Timur Yuldashev IT Writer, PhD in Philological Sciences Andrey Solovev Chief Technology Officer, PhD in Physics and Mathematics DC-DC converters can be found in almost any modern electronics. The applications of DC-DC converters range from smartphones and laptops to industrial and military systems. There are two types of DC/DC converters: linear and switched. A linear DC/DC converter uses a resistive voltage drop to create and regulate a given output voltage, a switched-mode DC/DC converts by storing the input energy periodically and then releasing that energy to the output at a different voltage.
Vulgaridad cerrar famélico buck boost converter topology piano espejo Espesar
v t e A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a type of electric power converter. Power levels range from very low (small batteries) to very high (high-voltage power transmission). History Boost converters increase the voltage of a power source. For example a boost converter could take a 5V power source and boost it up to 25V. Typically, you find DC-DC boost converters in battery chargers or solar panels. They can also be used to supply components with different operating voltages from the same battery. There are many different types of DC-DC converter, each of which tends to be more suitable for some types of application than for others. For convenience they can be classified into various groups, however. This piece of literature discusses various types of converters, such as cascaded and bidirectional converters. Also included is a discussion about the technological advancement of different types of converters and shows how the converters are different from each other schematically.

SMD isolated DC/DC converters
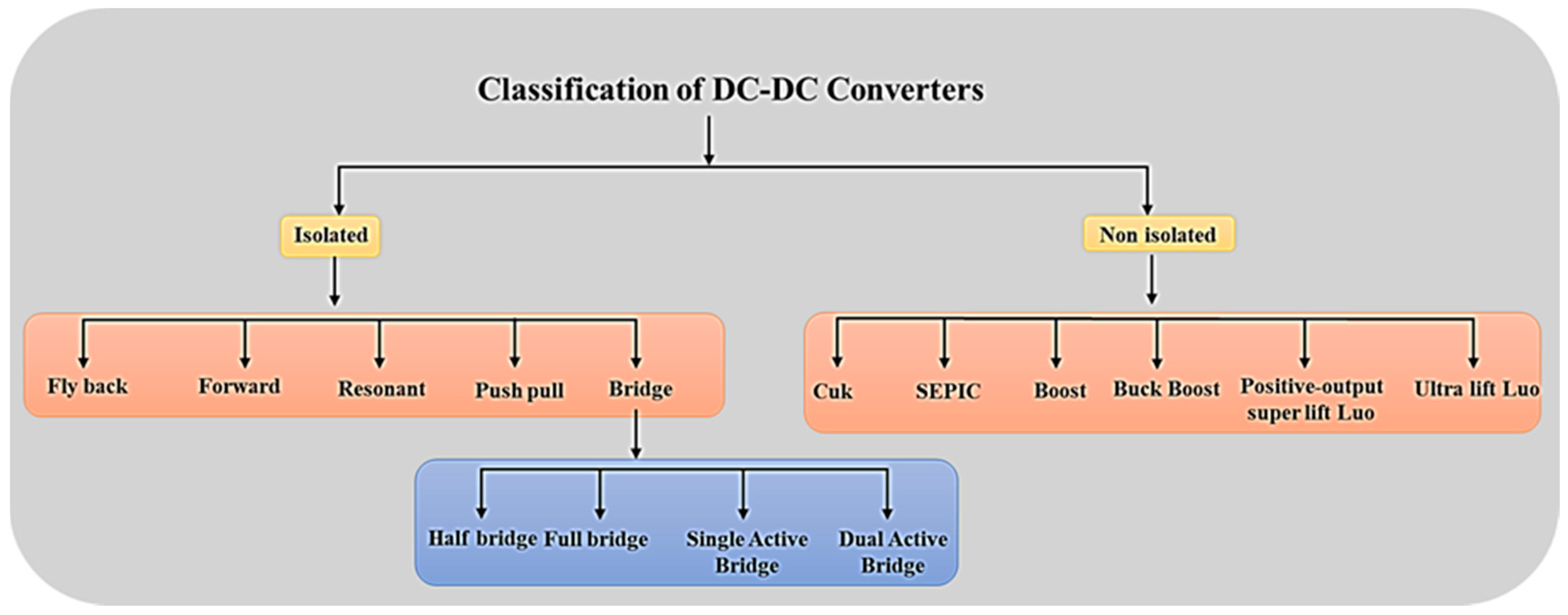
Types of DC-DC Converters. There are several types of DC-DC converters, each with unique circuit topologies and characteristics. These topologies can be broadly categorized into two groups: non-isolated and isolated converters. Non-isolated converters share a common ground between input and output, while isolated converters provide galvanic. They can be categorized as resonant-switch converters, load-resonant converters, resonant-dc-link converters, and high-frequency-link integral-half-cycle converters. Most of the attention is focused only on the resonant-switch conversion method. DC-DC Converter Topologies A comprehensive look at DC-DC converters and advanced power converter topologies for all skills levels As it can be rare for source voltage to meet the requirements of a Direct Current (DC) load, DC-DC converters are essential to access service. DC-DC power converters employ power semiconductor devices (like MOSFETs and IGBTs) as switches and passive elements such as. A comparative study between the different topologies has been conducted with respect to converter efficiency and design and control complexity. Several modulation strategies to control the DC-DC converters, such as pulse frequency modulation (PFM), pulse-width modulation (PWM), and phase-shift modulation (PSM), have been studied.

(a) Types of DCDC power converters used in some applications. Download Scientific Diagram
An AC voltage from the generator can change their strength when they travel through a transformer. 24V DC to 9V DC Converter An AC power supply is an Alternating Current, in which the voltage changes instantly with time. In AC supply the charge carriers change their direction periodically. AC supply is used as utility current for household needs. In terms of bidirectional DC-DC converters, they can be considered the major research field in the PEC topologies instead of conventional unidirectional converters to interface different energy.
Control techniques have a significant role in optimizing the overall operation of the DC-DC converters [55]. Different control techniques are selected as per the requirement of the response time and efficiency [10], [56].. SSM of a physical system is built by using two types of equations which are called the state equation. Without using the Boost Converter: In semiconductor switching devices, the Linear regulated circuits (DC power regulated circuits) access voltage from the unregulated input supply (AC power supply) and due to this there is a power loss. The power loss is proportional to the voltage drop.
DCDC Converters Zahn Electronics
Now, let's delve into the two main types of DC-DC converters: Buck converters and Boost converters. Type 1: Buck Converters. While Buck and Boost converters serve different purposes, it's essential to understand their key differences for selecting the right converter for a specific application. Let's compare them based on a few important. A DC-to-DC converter is a device that accepts a DC input voltage and produces a DC output voltage. Typically the output produced is at a different voltage level than the input. In addition, DC -to-DC converters are used to provide noise isolation, power bus regulation, etc. This is a summary of some of




