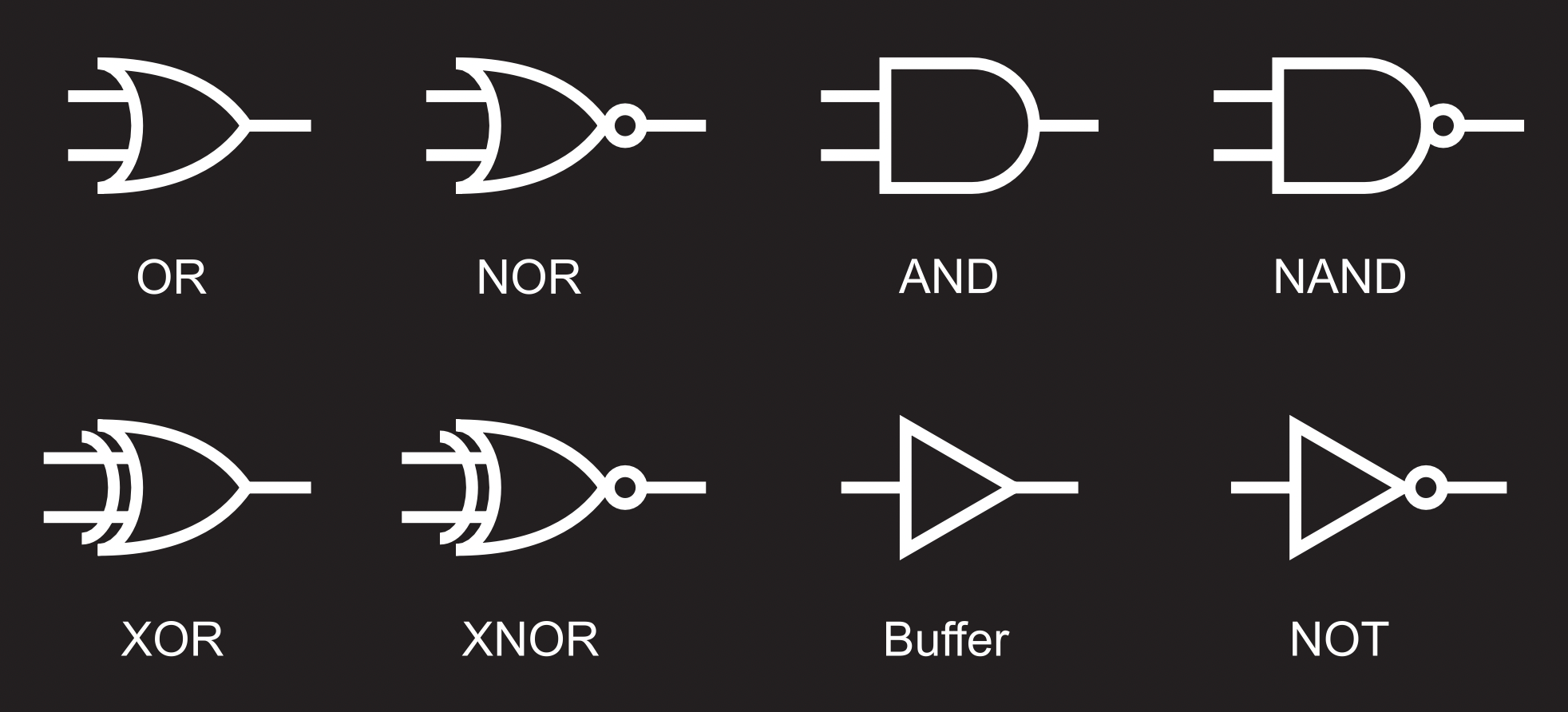
How Logic Gates Work OR, AND, XOR, NOR, NAND, XNOR, and NOT
There are seven basic logic gates: AND, OR, XOR, NOT, NAND, NOR and XNOR. The AND gate is named so because, if 0 is false and 1 is true, the gate acts in the same way as the logical "and" operator. The following illustration and table show the circuit symbol and logic combinations for an AND gate. Logic Gate Simulator A free, simple, online logic gate simulator. Investigate the behaviour of AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR and XOR gates. Select gates from the dropdown list and click "add node" to add more gates. Drag from the hollow circles to the solid circles to make connections. Right click connections to delete them. Introduction to Logic Gates Logic gates are the basic building blocks of any digital system. They are used to create digital circuits and perform logical operations on binary inputs. The main types of logic gates include AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. NAND NOR Exclusive OR (XOR) Exclusive NOR (XNOR) Let us see in detail about these logic gates, take a look at their logic symbols, and also build their truth tables. Logic Symbols and Truth Tables of Logic Gates NOT Gate The NOT logic gate has one input and one output where the output is a complement to the input.
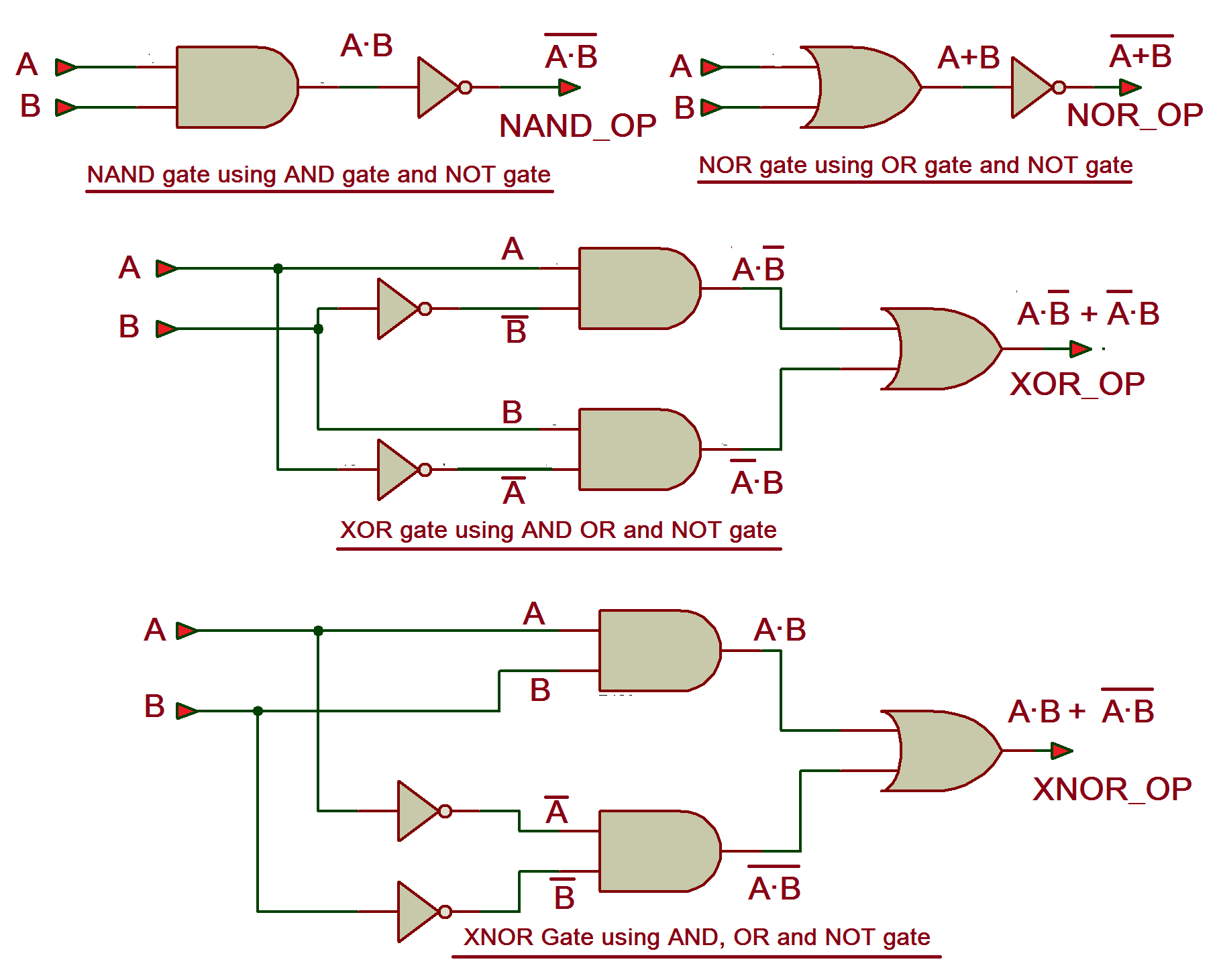
Circuit Diagram Of Xnor Gate Using Nand Wiring Diagram
NAND gate NOR gate XOR gate and XNOR gate Among these logic gates, some are universal while others are basic. The term universal gate is derived from the idea that operations that can be performed with the basic logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT can be performed with just a single logic gate. NOR; NAND; XOR; XNOR; Basic Logic Gates AND Gate. An AND gate has a single output and two or more inputs. When all of the inputs are 1, the output of this gate is 1. The AND gate's Boolean logic is Y=A.B if there are two inputs A and B. An AND gate's symbol and truth table are as follows: Input. The ^ operator computes the logical exclusive OR, also known as the logical XOR, of its operands. The result of x ^ y is true if x evaluates to true and y evaluates to false, or x evaluates to false and y evaluates to true. Otherwise, the result is false. The NOR gate is essentially an OR gate whose output is then fed into a NOT gate. Therefore, it is true only in the case where both inputs are zeroes (the only case that would have made an OR gate output a '0'). The XOR gate is true when the inputs are opposite of each other, but false when they are equal. For example, the two inputs '1' and '0.
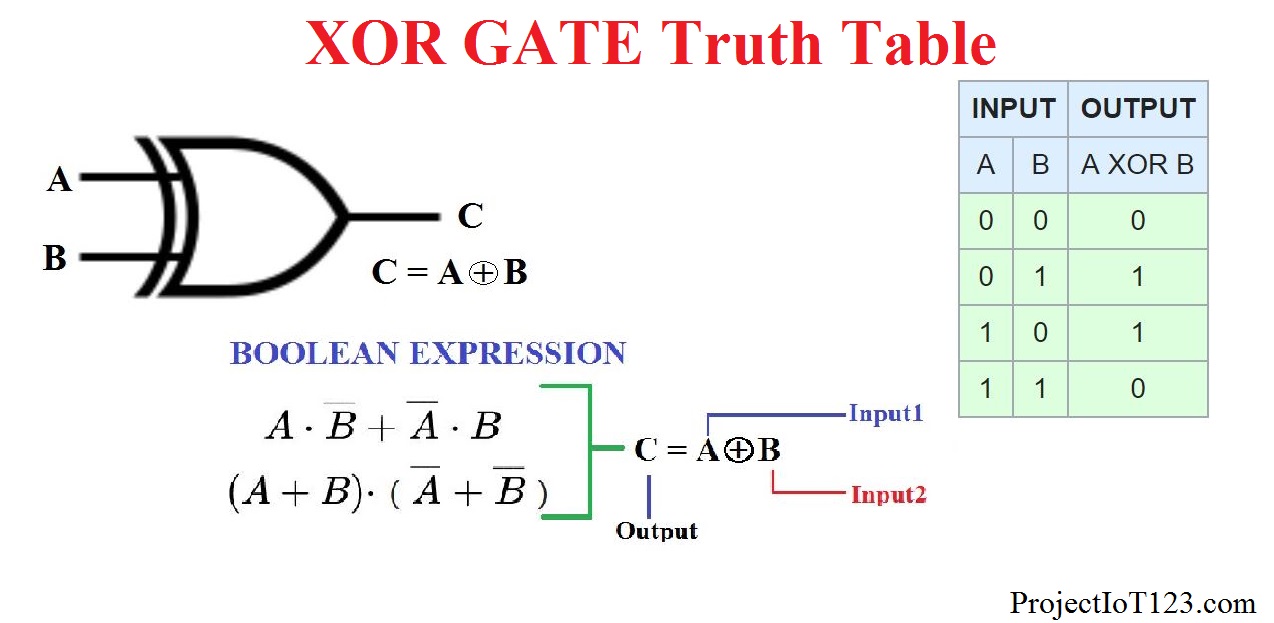
Truth Table And Or Not Xor Xnor Gates In Hindi
XOR gate (sometimes EOR, or EXOR and pronounced as Exclusive OR) is a digital logic gate that gives a true (1 or HIGH) output when the number of true inputs is odd. An XOR gate implements an exclusive or from mathematical logic; that is, a true output results if one, and only one, of the inputs to the gate is true.If both inputs are false (0/LOW) or both are true, a false output results. 'NOR' - an 'OR' gate combined with a 'NOT' gate 'XOR' (or 'eXclusive OR') - a variation on the 'OR' gate, if the two inputs to an 'OR' are both 'high' then their.
What is Boolean Algebra? The rules I mentioned above are described by a field of Mathematics called Boolean Algebra. In his 1854 book, British Mathematician George Boole proposed a systematic set of rules for manipulation of Truth Values. These rules gave a mathematical foundation for dealing with logical propositions. 1. The XNOR gate (sometimes ENOR, EXNOR, NXOR, XAND and pronounced as Exclusive NOR) is a digital logic gate whose function is the logical complement of the Exclusive OR ( XOR) gate. [1] It is equivalent to the logical connective ( ) from mathematical logic, also known as the material biconditional. The two-input version implements logical.

CircuitVerse XOR using NOR
The XOR gate also has the same number of inputs and output. This logic gate works like this-0 + 0 => 0 0 + 1 => 1 1 + 0 => 1 1 + 1 => 0. Here, the input needs to be exclusive. As you can see in the above flowchart, the output is false where both the inputs are true. NOR. The NOR gate is a NOT-OR gate which is a bit similar to the NOT gate. A logic gate is an electronic circuit that operates on one or more digital signals to produce an output signal. A logic gate performs a logical operation such as AND, OR, NOT, etc. on one more logic input (1 or 0) and produces a single logic output (1 or 0). Logic gates process signals which represent " true " or " false ".




