Unique among polymers PVC, PE, PP and PS are general purpose plastics. The features of a plastic are determined by its chemical composition and type of molecular structure (crystalline or amorphous). PVC has an amorphous structure that is directly related to the polar chlorine atoms in its molecular structure. Most crystalline polymers have amorphous regions, which means crystalline polymers are never completely crystalline.

La différence entre les polymères amorphes et semicristallins Sport and Life
The difference between the two lies in their molecular structure. Before you decide which to use, you need to understand the characteristics of each, as that will determine your injection moulding process. In this guide, we'll cover: What is an amorphous polymer? What is crystalline polymer? Examples of amorphous polymers Amorphous PVC to Semi/Crystalline PVC? Hello, Is it possible to convert the structure of PVC Polymer from Amorphous to semi/Crystalline by processing methods in Extrusion?. PVC is highly amorphous, with very low degrees of crystallinity from some syndiotactic polymer sequence as formed in typical commercial process. If the order is forced by polymerization conditions, such as extremely low reaction temperatures (−50 to −100 °C), then a crystalline PVC can be synthesized. AMORPHOUS POLYMERS - are characterized by having a disorganized pattern of polymers. The polymer chains are disoriented, random in length, and intertwined like a bowl of pasta. Amorphous comes from the Greek word for "shapeless." The random structure has definite advantages in terms of properties.

Difference between the crystalline and amorphous phases [17]. Download Scientific Diagram
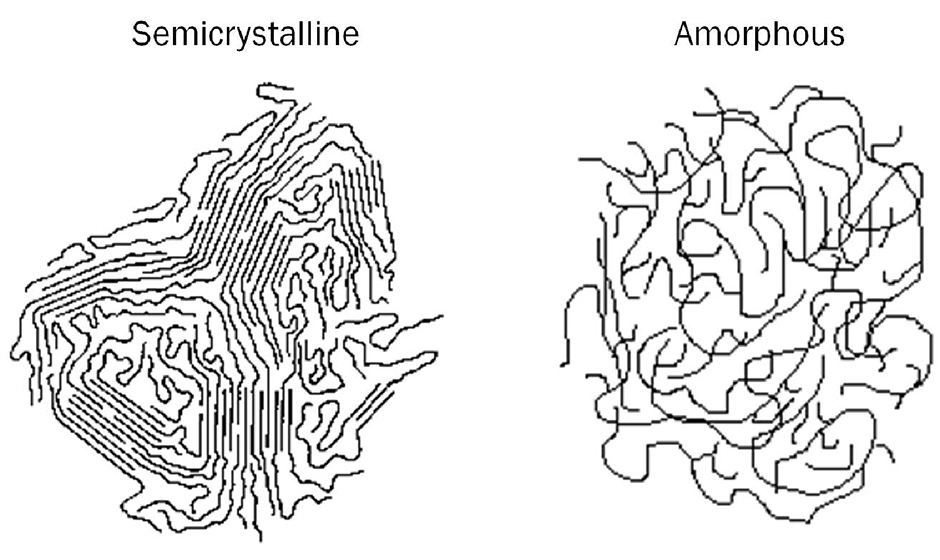
Describe at least two ways to determine experimentally whether a material is crystalline or amorphous. 6. Explain why each characteristic would or would not favor the formation of an amorphous solid. a. slow cooling of pure molten material. b. impurities in the liquid from which the solid is formed. The arrangement of molecular chains in amorphous and semicrystalline polymers. Solidification from the melt Polymers are composed of long molecular chains which form irregular, entangled coils in the melt. Some polymers retain such a disordered structure upon freezing and readily convert into amorphous solids. Polymer Crystallinity. To account for the physical differences between the different types of polymers, the nature of the aggregate macromolecular structure, or morphology, of each substance must be considered.Because polymer molecules are so large, they generally pack together in a non-uniform fashion, with ordered or crystalline-like regions, called crystallites, mixed together with. As a result, many polymers are semi-crystalline, with regions called lamellae where portions of chains have aligned parallel to each other, but also with large amorphous areas that are much more randomly oriented. As a result, a polymer sample might be 80% amorphous with only 20% of its chain lengths aligned in crystalline lamellae.
Basic Approach for the selection of Engineering Plastics
Crystalline and amorphous polymers. Polymers can exist as both crystalline and amorphous solids. In fact, most polymers are semicrystalline, which means that they contain a mixture of crystalline and amorphous regions. In this video, we'll see different examples of semicrystalline and amorphous polymers and learn how their structures can be. Polymers with an amorphous morphology have their atoms held together in a loose structure, but this structure is never orderly or predictable, which is why chemists will say that amorphous solids have no long-range order. To understand this better, think of a polymer chain as a piece of spaghetti.
Amorphous vs. Semi-Crystalline Polymers December 23, 2016 admin No Comments High temperature polymers are divided into two categories: amorphous and semi-crystalline. The difference between the two lies in their molecular structure. In this blog post, we ll discuss how amorphous and semi-crystalline thermoplastics differ from each other. Two broad types are semi-crystalline polymers and amorphous polymers, both within the thermoplastic classification. Semi-crystalline polymers tend to be more rigid, whereas amorphous polymers are more tolerant of impacts. This article will compare semi-crystalline vs. amorphous polymers and discuss the types, where they are used, and much more.

15 Schematic cooling (1) and heating (2) DSC curves, showing a range of... Download Scientific
Amorphous plastics typically have a shiny and smooth surface finish due to their non-crystalline structure. Some amorphous resins can transmit light which makes them well suited to aesthetic & optical applications. Shrinkage Amorphous plastics generally exhibit low and uniform shrinkage upon cooling. The observed heat of fusion of the mass polymer varied considerably with crystallization temperature, but was in the range 3-5% crystalline, i.e. 0.35-0.55 kJ monomer mol - 1 g: Onset Figure 3 lb Min Isothermal crystallization of PVC Isothcrmat 410 K 2b Metting ~E I I 380 480 K Figure 4 Melting endotherms of PVC 986 POLYMER, 1980, Vol 21.




