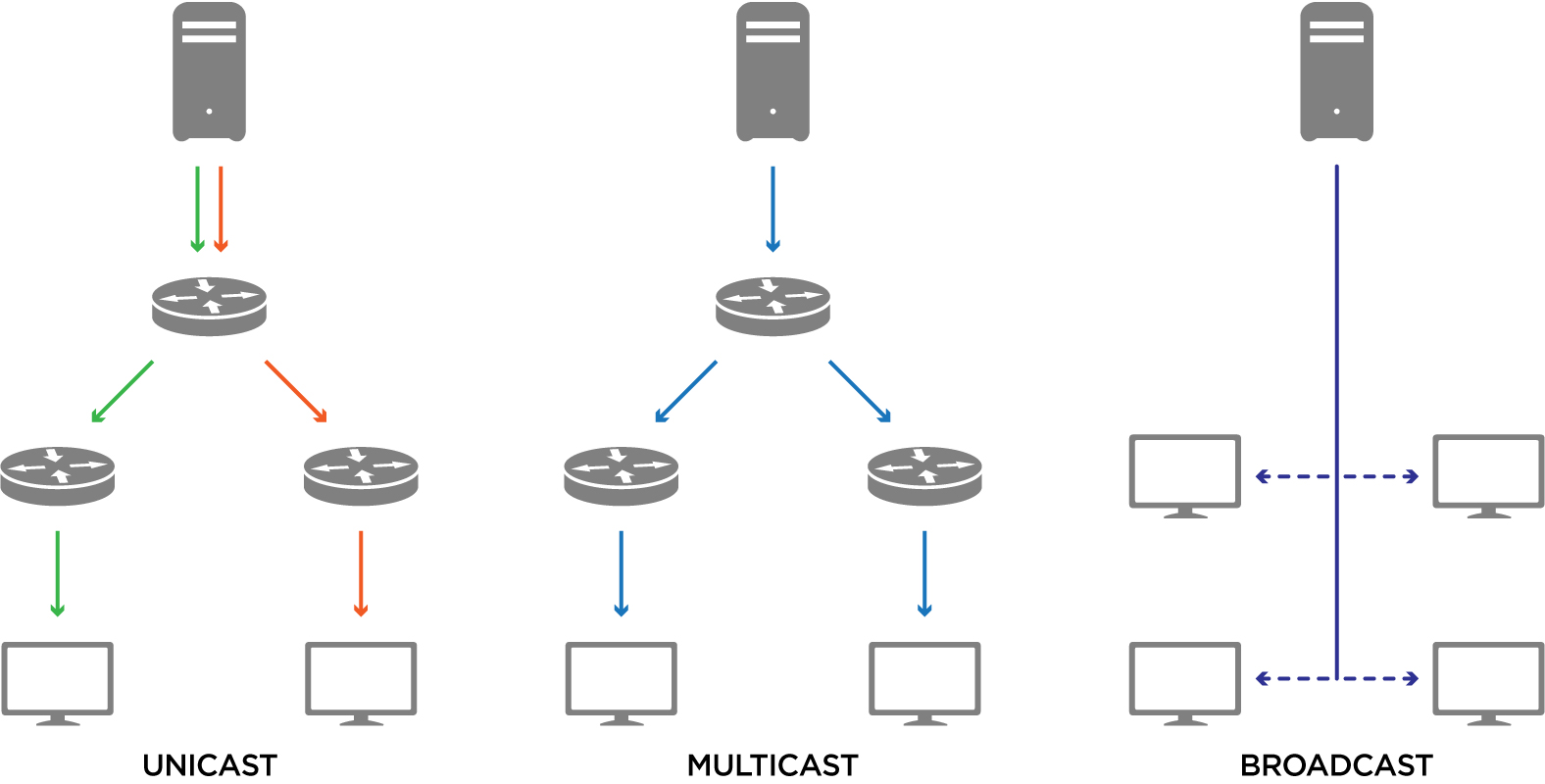
Multicast: In multicasting, one/more senders and one/more recipients participate in data transfer traffic. In this method traffic recline between the boundaries of unicast (one-to-one) and broadcast (one-to-all). Multicast lets servers direct single copies of data streams that are then simulated and routed to hosts that request it. Broadcast, unknown-unicast and multicast traffic (BUM traffic) is network traffic transmitted using one of three methods of sending data link layer network traffic to a destination of which the sender does not know the network address. This is achieved by sending the network traffic to multiple destinations on an Ethernet network. As a concept related to computer networking, it includes three.
Unicast vs Multicast vs Broadcast What's the Difference? Haivision
Unicast, multicast, and broadcast are address types. A unicast address represents a single interface. A multicast address represents a group of interfaces. A broadcast address represents all interfaces of the local network. Each frame contains two MAC addresses: a source address and a destination address. Multicast Transmission (One-to-Many) When the data is transmitted from a single source host to a specific group of hosts having the interest to receive the data, it is known as multicast transmission. Multicast can be more efficient than unicast when different groups of receivers need to see the same data. Example − Multicast is the technique. 5G multicast-broadcast for group communication: Why it matters and how it works. Through 5G NR multicast-broadcast functionality, 5G networks can now be equipped to support efficient, reliable and scalable group communication services. Below, we explore the 3GPP technologies bringing high-performance connectivity to mission critical use cases. Multicast. Multicasting addresses messages for a specific group of devices in a network. Note that, even if a group contains all the devices in a network, multicast is theoretically different from the broadcast. This difference consists that, in the multicast case, devices effectively subscribe to receive messages.

Moved Temporarily
Depending on how many devices an address represents, it can be classified in three types: unicast addresses, multicast addresses, and broadcast addresses. A unicast address represents a single device in the network. A multicast address represents a group of devices in the network. A broadcast address represents all devices in the network. This helps a network switch to distinguish between unicast and multicast addresses. One example of an Ethernet multicast address would be 01:00:0C:CC:CC:CC, which is the address used by CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol). 3. Broadcast Addresses. Broadcast addresses represent all devices on the LAN. Frames sent to a broadcast address will be. In computer networking, unicast is a one-to-one transmission from one point in the network to another point; that is, one sender and one receiver, each identified by a network address. [1] Unicast is in contrast to multicast and broadcast which are one-to-many transmissions. Internet Protocol unicast delivery methods such as Transmission. Multicast: Multicast is the middle ground between unicast and broadcast. Multicast traffic is destined to a "group" of hosts, called "multicast group". Hosts register into a multicast group in order to receive the traffic which is destined to that group. Multicast is used in Video over IP communication for example.

Diagrama De Tópicos De Diferenças De Compartilhamento De Arquivos De
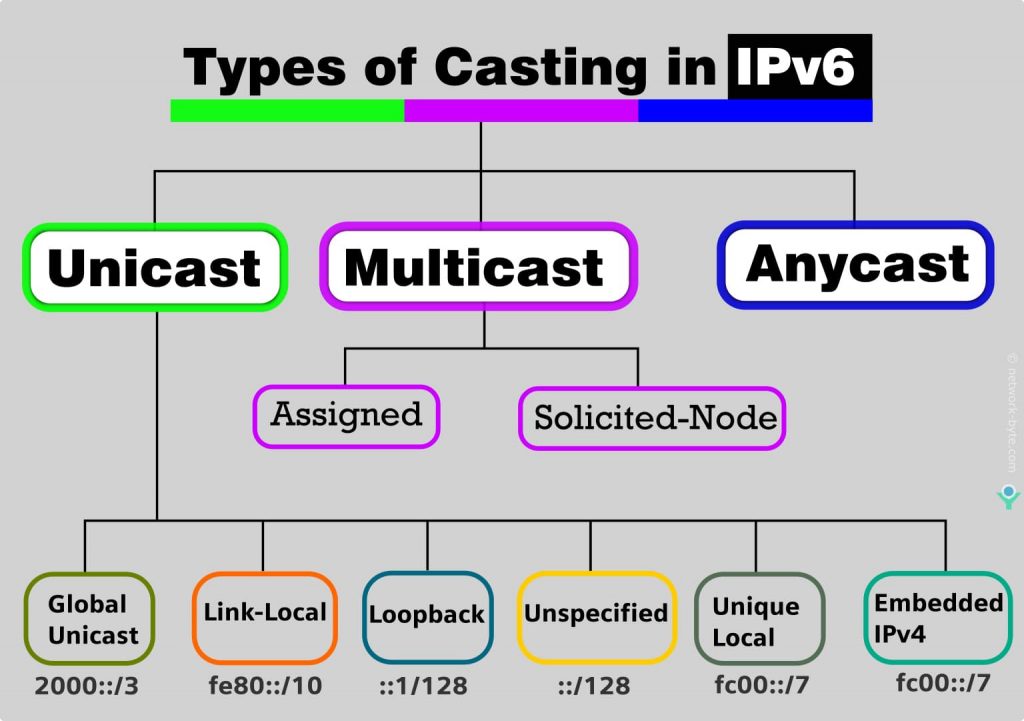
Unicast, multicast, and broadcast have various real-world applications. In video and audio distribution, multicast transmits data to multiple receivers. In online gaming, multicast transmits data to a specific group's members. In contrast, unicast is used for one-to-one communication. Broadcast is used to transmit data to all the devices on. In IPv6, we have Unicast, Multicast and Anycast. The concept of Unicast and Multicast are same in IPv4 and IPv6, except the changes in IPv6 Layer 3 addresses used for broadcast & multicast and the Layer 2 address used for multicast. Layer 2 address used for IPv6 multicast traffic starts from "33:33:" (in Ipv4, it is "01:00:5e").
Multicast uses UDP (User Datagram Protocol) for "broadcasting" a stream over a closed IP network such as a LAN (Local Area Network) or an IP Service provider's own network. Multicast streaming of live TV is commonly referred to as IPTV, whereas OTT is unicast over the internet. In a multicast IP network, the content sender only needs to. Multicast: In this method traffic recline between the boundaries of unicast (one point to one destination) and broadcast (one point to all destinations). And multicast is a "one source to many destinations" way of traffic distribution, which means that only the destinations that openly point to their requisite to accept the data from a.
UnicastBroadcastMulticastAnycast NetworkByte
Unicast only sends the data to one receiver, but broadcast sends the same data to all receivers connected in one LAN. Moreover, if you want to share some private or unique information with another person, you must use unicast network but not the broadcast. Here is a table to give you a clear comparison of unicast vs multicast vs broadcast. The IP multicast requires support from various other protocols such as Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast routing for the working. Also, Class D stays reserved for multicast groups in the case of Classful IP addressing. Difference Between Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast in Computer Network. Here is a list of the.




