Neural accommodation or neuronal accommodation occurs when a neuron or muscle cell is depolarised by slowly rising current ( ramp depolarisation) in vitro. [1] [2] The Hodgkin-Huxley model also shows accommodation. [3] The accommodation reflex is the visual response for focusing on near objects. It also has the name of the accommodation-convergence reflex or the near reflex. It is synkinesis which consists of the of both eyes, contraction of the ciliary muscle resulting in a change of lens shape (.
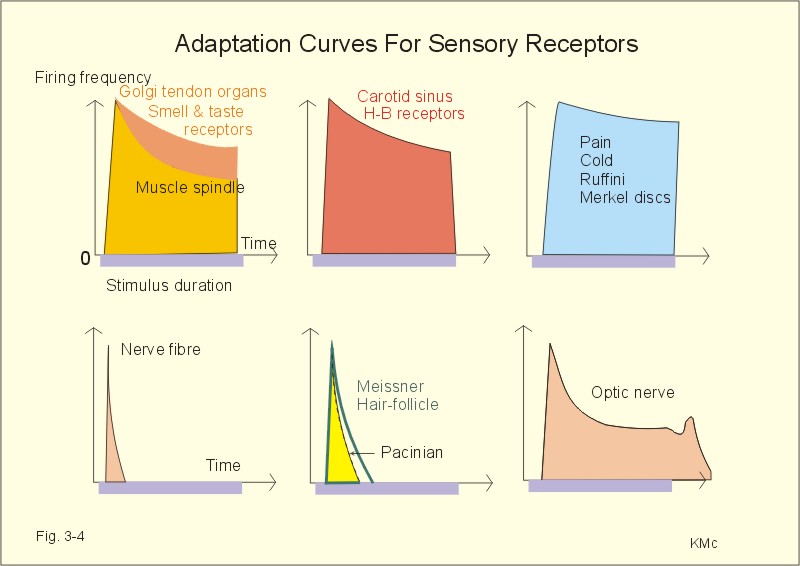
New Human Physiology Ch 3
The term "accommodation" is taken to embrace both the processes that oppose the increase in axonal excitability caused by long-lasting, subthreshold depolarizing currents and also the processes of adaptation that limit repetitive firing to a maintained subthreshold current. Accommodation of nerve Accommodation of nerve (Science: anatomy, nerve) The property of a nerve by which it adjusts to a slowly increasing strength of stimulus, so that its threshold of excitation is greater than it would be were the stimulus strength to have risen more rapidly. Last updated on July 21st, 2021 You will also like. Sensory Systems Accommodation for Near Vision The accommodation reflex (or near response) is a three-part reflex that brings near objects into focus through lens thickening, pupillary constriction, and inward rotation of the eyes—eye convergence. The accommodation reflex (or accommodation-convergence reflex) is a reflex action of the eye, in response to focusing on a near object, then looking at a distant object (and vice versa), comprising coordinated changes in vergence, lens shape ( accommodation) and pupil size.

The Vestibular System and EOMs Part 2 Anatomie und physiologie
Schacher theory of accommodation (2006) - This theory states that when the lens is in focus, there is increased tension on the lens through the equatorial zonular fibers and when there is contraction of the ciliary muscle, the zonular fibers located equatorially increase their tensile strength. Background Accommodation and breakdown of accommodation are important elements of information processing in nerve fibers, as they determine how nerve fibers react to natural slowly changing stimuli or electrical stimulation. The aim of the present study was to elucidate the biophysical mechanism of breakdown of accommodation, which at present is unknown. Results A model of a space-clamped. Abstract. The accommodative effects of alpha- and beta-adrenergic stimulation were investigated in human subjects by measuring changes in the response ACA ratio and in the response accommodative amplitude as a result of instilling hydroxyamphetamine hydrobromide and phenylephrine hydrochloride. Statistically significant increases in the ACA. Single-unit anatomical techniques have demonstrated that direct nerve connections between the midbrain near-response region and the cerebellum exist in rhesus monkeys. In the cerebellum, there are cell activities related to lens accommodation (Bando and Toda, 1991; Gamlin and Clarke, 1995; Gamlin et al., 1996; Zhang and Gamlin, 1998).
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/8324/Optic_Nerve_Draft_5__1_.png)
30 Which Part Of The Diagram Is Considered Nerve Fiber Wiring Diagram Database
305 612.816 Excitation and Accommodation in Nerve By A. V. Hill, F.R.S., Foulerton Research Professor of the Royal Society (From the Department of Physiology, University College, London) {Received November 19, 1935) I—Introduction When an electric current is passed through a living excitable tissue it 2022 Nov 15 Authors Mahsaw Motlagh , Ragi Geetha PMID: 31194346 Bookshelf ID: NBK542189 Excerpt The accommodation reflex is the visual response for focusing on near objects. It also has the name of the accommodation-convergence reflex or the near reflex.
Archive of all online content. January 1938 When a current is passed into an excitable tissue V is raised at the cathode, lowered at the anode: if V is raised enough, a state of instability is reached and "excitation" occurs. In a recent preliminary treatment of this subject (Hill, 1935, b) the name "cathode potential" was used.
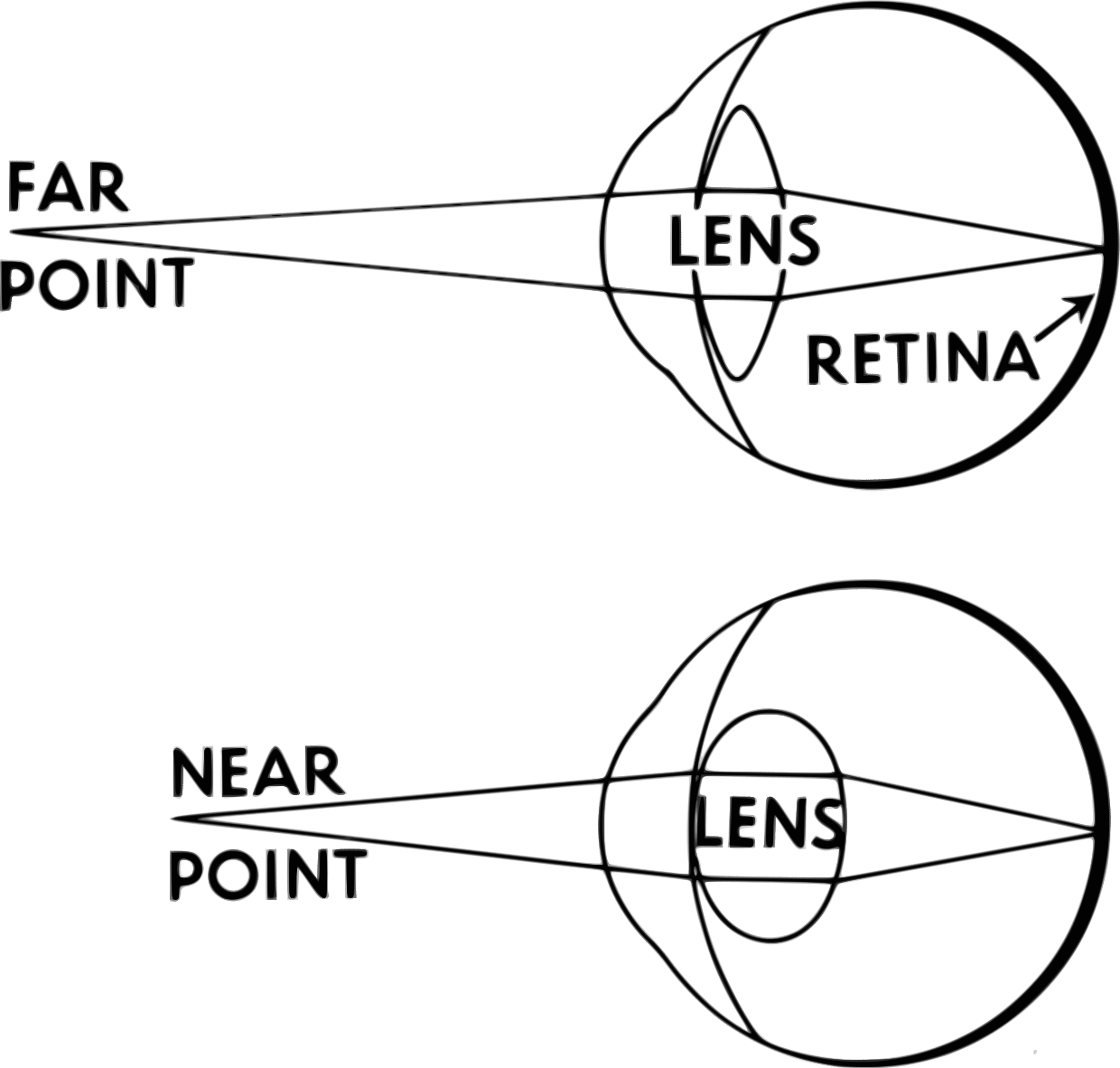
Ocular Refraction Neurology Teachmephysiology
Accommodation refers to dynamic changes in the refractive power of the lens, which is achieved by modifying the shape of the lens. The shape of the lens is controlled by two opposing forces: The internal elasticity of the lens, which tends to keep the lens rounded up. A more curved lens refracts light to a greater degree. Semantic Scholar extracted view of "THE BREAKDOWN OF ACCOMMODATIONNERVE AS MODEL SENSE-ORGAN" by C. Bernhard et al.


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/8324/Optic_Nerve_Draft_5__1_.png)

