This section describes the way to setup routing table as well as it explains the logic used to prioritize interfaces. The routing table is stored in the kernel which merely acts upon it. The route itself is set by the user-space tools. There is no preference as any tool created for this reason will do. It can be either a DHCP client, ip command. The current recommended way of printing the routing table in Linux is with the ip command followed by route, as demonstrated below.

FileLinux screenshot.jpg Wikipedia
Co to jest routing i tabela routingu w systemie Linux? Proces routingu oznacza transfer pakietu IP z jednego punktu do drugiego przez sieć. Gdy wysyłasz komuś wiadomość e-mail, w rzeczywistości przesyłasz serię pakietów IP lub datagramów ze swojego systemu na komputer drugiej osoby. In computer networking, a routing table, or routing information base ( RIB ), is a data table stored in a router or a network host that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics (distances) associated with those routes. The netstat command has always been a widely used method of printing routing table information in Linux. However, it is officially replaced by the ip route command. We are including it anyway as it is still an approach to retrieve the required information. Here is how you can use this command: $ netstat -rn Courses Jobs The IP/kernel routing table acts as a crucial map, determining how network packets are forwarded between different hosts and networks. By utilizing the route command, Linux administrators and users can establish static routes, enabling precise control over network connectivity and optimizing data transmission.
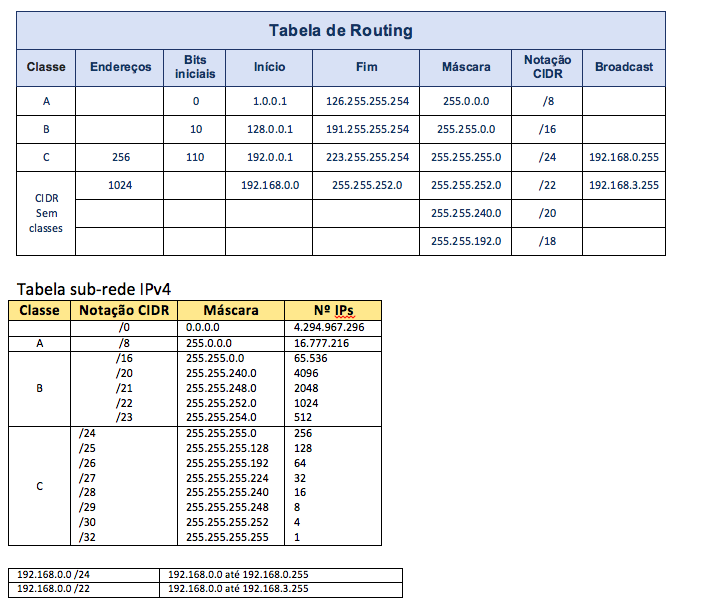
educar321 Routing sem classes
The easiest way to add a route on Linux is to use the "ip route add" command followed by the network address to be reached and the gateway to be used for this route. $ ip route add
/ via # Example $ ip route add 10.0.3.0/24 via 10.0.3.1 Provided by: route - show / manipulate the IP routing table -CFvnee modifies the routing tables. Without these options, displays the current contents of the routing tables. use the specified address family (eg `inet'; use `route --help' for a full list). operate on the kernel's FIB (Forwarding Information Base) routing table. Routing Tables. 4.8. Routing Tables. Chapter 4. IP Routing. Linux kernel 2.2 and 2.4 support multiple routing tables . Beyond the two commonly used routing tables ( routing tables), the kernel supports up to 252 additional routing tables. The multiple routing table system provides a flexible infrastructure on top of which to implement policy. First of all, in order to change a Linux system routing table, we require root privileges that can be provided with the sudo command or by elevating to the root user. In the following example, we add the "192.168.1.1" as the default route. $ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.1.1. 
Helpful Linux I/O stack diagram major.io
The following is an example of a route- interface file using the ip command arguments format. The default gateway is 192.168..1, interface enp1s0 and a leased line or WAN connection is available at 192.168..10. The two static routes are for reaching the 10.10.10./24 network and the 172.16.1.10/32 host: The default setting is to show table may either be the ID of a real table or one of the special values: - list all of the tables. - dump the routing cache. list cloned routes i.e. routes which were dynamically forked from other routes because some route attribute (f.e. MTU) was updated.
Linux Policy Routing Structure In this chapter we will now address how the Linux Policy Routing structure is implemented. We will cover how this structure interacts with the Packet Paths both native within the kernel and in conjunction with the packet filtering and network extensions. Obtaining & Compiling IPROUTE2 General command structure The ip route add Linux command is used to add a static route to the routing table of a Linux Kernel. Where options are: {NETWORK/MASK} specifies the network and subnet mask (CIDR) of the destination network. For example, 192.168.1./24 specifies the network 192.168.1. with a subnet mask of 255.255.255. or /24. This is Class C with 254 hosts. 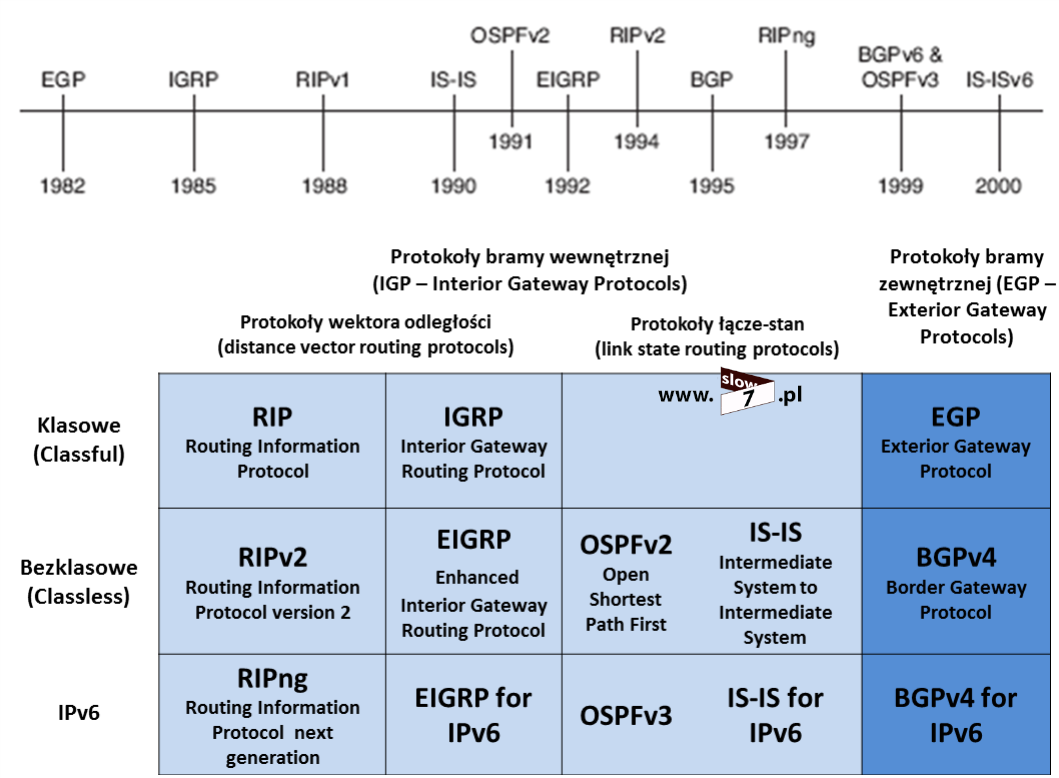
Sieci komputerowe Routing dynamiczny
This guide provides an overview of many of the tools available for IP network administration of the linux operating system, kernels in the 2.2 and 2.4 series. It covers Ethernet, ARP, IP routing, NAT, and other topics central to the management of IP networks. Configure Ubuntu 20.04 as Linux Router. Assign Static IP Addresses to the Linux Router. IP Address details on the router. Host on 172.16.1./24 Network: Host on 172.16../24 Network: Enable Kernel IP forwarding on Ubuntu Linux Router. Configure NATing and Forwarding on Linux Router. Configure Packet Forwarding. Configure NATing.




