0.89 °C 1.6 °F download data Key Takeaway: Earth's global average surface temperature in 2020 statistically tied with 2016 as the hottest year on record, continuing a long-term warming trend due to human activities. This graph shows the change in global surface temperature compared to the long-term average from 1951 to 1980. An IPCC special report produced in 2018 noted that human beings and their activities have been responsible for a worldwide average temperature increase between 0.8 and 1.2 °C (1.4 and 2.2 °F) since preindustrial times, and most of the warming over the second half of the 20th century could be attributed to human activities.
What makes the current global warming trend different from normal climate cycles of the past
Nov 11, 2021 This article is published in collaboration with The Conversation. An atmospheric scientist explores the key driving forces behind climate change and the impact it's having on the planet. Image: UNSPLASH/Mika Baumeister Betsy Weatherhead Senior Scientist, University of Colorado Boulder Our Impact Earth in 2021 was about 1.1°C (1.9°F) warmer than it was in the late 19th century, when the Industrial Revolution was underway and weather stations were popping up around the world. The map above depicts global temperature anomalies in 2021. Most of the planet is warming (yellow, orange, red). Only a few locations, most of them in Southern Hemisphere oceans, cooled over this time period. NOAA Climate.gov map, based on data from NOAA Centers for Environmental Information. About surface temperature The concept of an average temperature for the entire globe may seem odd. Climate Time Machine This series of visualizations shows how some of Earth's key climate indicators are changing over time. SELECT A TOPIC Vital Signs of the Planet: Global Climate Change and Global Warming. Current news and data streams about global warming and climate change from NASA.

Copy of "THE GLOBAL WARMING CHART"
Six graphics that explain climate change A breakthrough deal to attempt to limit global temperature rises was agreed at a conference of world nations in December 2015. These charts from the. 1. The world has been getting hotter The world is now nearly one degree warmer than it was before widespread industrialisation, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The. Video: Global Warming from 1880 to 2022 Video: Annual Arctic Sea Ice Minimum 1979-2022 with Area Graph Video: Ozone Watch 2018 Recent News & Features image feature Water-Watching Satellite Monitors Warming Ocean off California Coast news Google's 'A Passage of Water' Brings NASA's Water Data to Life News NASA to Showcase Earth Science Data at COP28 1. CO2 levels The amount of CO2 in the atmosphere reached record levels in 2020, hitting 417 parts per million in May. The last time CO2 levels exceeded 400 parts per million was around four.
Global warming презентация онлайн
21 June 2019 By Jonathan Amos BBC Science Correspondent Is this the simplest way to show what is meant by global warming? The chart below organises all the countries of the world by region,. Many scientists use the term "climate change" instead of "global warming.". This is because greenhouse gas emissions affect more than just temperature. Another effect involves changes in precipitation like rain and snow. Patterns in precipitation may change or become more extreme.
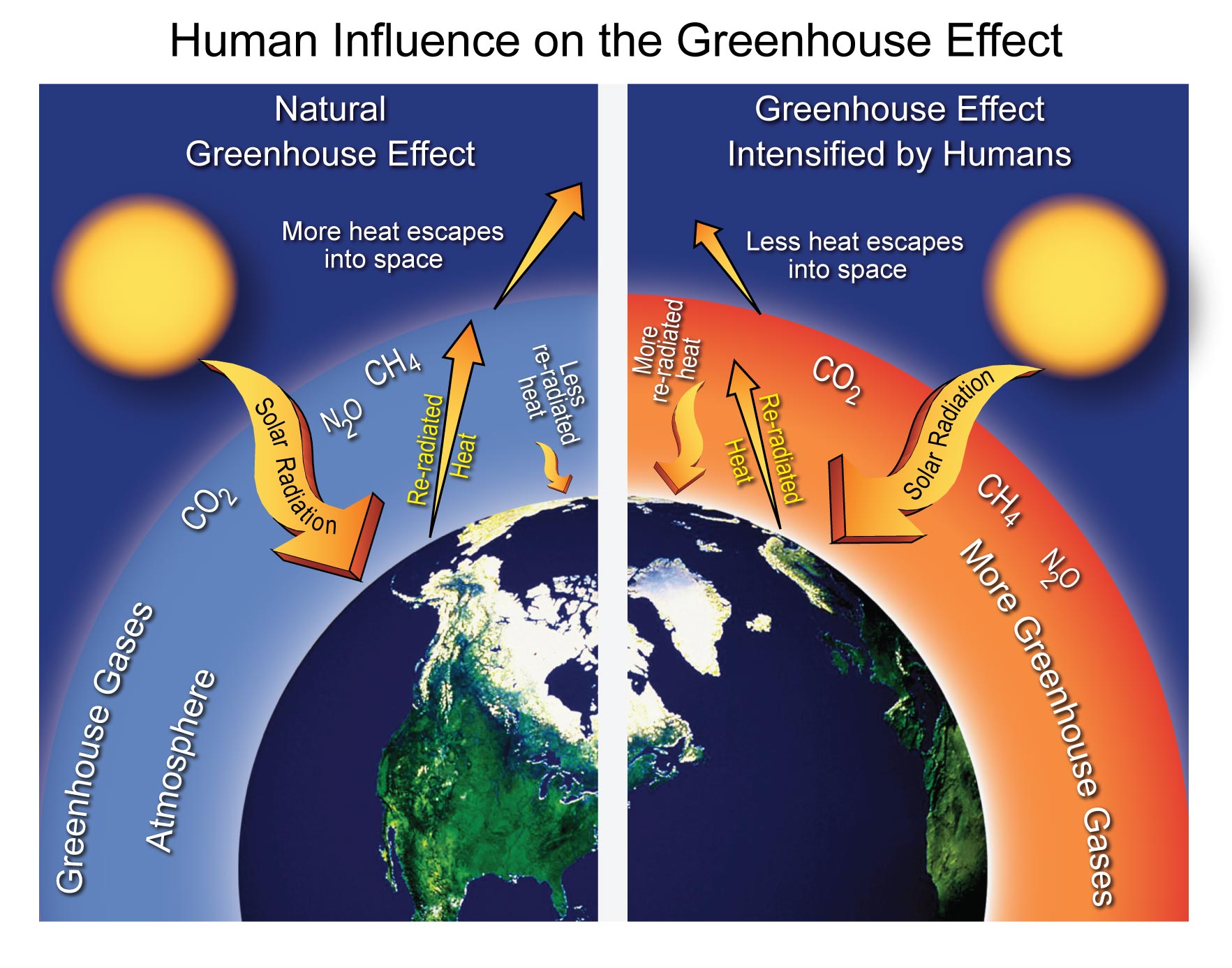
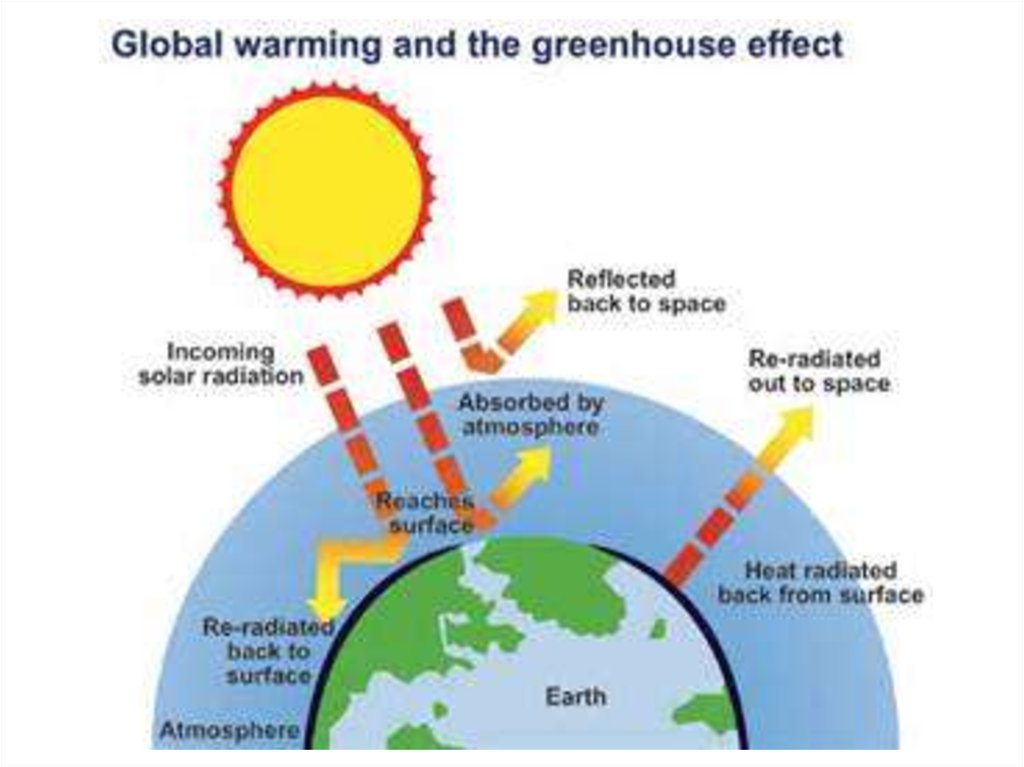
greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect.. The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear. French mathematician Joseph Fourier is sometimes given. A diagram showing the wavelengths of different types of energy. Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as mostly visible light. Earth reradiates that energy as infrared energy, which has a longer, slower wavelength.. Recently, I became embroiled in an online debate on the subject of anthropogenic global warming ("Claim") originated by a talk.

What Is the Greenhouse Effect and How Does It Cause Global Warming? Inverse
Global warming is the rise in temperature of the air and oceans globally. It is happening mainly because humans burn coal, oil, and natural gas; and cut down forests. [2] Average temperatures today are about 1 °C (1.8 °F) higher than before people started burning a lot of coal around 1750. [3] The Slow Carbon Cycle. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity, carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks, soil, ocean, and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle. On average, 10 13 to 10 14 grams (10-100 million metric tons) of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year.




