1. VFD Operating Principles and Structure The VFD is a kind of triode vacuum tube with three electrodes which are: Cathode Filament (s) Control Grids Illumination Anodes The electrons emitted from the cathode filaments are controlled by the grids. Typically, LED displays show only numbers (digits), each one made up of seven illuminated bars (or segments). They work equally well in darkness or light, but consume relatively large amounts of power. LCDs: More versatile than LEDs and also more compact, LCDs can show numbers, letters, words, or pretty much anything else.

VFD Motor Control Panels
A vacuum fluorescent display ( VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens . A VFD operates on the principle of cathodoluminescence, roughly similar to a cathode ray tube, but operating at much lower voltages. VFD displays have been replaced by the new display technologies today. But the quality of display, a VFD gives is unbeatable. You may find one in your Car, DVDs, Radios, Casette Players,etc.. Also, there are may kinds of VFD display modules available in the market. In this video I will be showing you just how simple a Vacuum Fluorescent Display ( VFD ) is to use. These things used to confuse me but they are actually rea. VFD displays are not trending anymore for some obvious reasons, they are made of glass ("uh cool!"), have an incandescent filament ("really??"), they are basically vacuum tubes ("interesting!"), they make a light so brilliant, sometimes colored, it needs a dark plastic on top ("uh, cool again!").
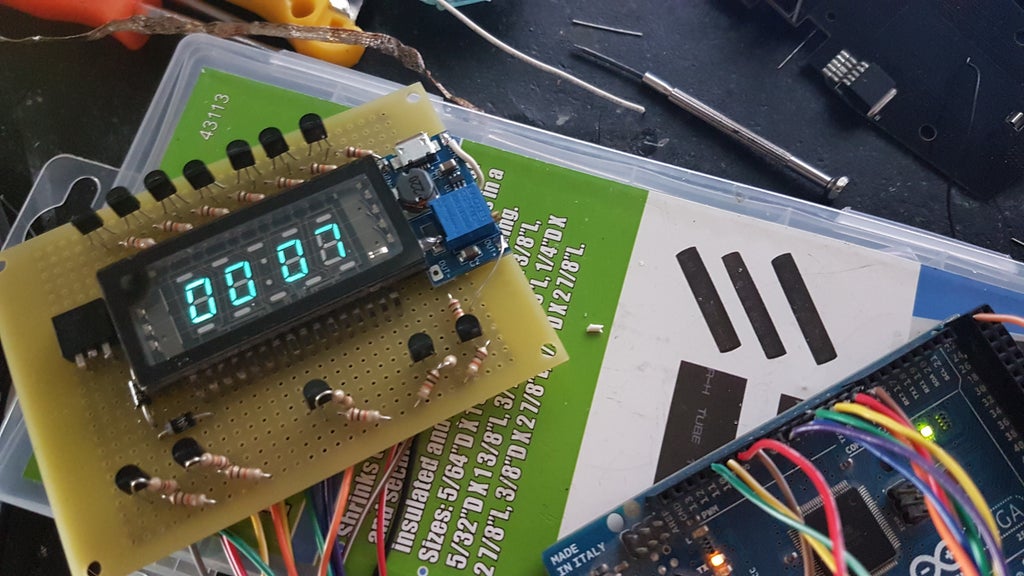
Arduino VFD Display Clock Tutorial a Guide to VFD Displays 10 Steps (with Pictures
The VFD (vacuum fluorescent display) circuit is a must-have for any electronic project or system. It's simple to use, cost-effective, and reliable. It's also one of the most versatile components in the market, making it a popular choice for many applications. On a basic level, a VFD display circuit is a device that emits light when electrical. The entire process takes place in a vacuum, hence the name Vacuum Fluorescent Display. The VFD technology operates on three key components: a filament, a grid, and phosphor anodes. The filament is heated to release electrons. The grid controls the flow of these electrons, and the phosphor anodes emit light when struck by the electrons. A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a type of display used commonly on consumer-electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens. Unlike liquid crystal displays (LCDs), a VFD emits a very bright light with clear contrast and can easily support display elements of various colors. VFD illumination varies proportional to the applied anode/grid voltage and the applied duty cycle. It ranges from 500 cd/m 2 for multiplexed displays where the grid pulse width may be only 30 μs to 4,000 cd/m 2 for multiplex drive displays with 1-μs grid pulse width. Sunlight view ability at 35,000 cd/m 2 is possible with static drive and high voltage (Iwase et al. 1995).
Vacuum Fluorescent Display Clock
A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a type of display used commonly on consumer-electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens. Unlike liquid crystal displays (LCDs), a VFD emits a very bright light with clear contrast and can easily support display elements of various colors. Using a VFD display with a very simple driver circuit.For more details, Check out - http://www.instructables.com/id/A-Simple-Driver-for-VFD-Displays
The amplitude of the signal determines the amount of voltage for the AC voltage, & the frequency of the signal will determine the frequency of the output of the VFD. In most cases the output frequency can be any value between 0-120 Hz. Some VFDs allow the upper frequency to reach 400 Hz. The output transistors are connected across the DC bus. A Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD) is a type of display that uses anodes coated in a fluorescent material. When electrons from a heated cathode collide onto the anodes, they become illuminated and visible.

VFD Display using a simple driver circuit YouTube
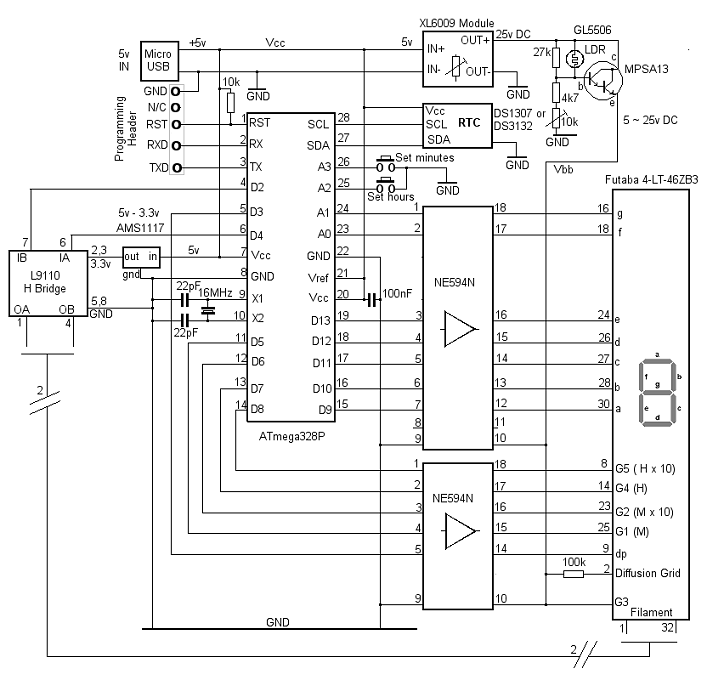
Introduction - The Arduino VFD Display Clock VFD Guide - Finding A (Suitable) VFD Display VFD Guide - Get To Know Your VFD Part I VFD Guide - Get To Know Your VFD Part II VFD Guide - Controlling Your VFD With A Microcontroller VFD Clock - The Hardware Design I: Part List VFD Clock - The Hardware Design II: Schematics & How It Works A variable frequency drive, or VFD, display circuit is an essential component for many different types of electrical and mechanical systems. A wiring diagram will help you understand the way your circuit works, as well as provide a visual representation that allows you to safely install and troubleshoot the system.




