Main Electrical Components: Diagram Circuit: Generator with a PMG As the PMG rotor rotates, it produces AC voltage in the PMG stator. The regulator rectifies this voltage and applies DC to the exciter stator. A three-phase AC voltage appears at the exciter rotor and is in turn rectified by the rotating rectifiers. What makes electric power possible—and indeed practical—is a superb electromagnetic device called an electricity generator: a kind of electric motor working in reverse that converts ordinary energy into electricity. Let's take a closer look at generators and find out how they work!

Electric Generator Diagram EEE Electronics Electrical Components
Electrical generator diagrams are visual representations of the internal components and connections of an electrical generator. They provide a clear and concise overview of how the generator functions and how the different components are connected to generate electricity. What Is an AC Generator? AC generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The AC Generator's input supply is mechanical energy supplied by steam turbines, gas turbines and combustion engines. The output is alternating electrical power in the form of alternating voltage and current. This training module has been developed to provide you with information pertaining to devices known as Basic AC Electric Generators. The information in this training module is designed to increase your knowledge and improve your abilities as they relate to the module. In electricity generation, a generator [1] is a device that converts motion-based power ( potential and kinetic energy) or fuel-based power ( chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit.
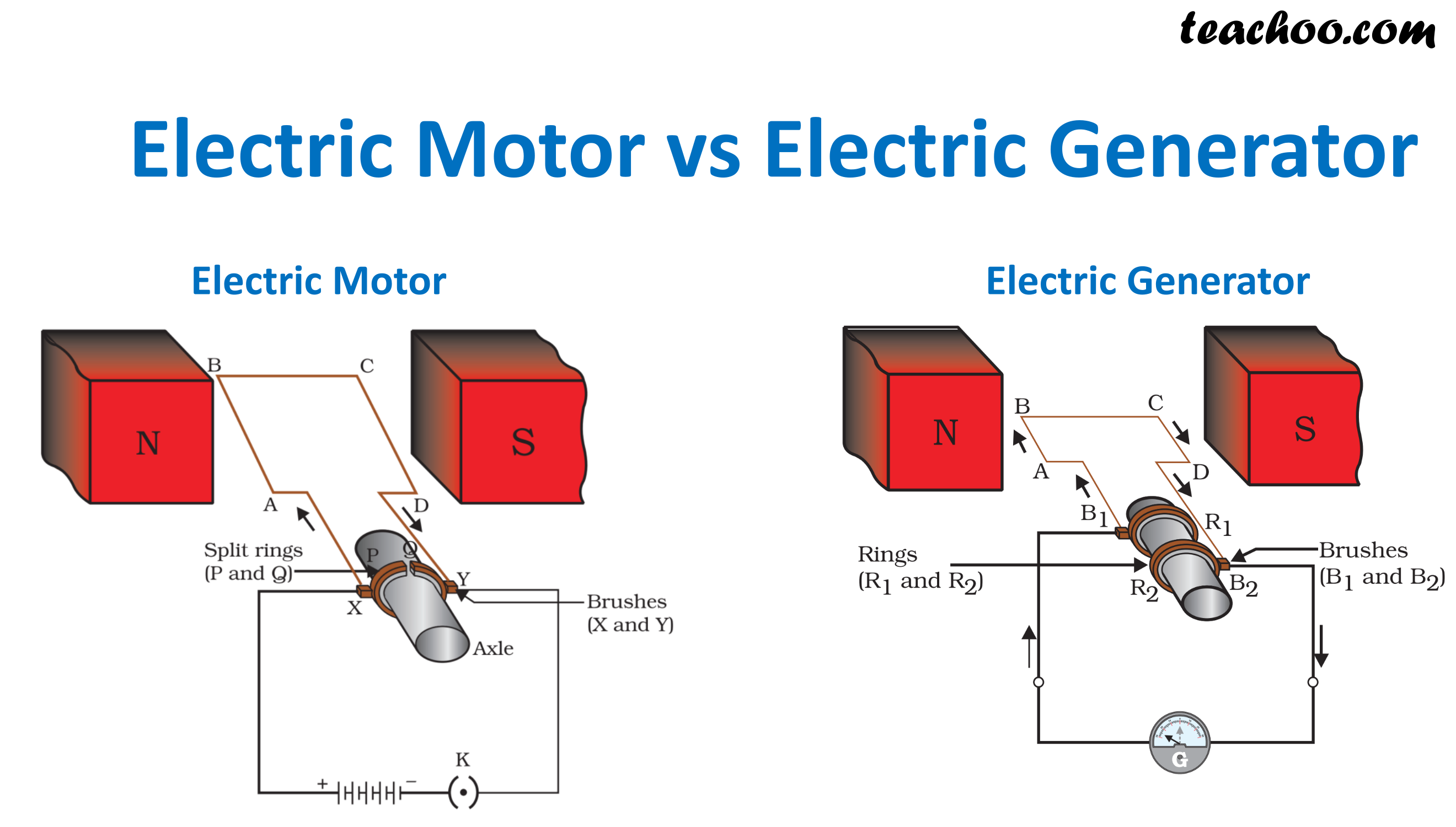
Difference between Electric Motor and Electric Generator Teachoo
Electric Generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The electricity being produced at various power stations is coming from the electric generator installed there. Cars use a type of ac generator called an alternator close alternator An electrical generator which produces alternating current,. The diagram shows four different positions of the coil in an. Electric generator diagram. Fig. 2: A diagram to show how an electric generator is used to help convert wind power into useful electric power for the national grid. The diagram above shows how an electric generator can help us generate electricity using a wind turbine. Firstly, the turbine is forced to spin by the wind. Electric generator schematic diagrams are essential for understanding the structure and functioning of electric generators. These diagrams depict the different components and connections of the generator, providing a visual representation of how electricity is generated. By understanding these diagrams, individuals can troubleshoot and repair.
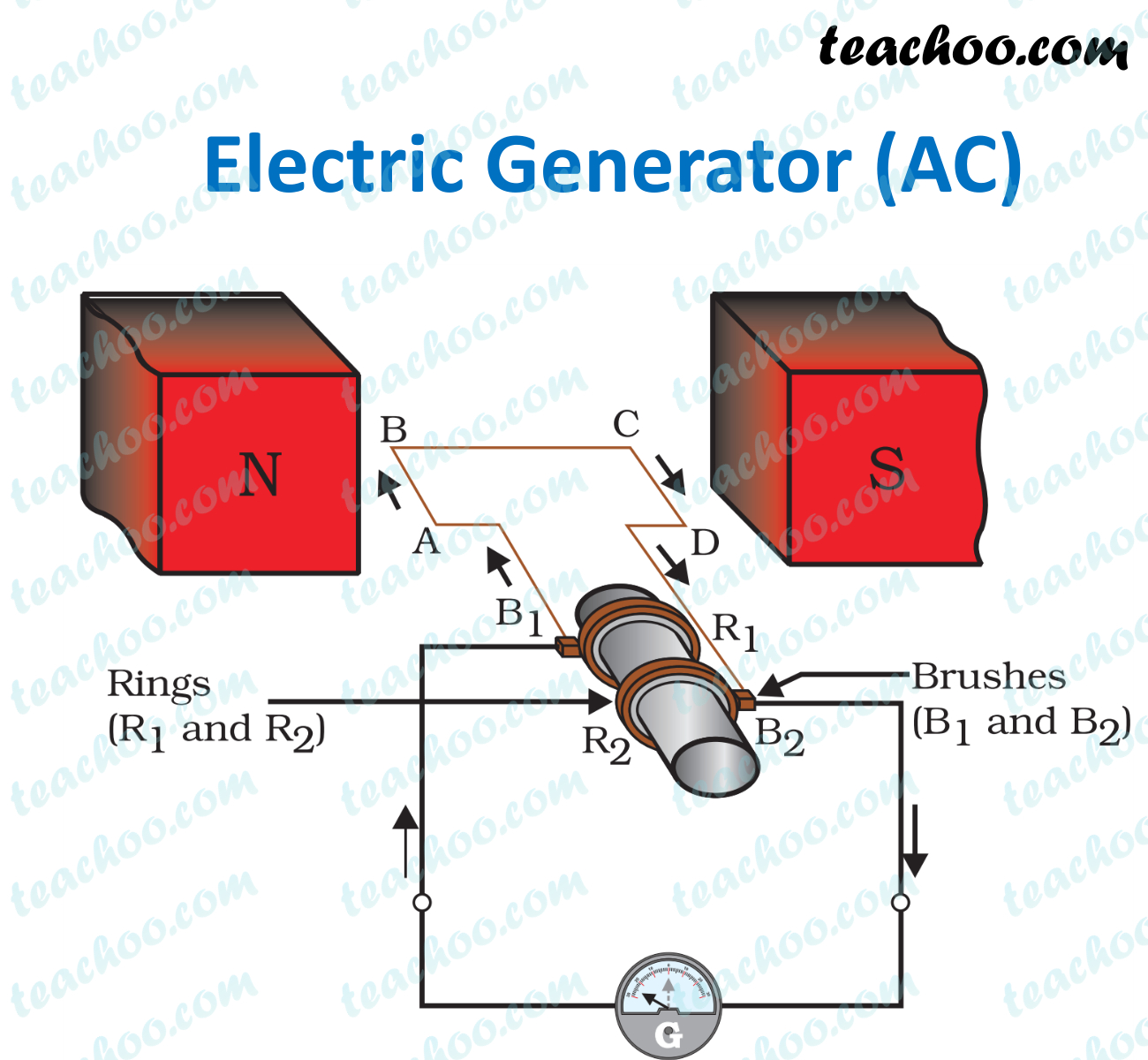
Electric Generator Class 10 Working, Principle, Diagram Teachoo
An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. NCERT Question 16 - The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that. Question 1 Page 237 - State the principle of an electric generator. Question 4 Page 237 - A rectangular coil of copper wire is rotated in a magnetic field. The electric generator or an AC electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of current or alternating emf. In other words, the electric generator converts its kinetic energy into potential difference without violating the law of conservation of energy.
An electric generator works by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. It operates based on the electromagnetic induction principle, which is the creation of an electric current by moving a wire next to a magnet. direct current. This type of generator is called D.C. generator. Similarly, instead of a half ring, if a full ring is used then, A.C. current can be generated and such a generator is called an A.C. generator.

Electric Generators Principle, Parts, Applications & More Embibe
The Electromechanical process of Electric Generator Diagram is shown schematically in Fig. 1.1. Under steady conversion conditions, TPM (prime mover) = TG (generator) and the turbine and generator run at steady speed. Other than lighting and heating, the major use of electric energy is made by converting it back to the mechanical form to run. A schematic diagram of the construction of a generator (Reference: bigrentz.com) Each part of the generator in detail 10 Parts of the Generator are: Engine Fuel System Voltage Regulator Alternator Cooling System Exhaust System Lubrication System battery Control Panel Main Assembly Frame




