Overview In this tutorial, we'll discuss some of the design principles and patterns that have been established over time to build highly concurrent applications. However, it's worthwhile to note that designing a concurrent application is a wide and complex topic, and hence no tutorial can claim to be exhaustive in its treatment. How to Kill a Java Thread Introduction to Thread Pools in Java (popular) Implementing a Runnable vs Extending a Thread wait and notify () Methods in Java Runnable vs. Callable in Java Difference Between Wait and Sleep in Java The Thread.join () Method in Java Using a Mutex Object in Java ThreadPoolTaskExecutor corePoolSize vs. maxPoolSize
Concurrency Design Patterns in Golang Level Up Coding
Concurrency Patterns and features found in Java, through multithreaded programming. Features: Threads and Runnables Locks Intrinsic Explicit Reentrant ReadWrite Synchronizers Latches Semaphores Barriers Synchronized Collections Concurrent Collections CopyOnWriteArrayList ConcurrentHashMap Blocking Queue Executors Fixed Thread Pool The Java platform is designed from the ground up to support concurrent programming, with basic concurrency support in the Java programming language and the Java class libraries. Since version 5.0, the Java platform has also included high-level concurrency APIs. Java Patterns for Concurrency - DZone DZone Software Design and Architecture Integration Java Patterns for Concurrency Java Patterns for Concurrency Want to learn more about. Concurrency is a conceptual property of software. Concurrent programs might or might not: Concurrent programming mainly deals with concepts and techniques that apply even if not parallel or distributed. • Threads and related constructs run on any Java platform • This tutorial doesn't dwell much on issuesspecific to parallelism and distribution.

javaconcurrencypatterns/UsingThreads.java at master · LeonardoZ/javaconcurrencypatterns · GitHub
Get started with Spring and Spring Boot, through the Learn Spring course: 1. Overview. In this tutorial, we'll discuss the incubator feature Structured Concurrency (JEP 428), which provides structured concurrency capabilities to Java 19. We'll guide you through the usage of the new APIs for managing multithreaded code. 2. In simple words, concurrency is the ability to run several programs or several parts of a program in parallel. Concurrency enables a program to achieve high performance and throughput by utilizing the untapped capabilities of the underlying operating system and machine hardware. Thread Congestion in Java Compare and Swap Non-blocking Algorithms Single-threaded Concurrency Creating and Starting Java Threads Race Conditions and Critical Sections Thread Safety and Shared Resources Thread Safety and Immutability Java Happens Before Guarantee CPU Cache Coherence in Java Concurrency Java ThreadLocal Thread Signaling Deadlock This course, Advanced Java 8 Concurrent Patterns is an in-depth presentation of advanced fundamentals you'll need to understand to write efficient concurrent applications, that support heavy concurrency and provide high throughput. You'll learn about how you can improve the quality of your concurrent code, by using sophisticated concurrent.
Java Concurrency
In this article we're going to discuss some new patterns for concurrent systems that are enabled by the new virtual threads feature from Java 21 and some related new features that "follow on" from virtual threads— specifically Structured Concurrency (JEP 453) and Scoped Values (JEP 446). The principal class of the structured concurrency API is StructuredTaskScope in the java.util.concurrent package. This class enables you coordinate a group of concurrent subtasks as a unit. With a StructuredTaskScope instance, you fork each subtask, which runs them in their own individual thread. After, you join them as a unit.
This post talks about some of the patterns we can use to solve concurrency issues relating to state shared across multiple threads. The goal is to provide some smarter alternatives to slapping synchronized on every method call, or around every block of code. The problem with synchronized is that is requires everyone to participate. If […] Chapter 1. Concurrent Object-Oriented Programming This book discusses some ways of thinking about, designing, and implementing concurrent programs in the Java™ programming language. Most presentations in this book assume that you are an experienced developer familiar with object-oriented (OO) programming, but have little exposure to concurrency.

Concurrency Patterns — С++ Russia 2023. Конференция для C++ разработчиков
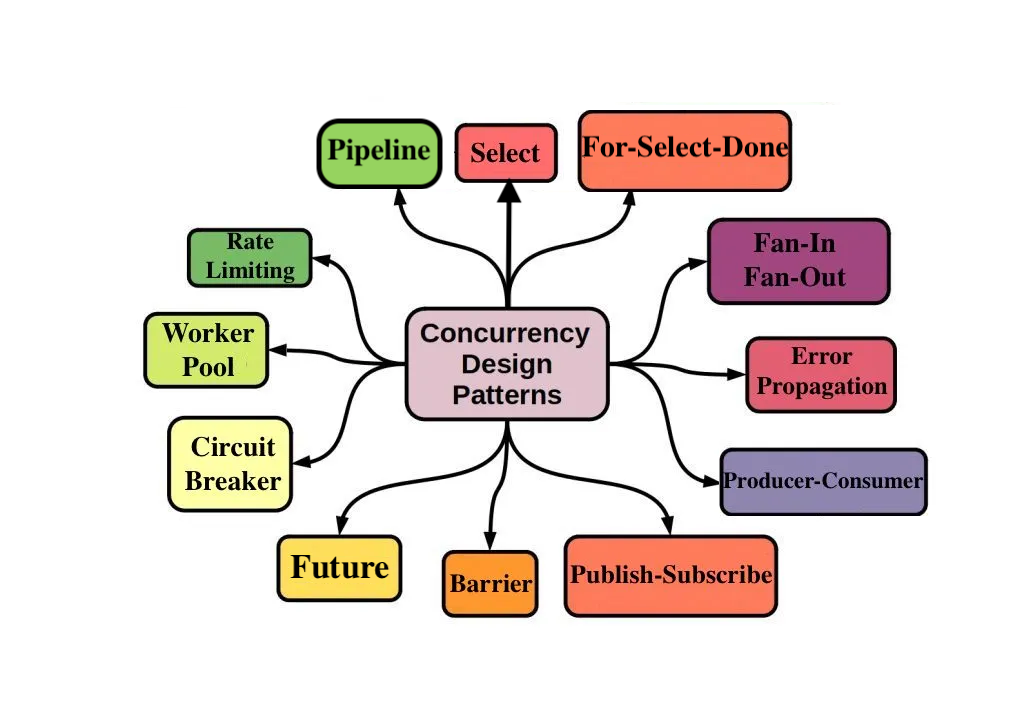
Java concurrency is a powerful feature that allows developers to write high-performance applications that can take full advantage of modern hardware. However, concurrent programming can be challenging, as it requires careful coordination of multiple threads of execution. In software engineering, concurrency patterns are those types of design patterns that deal with the multi-threaded programming paradigm. Examples of this class of patterns include: Active Object [1] [2] Balking pattern Barrier Double-checked locking Guarded suspension Leaders/followers pattern Monitor Object Nuclear reaction Reactor pattern



