Clarity refers to the surface irregularities (blemishes) and internal (inclusions) features of a polished diamond. Collectively, these blemishes and inclusions are termed as the diamond's clarity characteristics. This short video explains the GIA clarity scale and how GIA classifies diamonds with a clarity grade ranging from Flawless to I 3 by using a 10X magnification loupe and a microscope to see and plot the diamond's inclusions. Many inclusions and blemishes are too tiny to be seen by anyone other than a trained diamond grader.

Gia Inclusion Characteristics
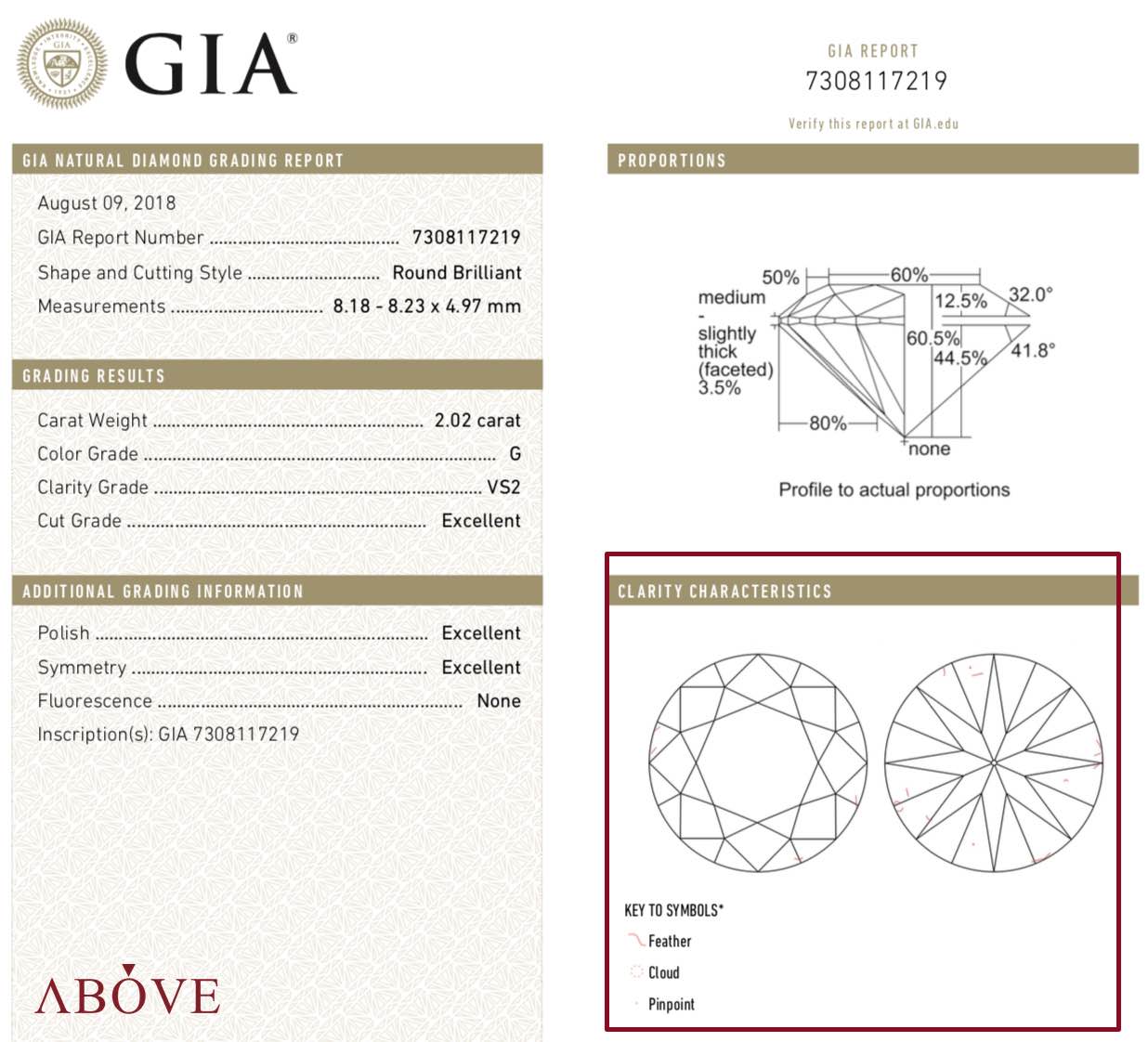
A plotting diagram is a map of a diamond's clarity characteristics. These are the blemishes that reside on a diamond's surface and the inclusions which are internal characteristics. The diagram is an important part of the GIA diamond grading report for D-to-Z color and colored diamonds. The GIA laboratory issues the Diamond Dossier for loose, natural diamonds between 0.15 and 1.99 carats, in the D-to-Z color range. The Diamond Dossier is not issued for laboratory-grown diamonds, simulants, mounted diamonds, diamonds that have undergone unstable treatments such as fracture filling or coating, or those that have been HPHT processed. The GIA clarity grade scale ranks these diamonds based on a strict set of criteria which they determine as follows: 'Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as how these affect the overall appearance of the stone. GIA's clarity chart, better known as the Official GIA Diamond Clarity Scale, is the standard used by jewelers worldwide and is regarded as the best diamond clarity scale in the industry.

The Best Diamond Clarity for Engagement Rings My Diamond Guide
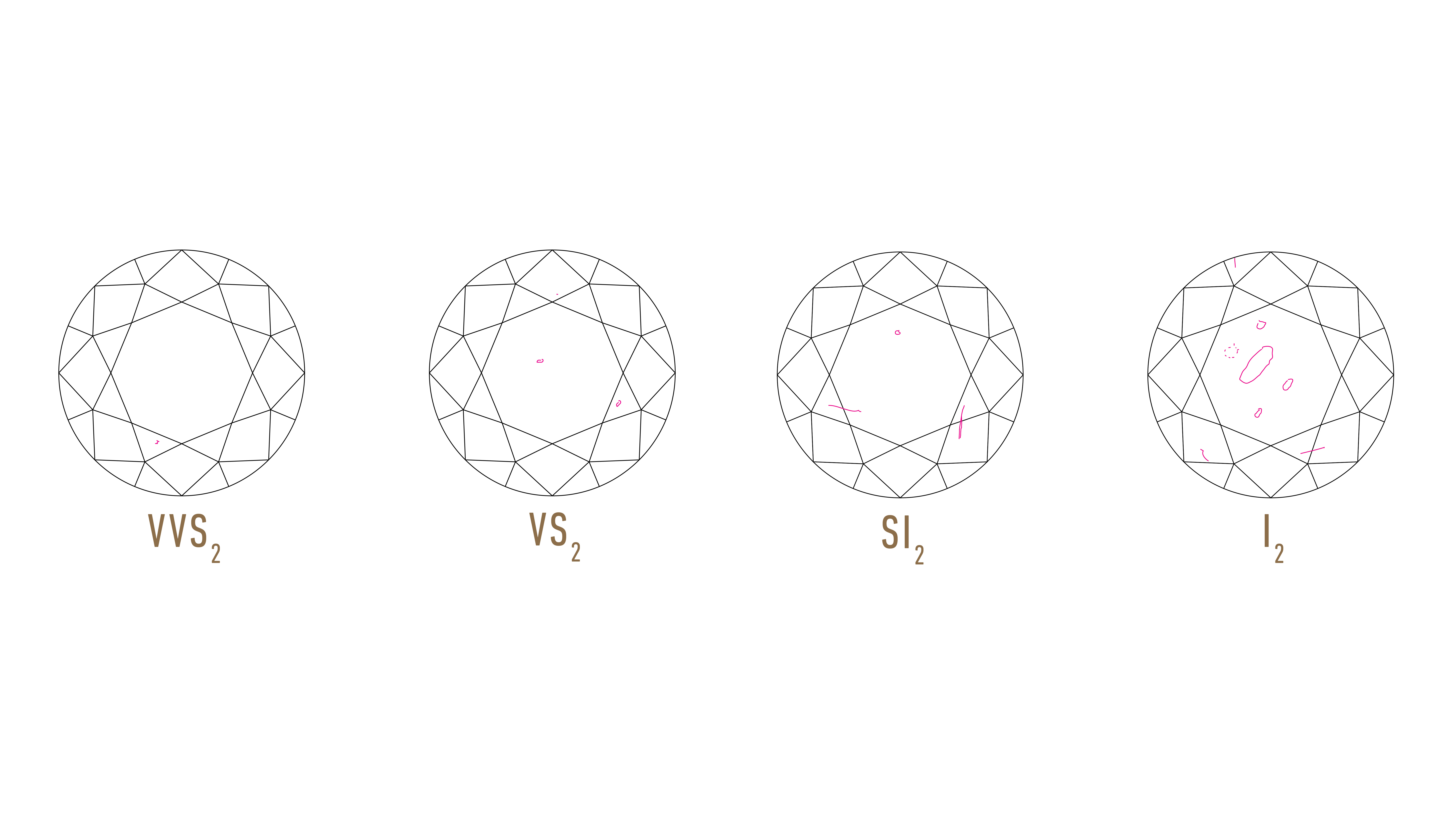
Diamond professionals use the grading system developed by GIA in the 1950s, which established the use of four important factors to describe and classify diamonds: Clarity, Color, Cut, and Carat Weight. Diamonds can be fashioned into a variety of shapes and still be beautiful. These are known as the 4Cs. Diamond Inclusions Defined Because diamonds form under tremendous heat and pressure, nearly every one possesses internal and external features called clarity characteristics. These characteristics help gemologists separate natural diamonds from synthetics and simulants, as well as identify individual gems. What Are Diamond Clarity Characteristics? Clarity characteristics can affect the appearance and price of a loose diamond. Knowing about diamond clarity when reviewing a Gemological Institute of America (GIA) diamond report or dossier can certainly be valuable. Diamond Clarity Characteristics GIA Clarity Scale. FL. IF. VVS1. VVS2. VS1. VS2. SI1. SI2. I1. I2. I3. Flawless Internally Flawless Very, Very Slightly Included Very Slightly Included Slightly Included Included. Diamond. Clarity Grading. Move the slider to view examples of different diamond clarity grades. Click marker for more information.. GIA is the creator of the 4Cs.
Clarity Characteristics Tips from Expert Gemologist • Above Diamond
GIA Clarity Scale The GIA Clarity Scale has six categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific grades. FLAWLESS (FL) No inclusions and no blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification INTERNALLY FLAWLESS (IF) No inclusions and only blemishes are visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification These flaws are called "Clarity Characteristics" in the GIA Diamond Report. In simpler terms, they are the type of flaws a diamond has. Flawless diamonds with clarity levels such as "Internally Flawless" or "IF" are diamonds that have no visible flaws even under a 10x magnifier.
Laboratory-grown diamonds have their own distinct characteristics, including inclusions and other features, which allow GIA scientists to distinguish them from natural diamonds. These clarity characteristics are evaluated using the same universally recognized scale and terms as those of natural diamonds—with the number, size, relief, nature, and position of the inclusions being taken into. In grading diamond clarity, the GIA considers the number, size, color, reflectivity, and position of every flaw visible under 10x magnification.. Besides the plot, there is also a comment section on the certificate where additional clarity characteristics are often noted. These are usually too minor to be reflected in the plot itself.
What is Diamond Clarity The 4Cs of Diamond Quality by GIA
GIA (Gemological Institute of America) is the foremost independent grading lab in the world. It examines diamonds and issues impartial evaluations for stones submitted to them.. These identify the stone's carat weight, color, and clarity. These characteristics are familiar to you if you understand the 4 C's of a diamond (carat, color. The GIA's clarity grading scale is the industry benchmark for assessing a diamond's clarity. This scale is one of the renowned 4Cs - carat, cut, color, and clarity - and is paramount in influencing a diamond's valuation. The spectrum of diamond clarity ranges from Flawless to I3 (or Included 3).




