Figure 5.21: a) Distillation apparatus arranged on the benchtop, b) Correct clamping of the round bottomed flask, c) Incorrect clamping. Assemble the Apparatus: To visualize the assembly of the apparatus, it may be helpful to first lay out the glassware on the benchtop before assembling the parts (Figure 5.21a). A completely sealed distillation apparatus could experience extreme and rapidly varying internal pressure, which could cause it to burst open at the joints. Therefore, some path is usually left open (for instance, at the receiving flask) to allow the internal pressure to equalize with atmospheric pressure.. Diagram of a typical industrial.
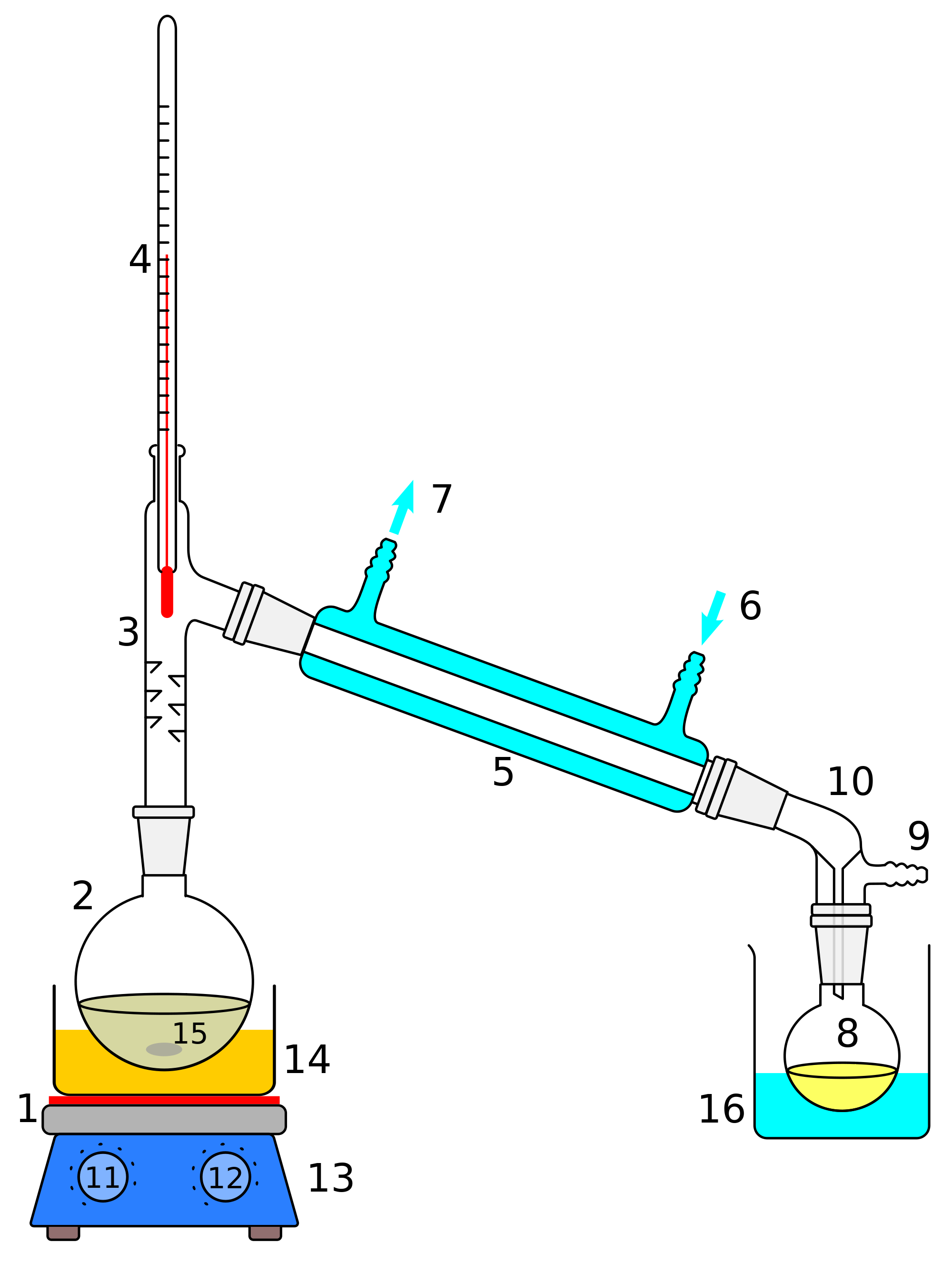
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Distillation (simple distillation, fractional
It is assumed that readers have previously performed a simple distillation, so in this section are described differences between simple and fractional distillation. Figure 5.43: Fractional distillation apparatus. Figure 5.44: a) Removal of glass wool plug on a beaded fractionating column, b) Insulating the column with foil, c+d) Condensation on. Learning Objectives. Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas: Sketch out a typical boiling point diagram for a binary liquid solution, and use this to show how a simple one-stage distillation works.; Explain the role of the lever rule in fractional distillation; Describe the purpose and function of a fractionating column; Sketch out boiling point diagrams for high. An apparatus using a steam line is shown in Figure 5.59. It is assumed that readers have previously performed a simple distillation, so in this section are described differences between simple and steam distillations. Figure 5.58: Steam distillation of orange peel using water in the distilling flask and a Bunsen burner. Vacuum Distillation Procedure. A vacuum distillation apparatus is shown in Figure 5.50, using a simple distillation setup. A fraction distillation can also be used. It is assumed that readers have previously performed a simple distillation under atmospheric pressure, so in this section are described differences between atmospheric and reduced pressure distillations.
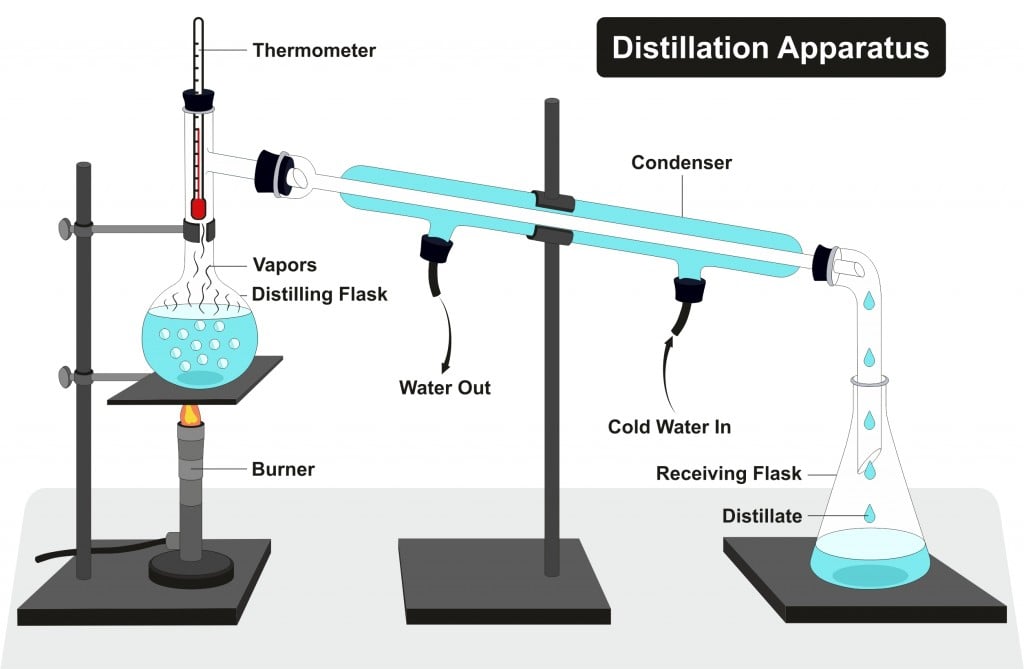
Denatured Alcohol Definition, Properties, Examples And Uses
and the distillation apparatus. Distillation relies on the fact that the vapor above a liquid mixture is richer in the. vapor/liquid diagrams for pairs of solvents. The graph below (Fig. 5) shows such a diagram for 2 solvents, A and B. A is the lower boiling material. The bottom of the graph shows the liquid state and the top of the graph Butte College. Distillation is a purification method for liquids, and can separate components of a mixture if they have significantly different boiling points. In a distillation, a liquid is boiled in the "distilling flask," then the vapors travel to another section of the apparatus where they come into contact with a cool surface. The distillation apparatus, commonly called a 'still', consists of a vessel for plant material and water, a condenser to cool and condense the vapour produced and a method of collection, or 'receiver'.Material from the appropriate part of the plant for extraction is immersed in water in the distillation vessel. This is then heated to boiling point and the steam (water vapour) carries. use apparatus to carry out reflux and adapt the apparatus for distillation, setting up the equipment using a variety of glassware, including Quickfit®, retort stands and clamps; Republic of Ireland. Junior Cycle. Science. Chemical world. Building blocks. 2.

chemistry Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
The liquid-and-gas phase has an elliptical shape with two corners at either end of the diagram. The two corners correspond to the boiling temperatures of both components.. In your distillation apparatus, you will basically collect close to pure A in your receiving flask. However, as mentioned before, simple distillation is most effective. Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize.It uses distillation to fractionate.Generally the component parts have boiling points that differ by less than 25 °C (45 °F) from each other under a pressure of one atmosphere.
distillation, process involving the conversion of a liquid into vapour that is subsequently condensed back to liquid form. It is exemplified at its simplest when steam from a kettle becomes deposited as drops of distilled water on a cold surface.Distillation is used to separate liquids from nonvolatile solids, as in the separation of alcoholic liquors from fermented materials, or in the. DISTILLATION APPARATUS Distillation is a common operation in many laboratories for the purpose of separating and/or purifying components of a liquid mixture. The apparatus used consists of three major parts: distillation flask (or 'pot') to heat the mixture and volatilize the components, a condenser to cool the vapors back to liquid state, and a collection vessel.
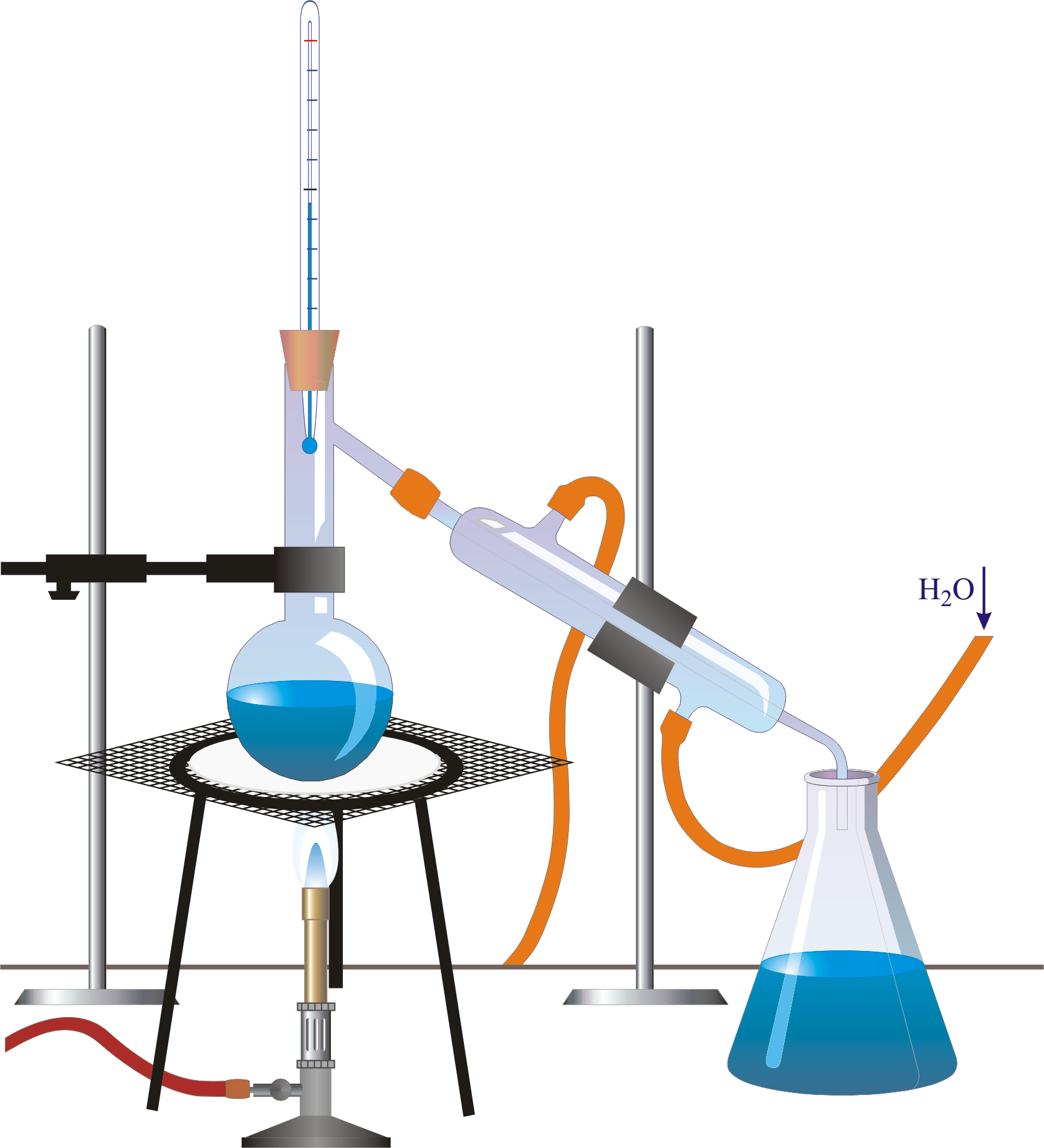
Chemistry Glossary Search results for 'distillation'
Distillation is a common practical completed in organic chemistry. Distillation is used as there are times that a reaction does not go to completion or there are other chemicals produced as well as the desired product. Distillation allows you to separate compounds by their boiling point. Chemicals with the lowest boiling point will distill first. Distillation is a separation technique is used to remove a solvent from a mixture and keep it rather than it mixing with the air and being lost. Learn more in this KS3 Chemistry guide from Bitesize.




