ThoughtCo. By Kenneth Beare Updated on June 26, 2019 Phoneticists (who study the sound of the human voice) divide consonants into two types: voiced and voiceless. Voiced consonants require the use of the vocal cords to produce their signature sounds; voiceless consonants do not. Which Sounds Are Voiced? Which Sounds Are Unvoiced? Voiced consonants need the vocal chord vibrations to produce the sound. The voiced consonants are as follows: /b/, /d/, /g/, /j/, /l/, /m/, /n/, /r/, /v/, /w/, /y/, /z/
Pronunciation Voiced and Unvoiced Consonants YouTube
What is the difference between voiced consonants and unvoiced consonants? For voiced consonants, the vocal cords are engaged, making sound. For unvoiced consonants, the vocal cords are not making sound, there is just air passing through them. YouTube blocked? Click here to see the video. Video Text: Voiced and unvoiced consonants. The only difference is that P is an unvoiced sound (no vibration of the vocal cords) while B is a voiced sound (vocal cords vibrate). Put your hand on your throat as you say the pairs below to feel the difference. Note that the first pair of consonants in the table ( p, b) is produced at the front of the mouth. In the video about how humans produce speech, we felt the difference between voiced and voiceless sounds: for voiced consonants like [z] and [v], the vocal folds vibrate. For voiceless sounds like [s] and [f], the vocal folds are held apart to let air pass through. Schwa Connected speech Voicing Voiced & voiceless sounds Some consonant sounds are voiced and some are voiceless. A voiceless sound is one that just uses air to make the sound and not.

Phone clusters for vowels, voiced consonants, and unvoiced consonants
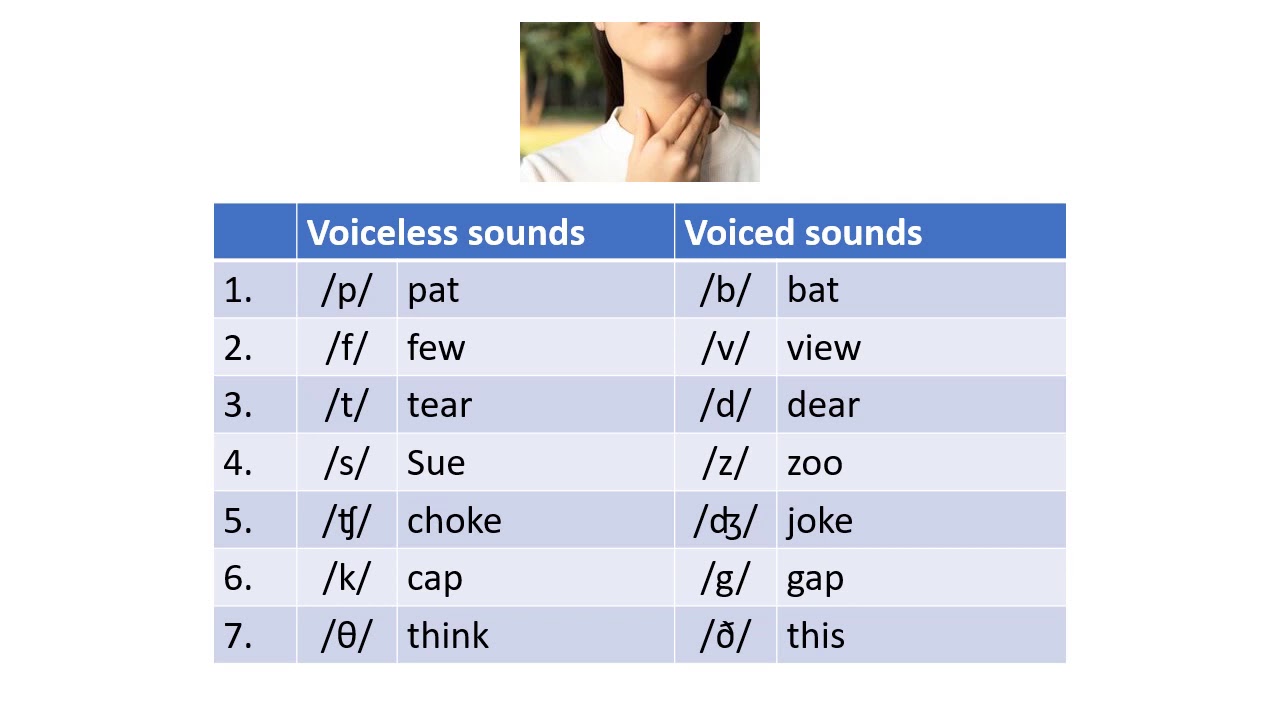
The only difference is the presence or absence of voice: /p/ is unvoiced (no vibration of vocal cords) and /b/ is voiced (vocal cords vibrate). Being aware of such differences is invaluable when teaching the pronunciation of -ed in the simple past tense and past participle of regular verbs. Here are some more voiced and unvoiced pairs. All the sounds in the first column are voiced while the matching pairs in the second column are unvoiced. The last pair is an interesting one though. Most people make both sounds, /w/ and /hw/, voiced. Instead of /window/ and /hwale/, we typically make both of the initial sounds voiced: /window/ and. Tell them that this is the main difference between the two sounds, because /z/ is voiced while /s/ is unvoiced. You could then give them a list of words and ask them to categorise the underlined consonant sound into these two categories. With /s/ and /z/, you might choose to include some third person singular verb and plural endings. There is one other consonant whose sound final
can mark. Say these two sentences carefully, paying special attention to the last sound you hear in each underlined word: I could not get my breath. I could not breathe. You should hear a difference between the final consonant sounds in the two words. The difference is called voicing. 
ESL VOICED V AND UNVOICED F CONSONANT SOUND PAIR for ESL EASY NATIVE
By Sabine Hobbel What are Consonants? English has 24 consonant sounds, and 21 consonants. When it comes to the pronunciation of these consonants, we divide them into 2 categories: voiced and voiceless consonants. Keep in mind, some consonant sounds are a combination of letters (e.g. ch or th). An Un-Voiced Consonant — Is any Consonant that is pronounced WITHOUT The Tone Of Your Voice. Meaning: You only make the sound with the use of the air and however you move your mouth. Well, Not Quite Like That…. But Close. ou can think of the sound of The Tone Of Your Voice as being a "Soft" sound. All Vowels are "Soft" sounds.
In American English, we have voiced and unvoiced sounds. All vowels are voiced. All diphthongs are voiced. Consonants can be either voiced or unvoiced. Unvoiced consonants are made just with air, no, uhh, sound from the vocal cords. For example, hh, sh, tt, pp. Voiced consonants do have voice in them, uhh, like: mm, bb, zh. @SHiNKiROU: this may be because the main acoustic difference between the voiced and voiceless stops are in a very concentrated part of the acoustic spectrum, and if one of your playback devices has difficulty transmitting that portion, you may lose the distinction. - Steven Sep 14, 2011 at 1:24 See voice onset time. - Paul Dexter 
Voiced S vs Unvoiced S 🤔 What's the difference? Learn with examples
v t e Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds (usually consonants ). Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless (otherwise known as unvoiced) or voiced. It's important to teach English language-learners the difference between "voiced" and "voiceless" consonant sounds and how they are formed. It's especially helpful to teach these sounds in pairs to contrast their pronunciation and identify their distinctive means of production.




