The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I c. 1365 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. The Middle Assyrian Empire was Assyria's first true period of ascendancy as an empire, although Assyrian kings had existed from perhaps as early as the 25th. Assyria was a dependency of Babylonia and later of the Mitanni kingdom during most of the 2nd millennium bce.It emerged as an independent state in the 14th century bce, and in the subsequent period it became a major power in Mesopotamia, Armenia, and sometimes in northern Syria.Assyrian power declined after the death of Tukulti-Ninurta I (c. 1208 bce).
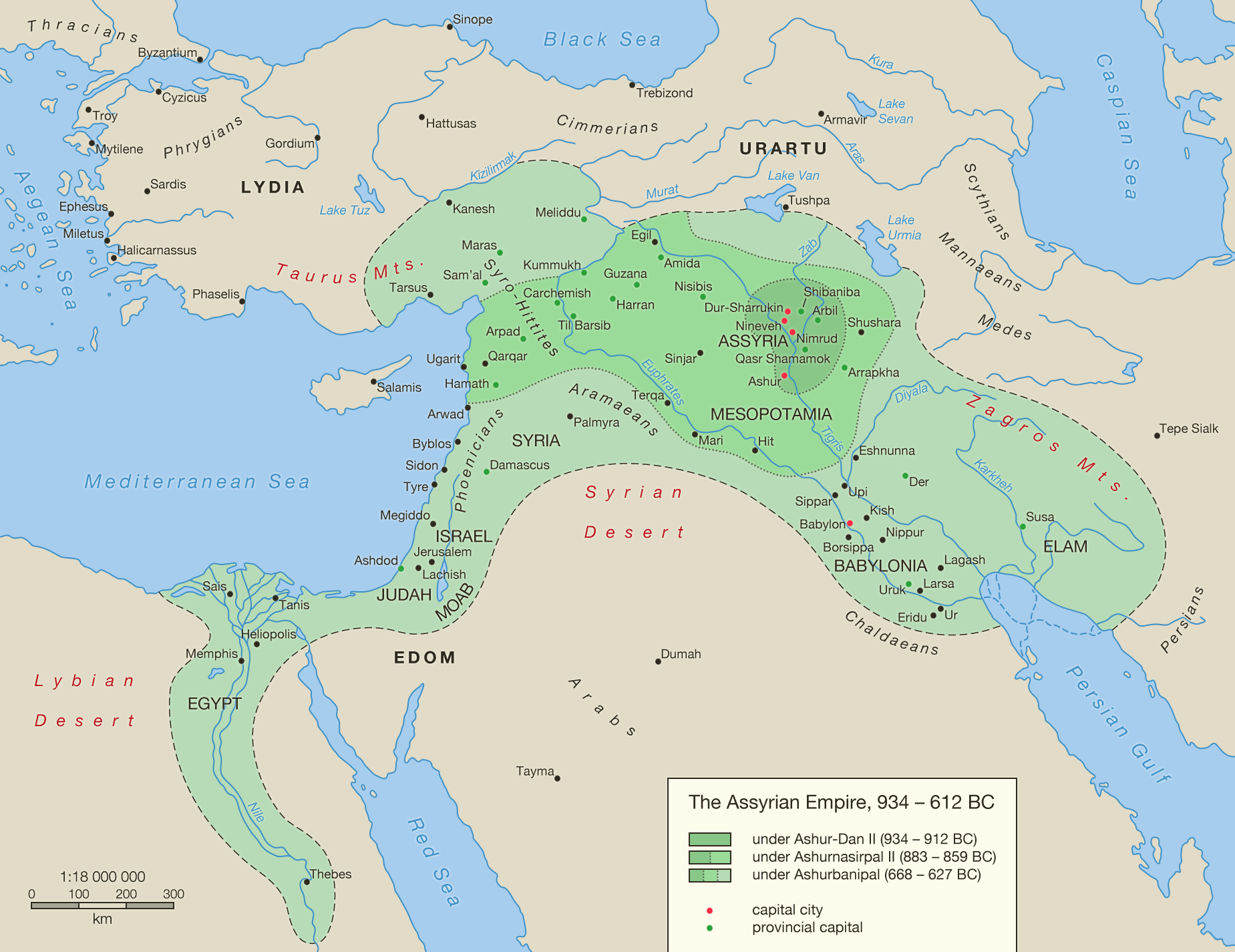
The Assyrian Empire, 934 612 BC by Undevicesimus on DeviantArt
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized:māt Aššur) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, then to a territorial state, and eventually an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC.. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian. The Assyrian Empire started off as a major regional power in Mesopotamia in the second millennium B.C.E., but later grew in size and stature in the first millennium B.C.E. under a series of powerful rulers, becoming one of the world's earliest . empires.. Assyria was located in the northern part of Mesopotamia, which corresponds to most parts of modern-day Iraq as well as parts of Iran. Assyria may have originated in the 2nd millennium bc, but it came to power gradually. Its greatest period began in the 9th century bc , when its conquests reached the Mediterranean Sea under Ashurnasirpal II (883-859), and again c. 746-609 bc , during the Neo-Assyrian empire, when it conquered much of the Middle East. Other articles where Middle Assyrian period is discussed: Ashur-uballit I:.Assyrian empire and initiated the Middle Assyrian period (14th to 12th century bc). With the help of the Hittites he destroyed the dominion of the Aryan Mitanni (a non-Semitic people from upper Iran and Syria who had subjugated Assyria), ravaged Nineveh (near present Mosul, Iraq), and sent off the image…
Who are the Assyrians? 10 Things to Know About Their History & Faith
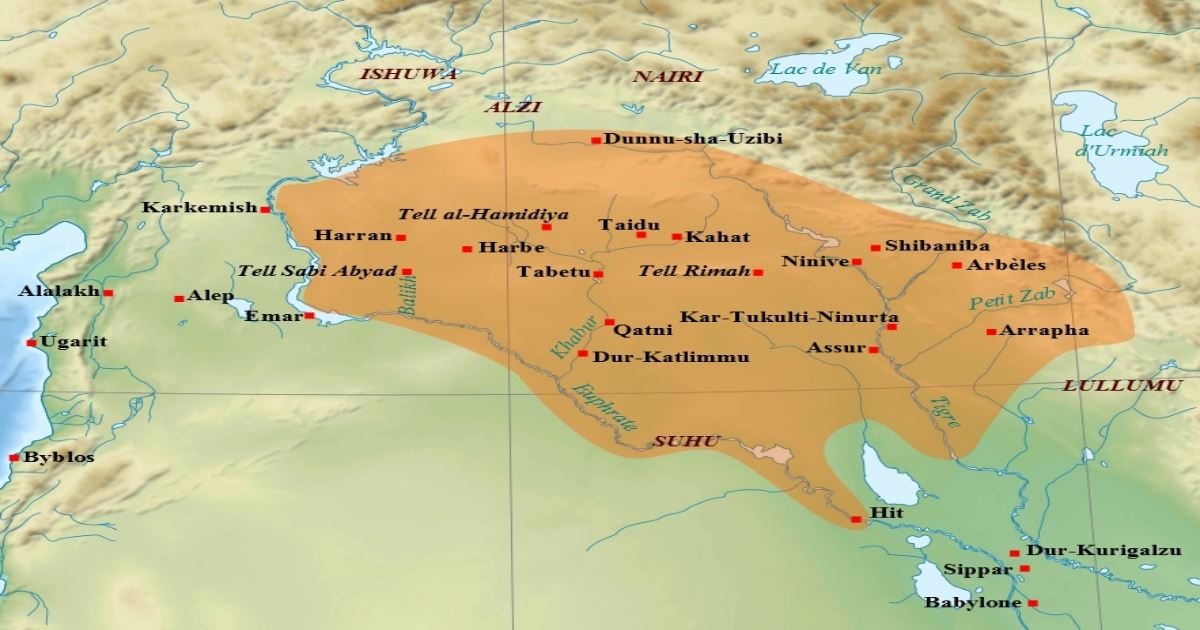
A map illustrating the political situation in the Ancient Near East around the first half of the second millennium BCE as Assyria reestablished its independence and broke Mitanni power in conjunction with the Hittites.Moreover, the Assyrians expanded their territories across Mesopotamia and established an empire reaching the Euphrates in the west and Babylonia in the south. The new conquests were consolidated by succeeding kings and, under Adad-nirari I (r. 1307-1275 B.C.), the remnants of the state of Mitanni were conquered and Assyrian control stretched to the Euphrates and the borders of the Hittite empire. Assyria reached its greatest extent during this so-called Middle Assyrian period under the warrior king. Assyria was the region located in the ancient Near East which, under the Neo-Assyrian Empire, reached from Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) through Asia Minor (modern Turkey) and down through Egypt.The empire began modestly at the city of Ashur (known as Subartu to the Sumerians), located in Mesopotamia north-east of Babylon, where merchants who traded in Anatolia became increasingly wealthy and. King Adad-Nirari I (1307 to 1275 B.C.) expanded the Assyrian empire in contrast to two proceeding kings who merely maintained control. King Adad-Nirari implemented the policy of deportation of segments of the population from one region to another, which remained a standard Assyrian policy from then on.

The Old Assyrian Period The Growth Towards An Empire About History
The Assyrians are well known for their vast ancient empire in the Middle East; ancient cities, such as Nimrud and Nineveh; and their fierce invasions, including into the Kingdom of Judah and Egypt. Middle Assyrian Period. In the 15th century BCE, Hurrians from Mitanni sacked Ashur and made Assyria a vassal. When Mitanni collapsed under pressure from the Hittites in Anatolia, Ashur again rose to power under Ashur-uballit I (1365-1330 BCE).He married his daughter to the Kassite ruler of Babylon with disastrous results: The Kassite faction in Babylon murdered the king and placed a pretender.
The archaeological and historical evidence for this early phase of the Assyrian Empire, also known as the Middle Assyrian period (ca. 1350-1050 BCE), has increased significantly over the past decades, with key evidence emerging from the Balikh Valley, the Upper Tigris region, the Lower Khabur, the Middle Euphrates, and most recently, Iraqi. In the Middle East, the Assyrian Empire was followed by others, from the Persian up to the Ottoman Empire. Although empire is a shape-shifting phenomenon, all these geopolitical entities were essentially based on a blueprint that the Assyrians were the first to create.

assyria_empire.png (3508×2481) Biblia Pinterest
Assyria experienced fluctuating fortunes in the Middle Assyrian period. Assyria had a period of empire under Shamshi-Adad I and Ishme-Dagan in the 19th and 18th centuries BCE. Following the reigns of these two kings, it found itself under Babylonian and Mitanni-Hurrian domination for short periods in the 18th and 15th centuries BCE, respectively. For 300 years, from 900 to 600 B.C., the Assyrian Empire expanded, conquered and ruled the Middle East, including Mesopotamia, Egypt, the eastern coast of the Mediterranean, and parts of today's Turkey, Iran and Iraq.




