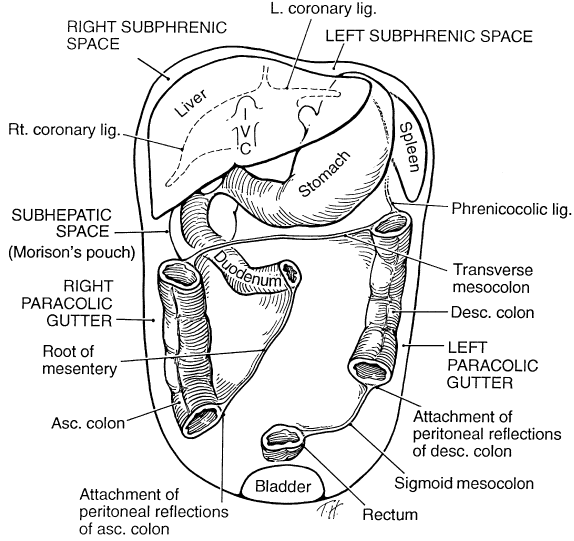
The left subphrenic space is a subcompartment of the left supramesocolic space located between the diaphragm and, the diaphragmatic surface of the spleen and gastric fundus. It is described to have anterior and posterior parts without clear delineation 1. Boundaries medially: falciform ligament The left subphrenic space is substantially larger than the right and has been described as having anterior and posterior segments. Overall, the left subphrenic space relates to the anterior parts of the cardia and fundus of the stomach, the spleen's diaphragmatic region and the anterosuperior extent of the anatomical left lobe of the liver.

Peritoneal Cavity Radiology Key
The posterior left subphrenic space (also known as the perisplenic space) is a potential space surrounding the spleen. Gross anatomy The posterior left subphrenic space is continuous with the anterior left subphrenic space, both are subcompartments of the left supramesocolic space. Boundaries Disease can spread either within the subperitoneal space or within the peritoneal cavity to distant sites in the abdomen and pelvis via these interconnecting pathways. Disease can also cross the peritoneum to spread from the subperitoneal space to the peritoneal cavity or vice versa. Keywords: Subperitoneal space, Peritoneal cavity, Anatomy The left paracolic gutter is separated from the left subphrenic space by the phrenocolic ligament. The peritoneal space is virtual, is completely occupied by the intraabdominal organs and can only be visualized by radiological means in the presence of air (organ perforation), liquid (ascites, pus, bile, gastrointestinal fluids) or tumor invasion. The anterior left subphrenic space is a subcompartment of the left supramesocolic space. Boundaries medial: falciform ligament (separates it from the anterior right subphrenic space) superior: left coronary and triangular ligaments anterior: anterior abdominal wall and anterior aspect of the left hemidiaphragm posterior: left lobe of the liver 3,4

EPOS™
Subphrenic abscesses refer to an accumulation of pus in the left or right subphrenic space. They are more common on the right side due to the increased frequency of appendicitis and ruptured duodenal ulcers (pus from the appendix can track up to the subphrenic space via the right paracolic gutter). Lesser Sac (Omental Bursa) [24-27] The left subphrenic space [Figure 4] is further arbitrarily subdivided into the immediate subphrenic space, the left subhepatic space, and the perisplenic space. The phrenicocolic ligament extends from the splenic flexure to the lateral diaphragm separating this space from the left paracolic gutter serving as a potential barrier of. Left Anterior Subphrenic Space (fig. a) Superiorly this space is bounded by the left triangular ligament and inferiorly by the general peritoneal cavity (fig. a). The falciform ligament forms the medial border and the space extends laterally as far as the spleen. The posterior extension of the left anterior subphrenic space is the left posterior subphrenic space also known as the perisplenic space (Fig. 6.12). The bare areas of the spleen that result from insertion of the gastrosplenic and splenorenal ligaments into the splenic hilum may be highlighted by fluid that surrounds the spleen within the.
c431Intraabdominal Abscess.pptx on emaze
Subphrenic abscesses represent infected collections bounded above by the diaphragm, and below by the transverse colon and mesocolon, and the omentum. [1] Described by Barlow in 1845, Von Volkman recorded the first surgical cure in 1879 through abdominal and thoracoscopic exploration. [1] The left subhepatic space, also known as the "left posterior perihepatic space" or "gastrohepatic recess," is located between the lateral segment of the liver anteriorly and the stomach posteriorly, to the left of the gastrohepatic ligament.
Introduction This review of perisplenic anatomy and pathology provides the radiologist a roadmap for navigating this intricately complex and oft-overlooked anatomical region. Knowledge of the peritoneal spaces, recesses, and ligaments is helpful in recognizing various perisplenic pathologies and routes of disease spread. Left subphrenic space ( Fig. 109-7 ) abscesses most commonly result from perforated anterior gastric or duodenal bulb ulcers or are a sequela of gastric, colonic, or splenic surgery. The negative intra-abdominal pressure beneath the diaphragm preferentially draws infected material toward the diaphragm. The phrenicocolic ligament and falciform.

Subphrenic and Subhepatic Spaces and Hepatorenal Recess YouTube
The subphrenic space is a peritoneal space between the anterior part of the liver and the diaphragm, separated into right and left by the falciform ligament, and postero-superiorly bounded by the coronary ligament. Left Subphrenic Abscesses. Abscesses in the left subphrenic space may result from perforated anterior ulcers of the stomach or duodenal bulb, but they are seen particularly as complications of gastric or colonic surgery and of splenectomy. The most consistent aspect of flow of fluid arising in the left upper quadrant is that it is.




