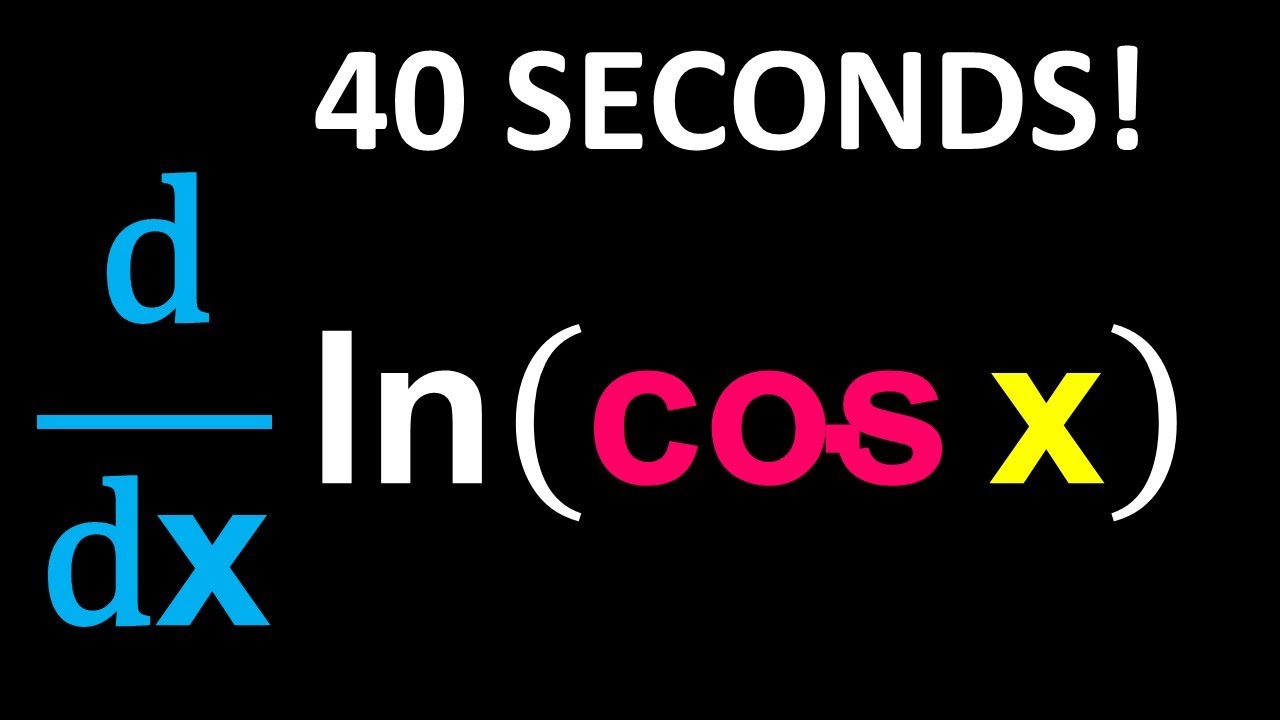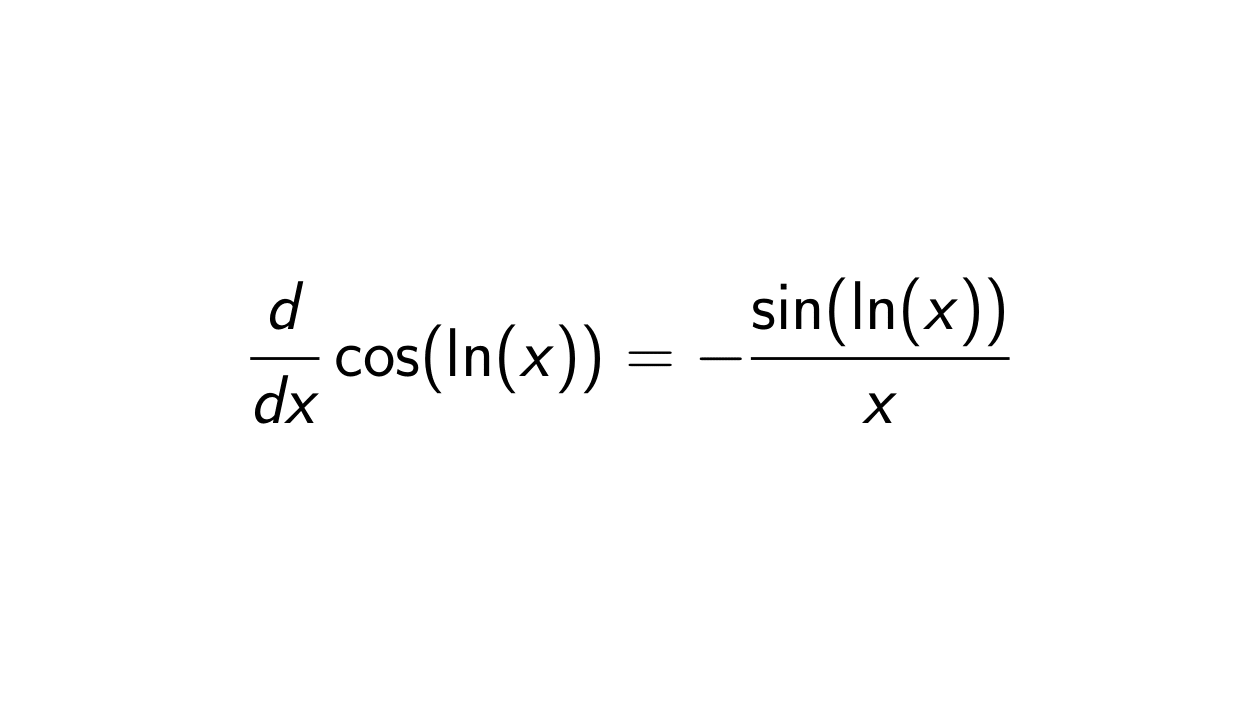.more 🏼 https://integralsforyou.com - Integral of cos (ln (x)) - How to integrate it step by step using integration by parts!🔍 𝐀𝐫𝐞 𝐲𝐨𝐮 𝐥𝐨𝐨𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐟𝐨𝐫. Free derivative calculator - differentiate functions with all the steps. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph

Integral of cos(ln(x)) (by parts) YouTube
1 Answer Jim H Aug 30, 2015 Integrate by parts (twice). Explanation: Looking at ∫cos(lnx)dx, we realize that if can't integrate straight away. Next thought is, perhaps we could use substitution. We would need cos(lnx) 1 x to integrate by substitution. Arithmetic Matrix Simultaneous equation Differentiation Integration Limits Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. Trigonometry Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Figure 7.1.1: To find the area of the shaded region, we have to use integration by parts. For this integral, let's choose u = tan − 1x and dv = dx, thereby making du = 1 x2 + 1 dx and v = x. After applying the integration-by-parts formula (Equation 7.1.2) we obtain. Area = xtan − 1x|1 0 − ∫1 0 x x2 + 1 dx.

Integration by Parts Integral of cos(ln x) dx YouTube
Example 3.5.2: Finding the Derivative of a Function Containing cos x. Find the derivative of g(x) = cosx 4x2. Solution. By applying the quotient rule, we have. g′ (x) = ( − sinx)4x2 − 8x(cosx) (4x2)2. Simplifying, we obtain. g′ (x) = − 4x2sinx − 8xcosx 16x4 = − xsinx − 2cosx 4x3. Figure 6.2.7: Setting up Integration by Parts. Putting this all together in the Integration by Parts formula, things work out very nicely: $$\int \ln x\,dx = x\ln x - \int x\,\frac1x\,dx.\] The new integral simplifies to ∫ 1dx, which is about as simple as things get. Its integral is x + C and our answer is. so basically the derivative of a function has the same domain as the function itself. Therefore the derivative of the function f (x)= ln (x), which is defined only of x > 0, is also defined only for x > 0 (f' (x) = 1/x where x > 0). i hope this makes sense. ( 2 votes) WolframAlpha Online Integral Calculator Solve integrals with Wolfram|Alpha x sin x2 d x Natural Language Math Input More than just an online integral solver Wolfram|Alpha is a great tool for calculating antiderivatives and definite integrals, double and triple integrals, and improper integrals.
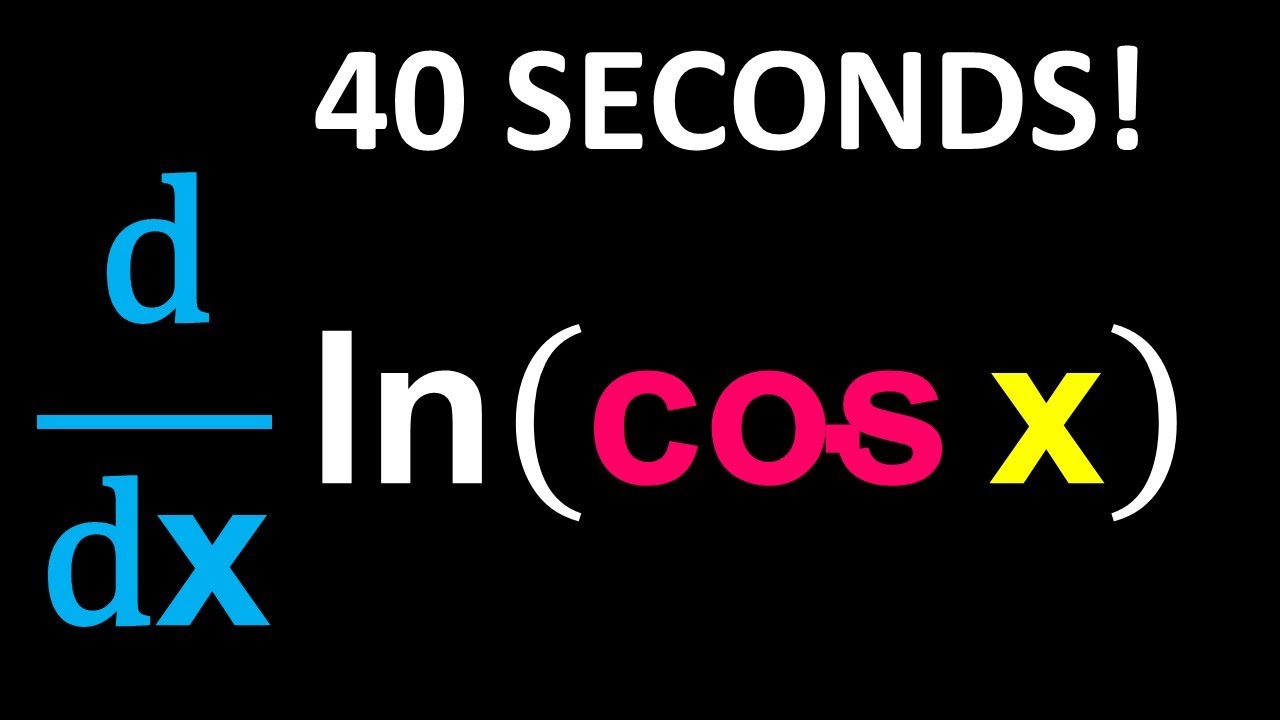
Derivative of ln(cos(x)) done in 40 seconds! YouTube
The cosine calculator allows through the cos function to calculate online the cosine of an angle in radians, you must first select the desired unit by clicking on the options button calculation module. After that, you can start your calculations. To calculate cosine online of π 6 π 6, enter cos ( π 6 π 6), after calculation, the result 3. integral of cos (ln (x)) with u sub: @0:00 integral of cos (ln (x)) without u sub, @8:20subscribe to @bprpcalculus for more calculus tutorialsCheck out my 100 in.
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8NysIntegration by Parts the Integral of cos(ln(x)) We calculate the definite integral of ln(cos x) over the interval from 0 to pi/2.Playlist: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PL22w63XsKjqzJpcuD6InKWZXep2L0z1.
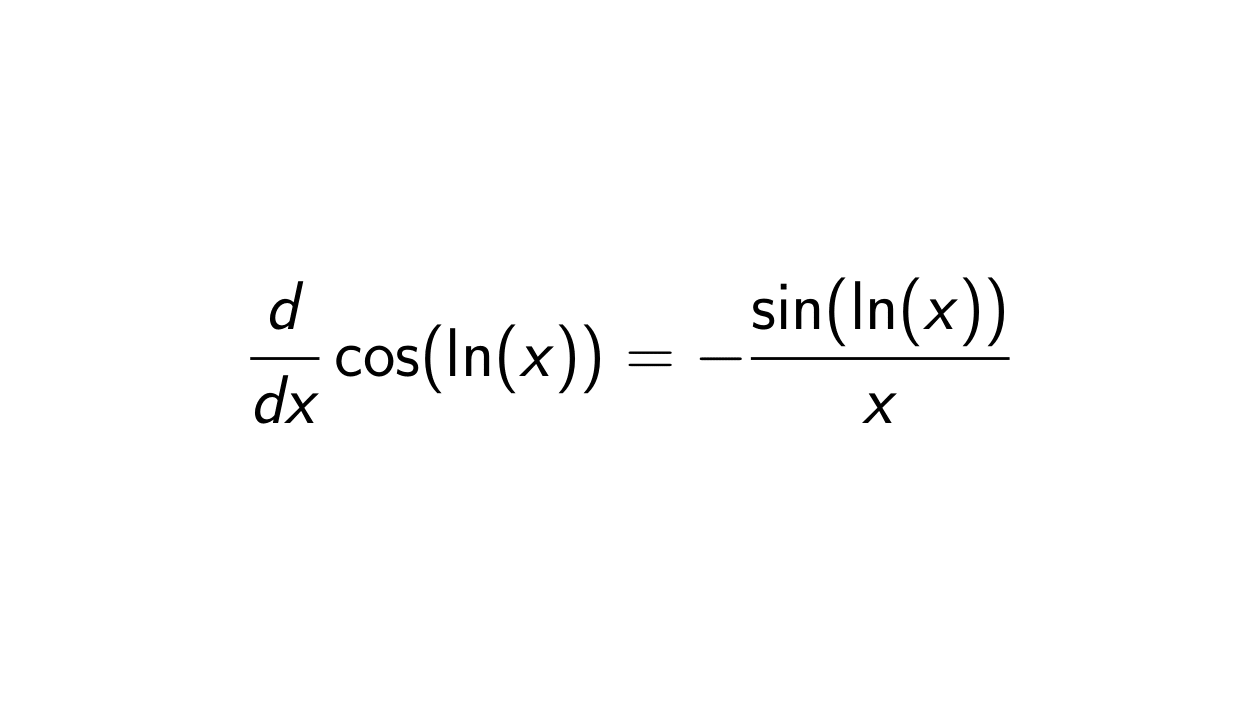
What is the derivative of cos(ln(x))? Epsilonify
Integration by Parts: Integral of cos(ln x) dx#calculus #integral #integrals #integration #integrationbyparts The integral of cos (lnx) is an antiderivative of cos (ln x) function which is equal to ½ [xsin (ln x) + xcos (ln x)]. It is also known as the reverse derivative of sine function which is a trigonometric identity. The sine function is the ratio of adjacent side to the hypotenuse of a triangle which is written as: cos = adjacent side / hypotenuse