Organic Chemistry Addition Reactions of Alkenes Hydroboration-Oxidation: The Mechanism Hydroboration-oxidation converts alkenes into alcohols: THF (tetrahydrofuran) is the solvent that is used to stabilize the BH 3 which otherwise tends to form a dimer, B 2 H 6 - a flammable, toxic, and explosive gas: Hydroboration-Oxidation is a two step pathway used to produce alcohols. The reaction proceeds in an Anti-Markovnikov manner, where the hydrogen (from BH 3 or BHR 2) attaches to the more substituted carbon and the boron attaches to the least substituted carbon in the alkene bouble bond. Furthermore, the borane acts as a lewisAnti-Markovnikov.
Hydroboration Oxidation of Alkenes Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
Hydroboration-oxidation reaction is a two-step hydration reaction that converts an alkene into an alcohol. [1] The process results in the syn addition of a hydrogen and a hydroxyl group where the double bond had been. Hydroboration-oxidation is an anti-Markovnikov reaction, with the hydroxyl group attaching to the less-substituted carbon. Hydroboration-oxidation is a useful and important method for forming alcohols from alkenes. The reaction involves treatment of an alkene ( also known as an olefin) with a borane ( a neutral molecule containing a B-H bond ). Hydroboration-oxidation is a two step pathway used to produce alcohols. The reaction proceeds in an anti-Markovnikov manner, where the hydrogen (from BH 3 or BHR 2) attaches to the more substituted carbon and the boron attaches to the least substituted carbon in the alkene double bond. Furthermore, the borane acts as a Lewis acid by accepting two electrons in its empty p orbital from an alkene. Hydroboration-oxidation: Mechanism Alkene halogenation Halohydrin formation Epoxide formation and anti dihydroxylation Syn dihydroxylation Ozonolysis Science > Organic chemistry > Alkenes and alkynes > Alkene reactions © 2024 Khan Academy Hydroboration-oxidation: Mechanism Google Classroom About Transcript
chemistry world HYDROBORATION / OXIDATION
Stereospecific Hydroboration Oxidation of Alkynes. Step 1: Hydroboration of terminal alkynes reacts in an anti-Markovnikov fashion in which the Boron attacks the less substituted carbon which is the least hindered. It is a stereospecific reaction where syn addition is observed as the hydroboration occurs on the same side of the alkyne and results in cis stereochemistry. About Transcript Two-step reaction in which an alkene is converted to an alkene with a hydroxyl substituent (which may tautomerize to a carbonyl). Created by Jay. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted packshack 10 years ago Why is this reaction anti-Markovnikov? • ( 5 votes) Upvote Flag jm.macarulay 10 years ago Video transcript. - [Voiceover] Here's the general reaction for hydroboration-oxidation. We start with an alkene and in the first step this is our hydroboration-oxidation step we're adding borene which is BH3 and tetrahydrofuran which is THF. Our second step is the oxidation where we add hydrogen peroxide and a source of hydroxide ions, and we. Hydroboration - Oxidation Reaction Mechanism The Organic Chemistry Tutor 7.25M subscribers Join Subscribe Subscribed 3.2K Share 293K views 5 years ago New Organic Chemistry Playlist This organic.

HydroborationOxidation The Mechanism Chemistry Steps
The Hydroboration Oxidation reaction is an organic chemical reaction which is employed for the conversion of alkenes into alcohols that are neutral. This is done via a two-step process which includes a hydroboration step and an oxidation step. This is done by a net addition (across the entire double bond) of water. A two-step reaction that converts an alkane double bond to a single bond, with regioselective and stereoselective addition of a hydroxyl group.Watch the next.
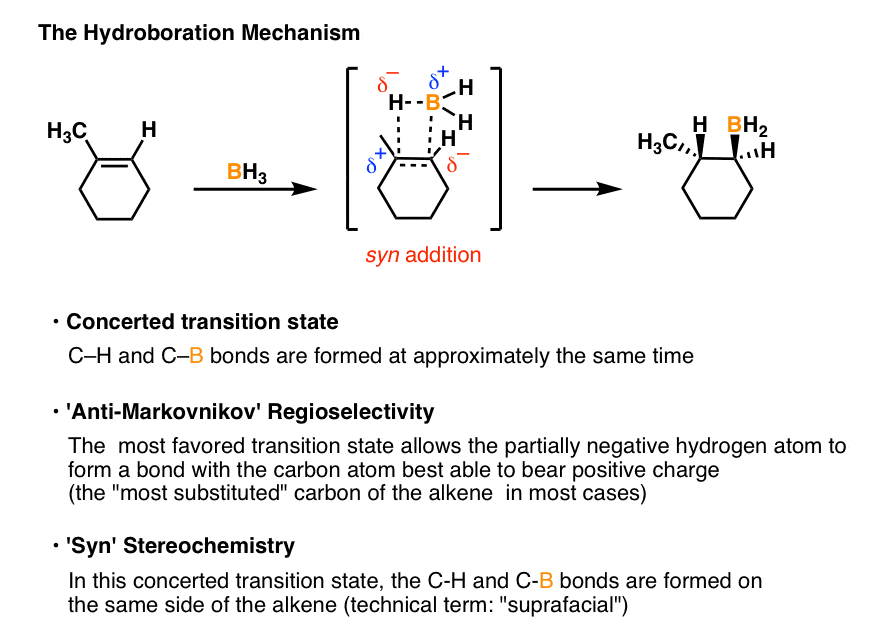
Hydroboration-oxidation is a two step pathway used to produce alcohols. The reaction proceeds in an anti-Markovnikov manner, where the hydrogen (from BH 3 or BHR 2) attaches to the more substituted carbon and the boron attaches to the least substituted carbon in the alkene double bond. Furthermore, the borane acts as a Lewis acid by accepting two electrons in its empty p orbital from an alkene. The hydroboration-oxidation mechanism is shown in figure 1. The first step of the sequence, hydroboration, involves addition of borane across the double bond. In this addition H and BH2 are added to the alkene carbons. The hydrogen goes to the more substituted carbon while the BH2 goes to the less substituted carbon.

HydroborationOxidation of Alkenes Regiochemistry and Stereochemistry with Practice Problems
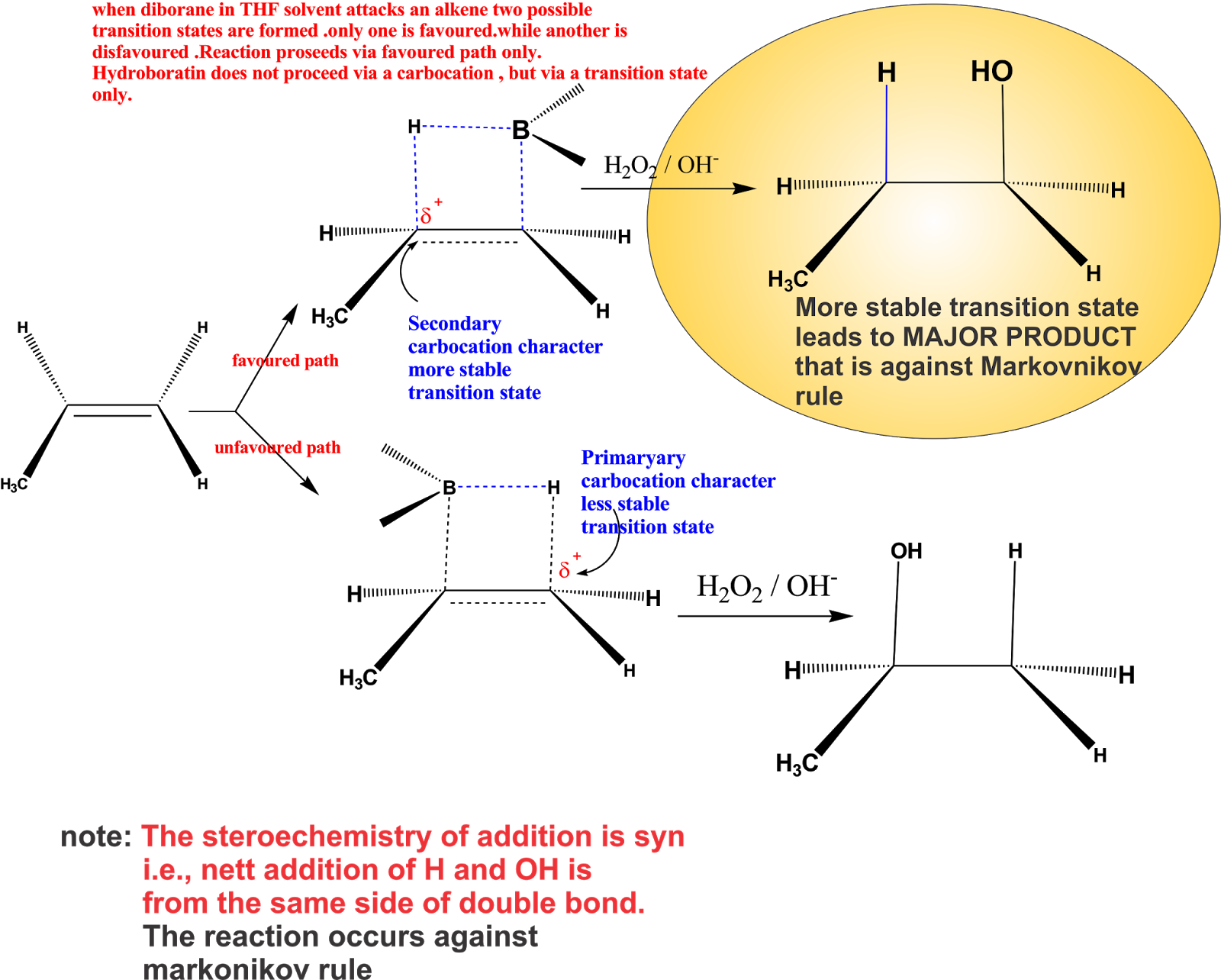
The mechanism for the hydroboration-oxidation sequence proceeds through the proposed mechanism below. Oxidation occurs at the terminal olefin carbon (in an anti-Markovnikov sense) and a reduction of the carbon at the proximal end of the olefin. This is thought to be the result of the decreased steric resistance associated with having the. The mechanism of hydroboration oxidation reaction can be illustrated in the following steps: Step 1: Addition of diborane to double bond. The first step is hydroboration in which the boron and hydrogen atom from the diborane is added to the carbon-carbon double bond in a concerted manner from the same direction i.e syn addition.




