This video shows a ciliate; a type of single-celled organism that inhabits a wide range of freshwater habitats. Ciliates feed upon smaller microscopic organi. Habitats. Ciliates are divided into free living and parasitic. Whereas free living ciliates (can live outside a host) can be found in just about any given environment, parasitic ciliates live in the body of the host. Paramecium is an example of free living. Such paramecia as Paramecium caudatum can be found free living in fresh water bodies.
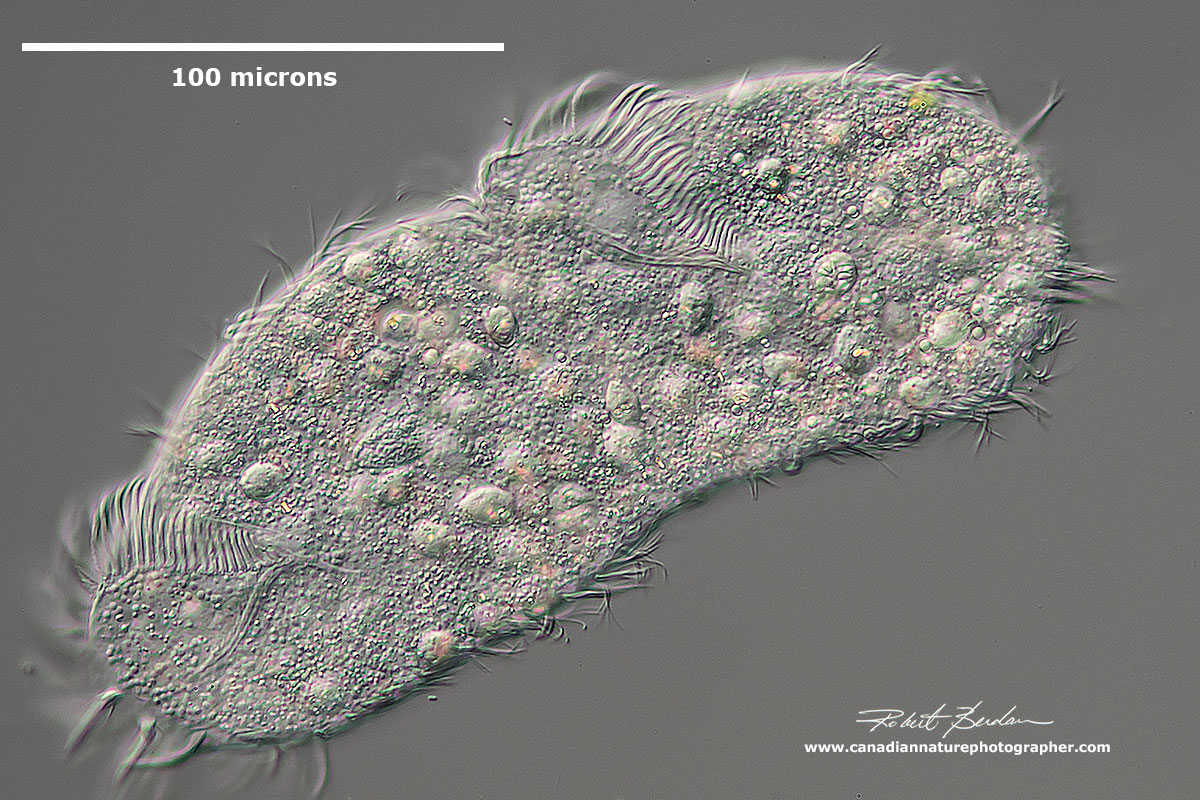
Photographing Ciliates The Canadian Nature Photographer
Ciliates are recovering from a piece of frozen, dried mosses and wandering around. The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle. This video shows a species of Opercularia. These are ciliates that are found attached to surfaces (they are sessile), and that typically live in colonies. He. The Ciliates are probably the best known and the most frequently observed of the microscopic unicells. Nearly 10,000 species, both freshwater and marine, have been described, and probably many more remain to be discovered. They are characterized by the possession of cilia (Latin cilium, eyelash) -- tiny hairs covering all or part of their.

Ciliate under microscope YouTube
Ciliates are basically ciliated protozoans. Protozoans are another term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes. They are either parasitic or free-living and feed on organic matter such as debris, organic tissues, or other microorganisms. Contents show. How ciliates got their nuclei. Biologists who spend time observing environmental samples under the microscope are used to the incredible range of shapes, sizes, and behaviors displayed by eukaryotic microorganisms, which rivals or exceeds that of animals, just on a smaller scale. These are lumped together as "protists" and generally. Place a drop of pond water under the microscope, and you will likely find an ocean of extraordinary and diverse single-celled organisms called ciliates. This remarkable group of single-celled organisms wield microtubules, active systems, electrical signaling, and chemical sensors to build intricate geometrical structures and perform complex behaviors that can appear indistinguishable from. Lab #3 Ciliates under Compound Microscope. 9/7/17. Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to allow students to observe ciliates in greater detail with the higher magnification of the compound microscopes, compared to the dissecting microscopes. students will also get the opportunity to practice operating a compound microscope. Materials:
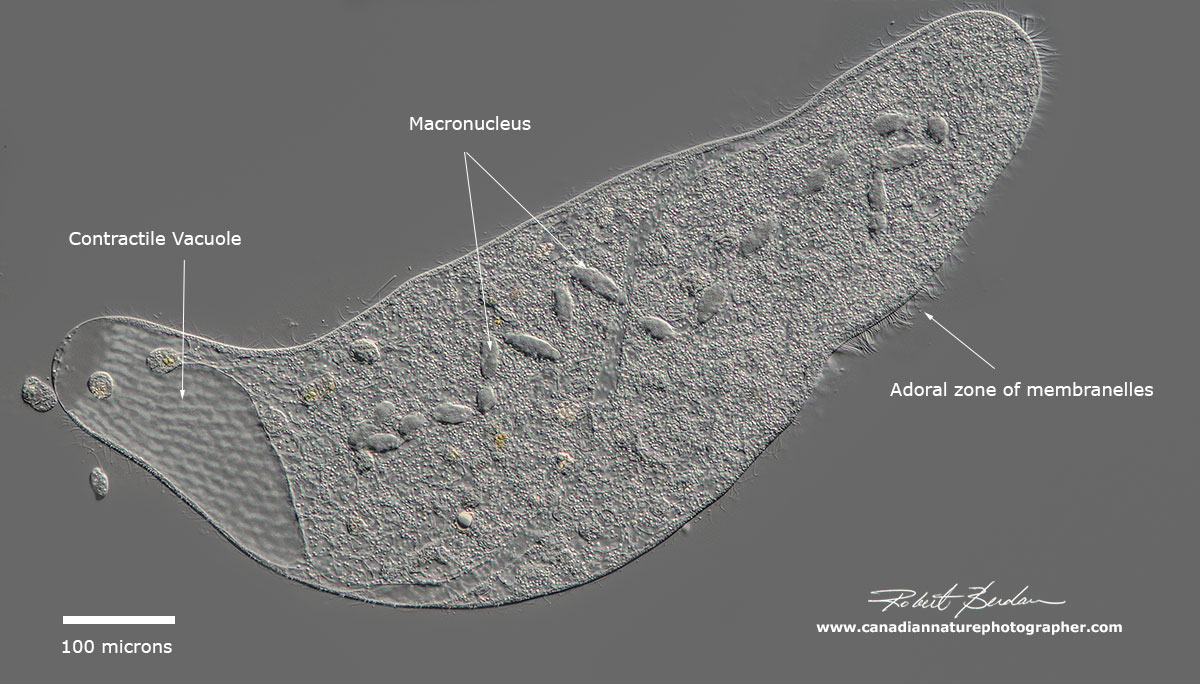
Photographing Ciliates The Canadian Nature Photographer
9/7/17- Identifying Ciliates With A Compound Microscope. Rationale: The rationale of this experiment was to familiarize ourselves with compound microscopes and to compare the compound and dissecting microscopes to one another. We also learned how to calculate magnification by multiplying the ocular lense (10x) by the objective lense (either 4x. To determine the handedness of helical swimming of ciliate Tetrahymena in free-space (Supplementary Movie 1), 3D swimming trajectories of Tetrahymena cells were tracked using a tPOT microscope.
ciliate, any member of the protozoan phylum Ciliophora, of which there are some 8,000 species; ciliates are generally considered the most evolved and complex of protozoans. Ciliates are single-celled organisms that, at some stage in their life cycle, possess cilia, short hairlike organelles used for locomotion and food gathering.. The cilia are usually arranged in rows, known as kineties, on. The Litostomatea are a class of ciliates. The group consists of three subclasses: Haptoria, Trichostomatia and Rhynchostomatia. Haptoria includes mostly carn.
Under the microscope a ciliate YouTube
Place this slide under the microscope and observe clearer images and descriptions of the ciliate you are able to gather using the different magnifications of the microscope. Repeat this process as many times as necessary to gain accurate observations and pictures of the ciliates. Record all of your observations. Biologists who spend time observing environmental samples under the microscope are used to the incredible range of shapes, sizes, and behaviors displayed by eukaryotic microorganisms, which rivals or exceeds that of animals, just on a smaller scale.. ciliates. Due to their impressive size, ubiquity, and—for lack of a better word—elegance.




