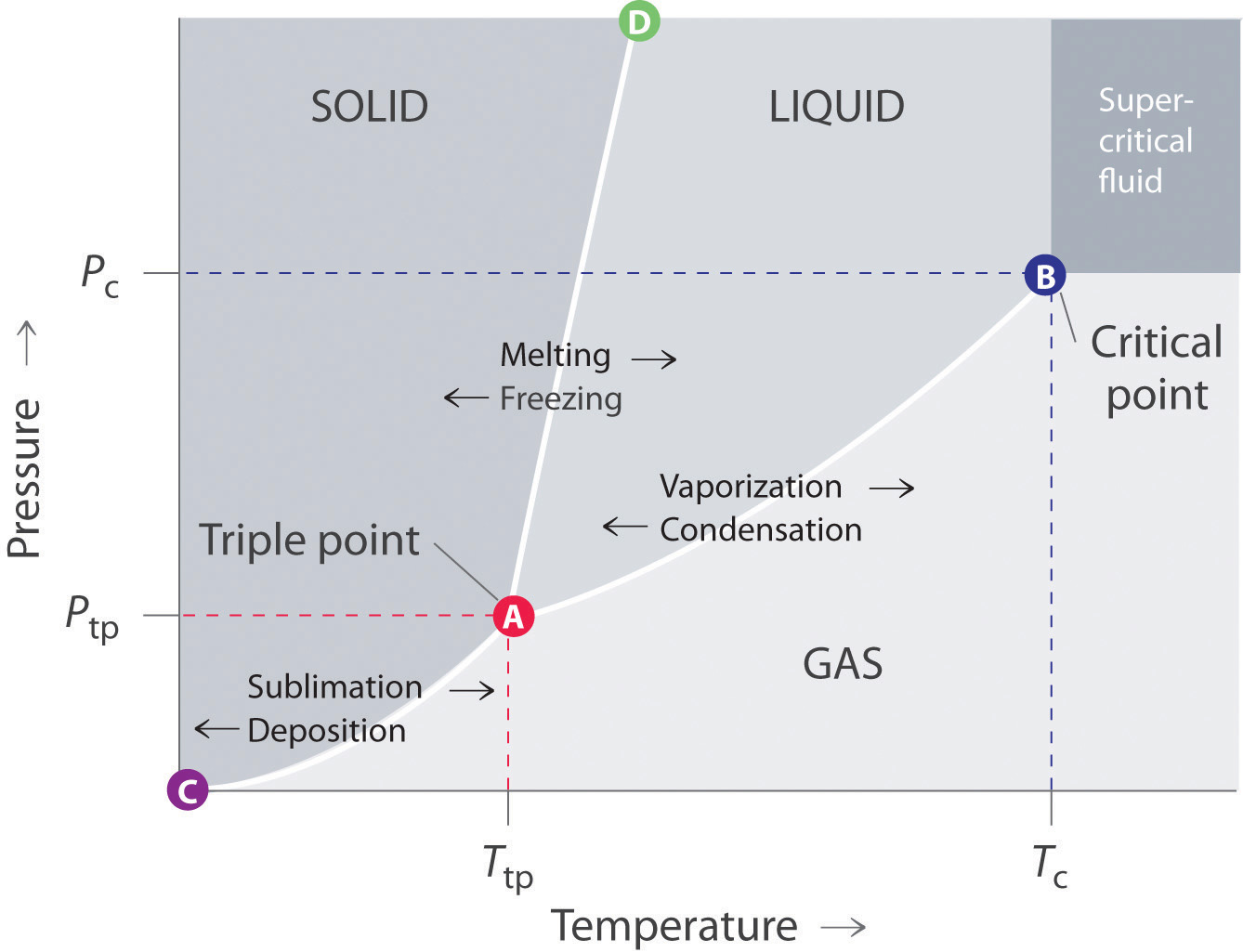
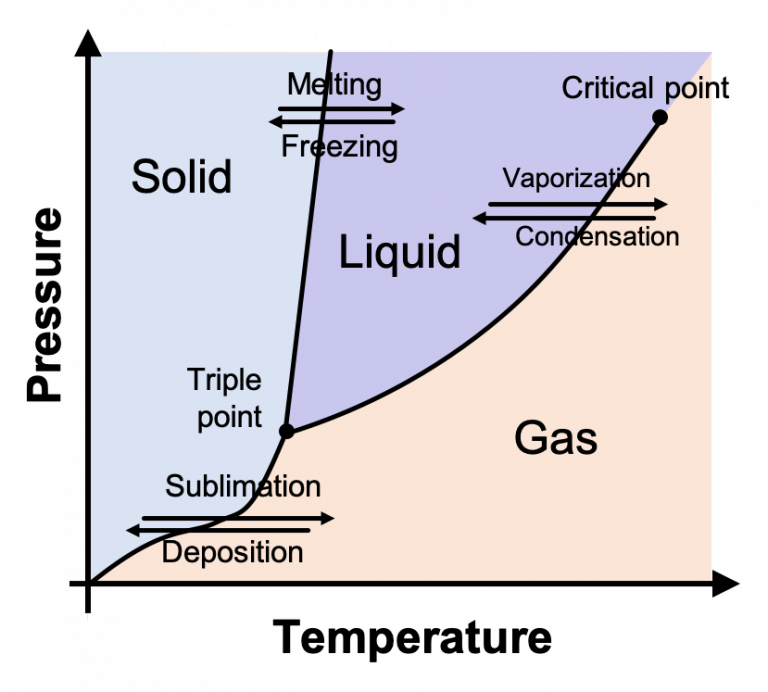
Lesson 1: States of matter States of matter States of matter follow-up Specific heat and latent heat of fusion and vaporization Specific heat, heat of fusion and vaporization example Chilling water problem Change of state example Vapor pressure Phase diagrams Representing solids, liquids, and gases using particulate models Phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. A typical phase diagram has pressure on the y-axis and temperature on the x-axis. As we cross the lines or curves on the phase diagram, a phase change occurs. In addition, two states of the substance coexist.
How do you draw a phase diagram with a differential equation? Socratic
A binary phase diagram shows the phases formed in differing mixtures of two elements over a range of temperatures. Compositions run from 100% Element A on the left of the diagram, through all possible mixtures, to 100% Element B on the right. The composition of an alloy is given in the form A - x%B. phase diagrams is a type of graph used to show the equilibrium conditions between the thermodynamically-distinct phases; or to show what phases are present in the material system at various T, p, and compositions "equilibrium" is important: phase diagrams are determined by using slow cooling conditions ⇒ no information about kinetics A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in [link]. The physical state of a substance and its phase-transition temperatures are represented graphically in a phase diagram. To illustrate the utility of these plots, consider the phase diagram for water shown in [link]. [1] is the temperature below which the substance is stable in the solid state. The is the temperature above which the substance is stable in a liquid state. There may be a gap between the solidus and liquidus; within the gap, the substance consists of a mixture of crystals and liquid (like a " [2]
Features of Phase Diagrams (M11Q1) UWMadison Chemistry 103/104 Resource Book
Example 12.4. 1: Water. Referring to the phase diagram of water in Figure 12.4. 2: predict the physical form of a sample of water at 400°C and 150 atm. describe the changes that occur as the sample in part (a) is slowly allowed to cool to −50°C at a constant pressure of 150 atm. Phase Diagrams. The figure below shows an example of a phase diagram, which summarizes the effect of temperature and pressure on a substance in a closed container. Every point in this diagram represents a possible combination of temperature and pressure for the system. The diagram is divided into three areas, which represent the solid, liquid. A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapour (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance. Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/states-of-matter-a.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phase_diagram_generic-56a12a1b5f9b58b7d0bca817.png)
Phase Diagrams Phases of Matter and Phase Transitions
4.4 Multi-Component Phase Diagrams. So far we have only dealt with phase diagrams of pure components but typically you will deal with either binary, ternary, quaternary, etc. phase diagrams.. Let's take a look at a relatively simple phase diagram, a Binary Lens phase diagram which holds for ideal solution scenarios. (Side Note: When I say something is simple please do not interpret this as. 0:00 / 21:49 How to Draw Phase Diagrams and What they Mean! | Doc Physics Doc Schuster 148K subscribers Subscribe 76K views 10 years ago AP Ch 17 - Ideal Gases and Phase Ch-Ch-Ch-Changes.
ODE | Phase diagrams commutant 37.5K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 2.3K Share 223K views 11 years ago Ordinary Differential Equations Examples and explanations for a course in ordinary. A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapor (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance. These diagrams (including this one) are nearly.

phase Thermodynamics of SolidLiquid Chemistry Stack Exchange
to draw topological phase diagrams, calculate topological invariants, or explore topological band structures. On the other hand, an unsupervised learning strategy consists of extracting. draw a phase diagram Natural Language Math Input Extended Keyboard Examples Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phase_diagram_generic-56a12a1b5f9b58b7d0bca817.png)

